Peripheral tolerance
... The problem of self-nonself discrimination • The immune system responds to many foreign (microbial) antigens but not to self antigens • Developing lymphocytes express a large number of antigen receptors, not biased by specificity • Therefore, all individuals produce lymphocytes with the ability to ...
... The problem of self-nonself discrimination • The immune system responds to many foreign (microbial) antigens but not to self antigens • Developing lymphocytes express a large number of antigen receptors, not biased by specificity • Therefore, all individuals produce lymphocytes with the ability to ...
plant immunology lecture 9.
... • This is a rapid apoptosis response that kills cells in the area of infection. • It can be induced by the interaction of an R gene carrying plant with an Avr carrying microbe. • In the lab one can infiltrate bacteria into the whole leaf, causing a massive cell death response but in the field the HR ...
... • This is a rapid apoptosis response that kills cells in the area of infection. • It can be induced by the interaction of an R gene carrying plant with an Avr carrying microbe. • In the lab one can infiltrate bacteria into the whole leaf, causing a massive cell death response but in the field the HR ...
Powerpoint Infectious Diseases
... Tuberculosis Pathogenesis Inhalation of infected droplets (human-to human transmission) Facultative intracellular pathogen of macrophages Spread to regional lymph nodes with bacteremia and diffuse metastatic foci Control by Th1 cell immunity and macrophage activation Latent for years in caseating g ...
... Tuberculosis Pathogenesis Inhalation of infected droplets (human-to human transmission) Facultative intracellular pathogen of macrophages Spread to regional lymph nodes with bacteremia and diffuse metastatic foci Control by Th1 cell immunity and macrophage activation Latent for years in caseating g ...
Week 2 Immunology
... • Bone marrow transplant – Major reduction of immune system function due to absence and function of bone marrow • Solid organ transplant – Mild suppression due to lifelong use of immune suppressant drugs to prevent ...
... • Bone marrow transplant – Major reduction of immune system function due to absence and function of bone marrow • Solid organ transplant – Mild suppression due to lifelong use of immune suppressant drugs to prevent ...
Basic Immunology Course Code: Credit Units: 3
... Course Objectives: To establish foundations of immunology by gaining thorough understanding of basic concepts of Immunology Pre-requisites: Basic knowledge of biological sciences Student Learning Outcomes: At the end of this course, the students will be able to: ...
... Course Objectives: To establish foundations of immunology by gaining thorough understanding of basic concepts of Immunology Pre-requisites: Basic knowledge of biological sciences Student Learning Outcomes: At the end of this course, the students will be able to: ...
The Immune System
... swallowed and then digested – Tears, sweat and saliva all contain lysozyme, an enzyme that can break down the cell wall of some bacteria. ...
... swallowed and then digested – Tears, sweat and saliva all contain lysozyme, an enzyme that can break down the cell wall of some bacteria. ...
File
... MOLECULE ON A PATHOGEN OR A TOXIN. • ANTIGEN-ANTIBODY COMPLEXES MAY INACTIVATE A PATHOGEN OR TOXIN OR RENDER IT MORE SUSCEPTIBLE TO PHAGOCYTOSIS. • IN OTHER CASES THE ANTIGEN-ANTIBODY COMPLEX STIMULATES A RESPONSE WHICH RESULTS IN CELL LYSIS. • B LYMPHOCYTES ACTIVATED BY ANTIGEN PRESENTING CELLS AND ...
... MOLECULE ON A PATHOGEN OR A TOXIN. • ANTIGEN-ANTIBODY COMPLEXES MAY INACTIVATE A PATHOGEN OR TOXIN OR RENDER IT MORE SUSCEPTIBLE TO PHAGOCYTOSIS. • IN OTHER CASES THE ANTIGEN-ANTIBODY COMPLEX STIMULATES A RESPONSE WHICH RESULTS IN CELL LYSIS. • B LYMPHOCYTES ACTIVATED BY ANTIGEN PRESENTING CELLS AND ...
Chapter 20- Lymphatic system
... multiple layers and forms of defense. In this section we focus on the organs closely associated with cellular response of the immune system. The immune system identifies and attacks specific pathogens. • A. Lymphocytes and other cells of the immune system- Inflammation may be the first response to i ...
... multiple layers and forms of defense. In this section we focus on the organs closely associated with cellular response of the immune system. The immune system identifies and attacks specific pathogens. • A. Lymphocytes and other cells of the immune system- Inflammation may be the first response to i ...
File
... Genes for MHC are present on chromosome 6 and inherited. Sexual selection makes MHC individual specific Antigen Receptors present on the lymphocytes can recognize our own MHC from foreign antigens. ...
... Genes for MHC are present on chromosome 6 and inherited. Sexual selection makes MHC individual specific Antigen Receptors present on the lymphocytes can recognize our own MHC from foreign antigens. ...
12967_2016_983_MOESM1_ESM
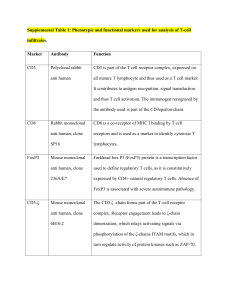
... Supplemental Table 1: Phenotypic and functional markers used for analysis of T-cell infiltrates. Marker ...
