Teaching Cryptologic Mathematics
... and to discover the usefulness and properties of prime numbers. Also the subject of standard computational complexity classes may be introduced. As a side excursion, it is possible to explain digital signatures based on RSA cipher. Digital signatures also allow the introduction of a specific kind of ...
... and to discover the usefulness and properties of prime numbers. Also the subject of standard computational complexity classes may be introduced. As a side excursion, it is possible to explain digital signatures based on RSA cipher. Digital signatures also allow the introduction of a specific kind of ...
Public Key Encryption and Digital Signatures
... • Encoding method E and decoding method D are inverse functions on message M: – D(E(M)) = M • Computational cost of E, D reasonable • D cannot be determined from E, the algorithm, or any amount of plaintext attack with any computationally feasible technique • E cannot be broken without D (only D wil ...
... • Encoding method E and decoding method D are inverse functions on message M: – D(E(M)) = M • Computational cost of E, D reasonable • D cannot be determined from E, the algorithm, or any amount of plaintext attack with any computationally feasible technique • E cannot be broken without D (only D wil ...
Cryptanalysis of Stream Cipher
... ciphertext attack To preclude chosen ciphertext attack 1) if tag verification fails, the decrypted plaintext should not be given as output 2) the tag size should be sufficiently large to resist a chosen-ciphertext attack (128-bit tag recommended) ...
... ciphertext attack To preclude chosen ciphertext attack 1) if tag verification fails, the decrypted plaintext should not be given as output 2) the tag size should be sufficiently large to resist a chosen-ciphertext attack (128-bit tag recommended) ...
Chapter 08
... Cryptography is the science of encoding data, typically using a key, so that people without the key cannot read the data Cryptography protects computer networks against sniffers, programs that allow crackers to see data passing along a network Many different algorithms are used to encrypt data and t ...
... Cryptography is the science of encoding data, typically using a key, so that people without the key cannot read the data Cryptography protects computer networks against sniffers, programs that allow crackers to see data passing along a network Many different algorithms are used to encrypt data and t ...
Chapter 8: Network Security
... An important additional property of public-key ciphers is that the private key can be used with the encryption algorithm to encrypt messages so that they can only be decrypted using the public “encryption” key. This property clearly wouldn’t be useful for confidentiality since anyone with the public ...
... An important additional property of public-key ciphers is that the private key can be used with the encryption algorithm to encrypt messages so that they can only be decrypted using the public “encryption” key. This property clearly wouldn’t be useful for confidentiality since anyone with the public ...
Cryptography and Coding Theory
... IT662 Cryptography and Coding Theory L – T – P: 3 – 0 – 0 Credit: 3 Objectives: The objective of the course is to provide detail knowledge of cryptography and Coding Theory Pre-requisite: Cryptography knowledge of under grad level. Outcome: Should have earned knowledge of several cryptographic algor ...
... IT662 Cryptography and Coding Theory L – T – P: 3 – 0 – 0 Credit: 3 Objectives: The objective of the course is to provide detail knowledge of cryptography and Coding Theory Pre-requisite: Cryptography knowledge of under grad level. Outcome: Should have