... Supplemental Table 1: Phenotypic and functional markers used for analysis of T-cell infiltrates. Marker ...
study_guide_2007_hazbun - Welcome to people.pharmacy
... 4. How does inflammation occur? Why is inflammation good but sometimes can be bad? 5. Understand the concept of clonal amplification 6. Know the hematopoietic system – how we can stimulate it in some cases such as neulasta 7. Know the basic anatomy of secondary lymphoid tissue (e.g. lymph node – Tce ...
... 4. How does inflammation occur? Why is inflammation good but sometimes can be bad? 5. Understand the concept of clonal amplification 6. Know the hematopoietic system – how we can stimulate it in some cases such as neulasta 7. Know the basic anatomy of secondary lymphoid tissue (e.g. lymph node – Tce ...
DOC - ADAM Interactive Anatomy
... When tissues are injured, macrophages release chemical mediators, called inflammatory mediators. These chemical mediators cause two key effects: • __________________, which causes redness and heat • ______________________, which causes swelling and, thus, pain ...
... When tissues are injured, macrophages release chemical mediators, called inflammatory mediators. These chemical mediators cause two key effects: • __________________, which causes redness and heat • ______________________, which causes swelling and, thus, pain ...
T cell receptor
... ● T-cells undergo V(D)J recombination to create a diverse number of TCRs, similar to Immunoglobulins but they do not undergo somatic hypermutation . This process is initiated by the enzymes Rag1 and Rag2 which induce double-strand breaks at the border between a recombination signal sequence and a co ...
... ● T-cells undergo V(D)J recombination to create a diverse number of TCRs, similar to Immunoglobulins but they do not undergo somatic hypermutation . This process is initiated by the enzymes Rag1 and Rag2 which induce double-strand breaks at the border between a recombination signal sequence and a co ...
Immunity - Yengage
... Lymphocytes burr holes in the cells Plasma cells synthesize and release to be destroyed by releasing free antibodies in to circulation ...
... Lymphocytes burr holes in the cells Plasma cells synthesize and release to be destroyed by releasing free antibodies in to circulation ...
Name - Medical Mastermind Community
... A. They primarily secrete IL-2 and Interferon-gamma upon activation B. They give help to B cells to produce IgG2a C, They primarily secrete TGF-beta upon activation D. They suppress T helper I cells, but not T helper 2 cells E. They are the primary T cell in delayed type hypersensitive responses 14. ...
... A. They primarily secrete IL-2 and Interferon-gamma upon activation B. They give help to B cells to produce IgG2a C, They primarily secrete TGF-beta upon activation D. They suppress T helper I cells, but not T helper 2 cells E. They are the primary T cell in delayed type hypersensitive responses 14. ...
LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AND IMMUNITY
... antibodies specific to a given antigen. Antibodies bind to the antigens on invaders and kill or inactivate them in several ways. Most antibodies are themselves proteins or are a mix of protein and polysaccharides. Antigens can be any molecule that causes an immune system response. There are two type ...
... antibodies specific to a given antigen. Antibodies bind to the antigens on invaders and kill or inactivate them in several ways. Most antibodies are themselves proteins or are a mix of protein and polysaccharides. Antigens can be any molecule that causes an immune system response. There are two type ...
c. Section 1.3 The Immune System
... • A disease is said to be endemic when it is at a constant, “normal” occurrence within a given geographical area. In this case, low numbers of people become sick. • A disease becomes an epidemic when it affects an unusual number of people in a community or region at the same time. A higher number o ...
... • A disease is said to be endemic when it is at a constant, “normal” occurrence within a given geographical area. In this case, low numbers of people become sick. • A disease becomes an epidemic when it affects an unusual number of people in a community or region at the same time. A higher number o ...
SUN-206 Inhibition of MMP-9 gene expression and cancer cell
... correlation of cell proliferation with the angiogenic factor concentrations, correlated moreover with decreased apoptosis, especially in the time range 3–24 hrs. When applying MMP-1 the effects are similar with the ones induced by VEGF in HED, while control cells display an inverse cellular behavior ...
... correlation of cell proliferation with the angiogenic factor concentrations, correlated moreover with decreased apoptosis, especially in the time range 3–24 hrs. When applying MMP-1 the effects are similar with the ones induced by VEGF in HED, while control cells display an inverse cellular behavior ...
B cells. - School
... Others prevent enzymes essential for the production of new virus particles from working. ...
... Others prevent enzymes essential for the production of new virus particles from working. ...
versus hydrocortisone treatment in late
... of Munich, Germany Graves’ ophthalmopathy (GO) results from a complex interplay of genetic, immunological, hormonal and environmental factors. Various genes, including those coding for HLA, may determine a patient’s susceptibility to the disease and its severity, but in addition, environmental facto ...
... of Munich, Germany Graves’ ophthalmopathy (GO) results from a complex interplay of genetic, immunological, hormonal and environmental factors. Various genes, including those coding for HLA, may determine a patient’s susceptibility to the disease and its severity, but in addition, environmental facto ...
Immune and Autoimmune Responses to cytosolic
... The presence of DNA and aberrant RNA in the cytoplasm is a danger signal that alerts the host immune system to eliminate microbial infections, but inappropriate activation of these pathways can also lead to autoimmune diseases. In this seminar, I will first summarize our work on the biochemical diss ...
... The presence of DNA and aberrant RNA in the cytoplasm is a danger signal that alerts the host immune system to eliminate microbial infections, but inappropriate activation of these pathways can also lead to autoimmune diseases. In this seminar, I will first summarize our work on the biochemical diss ...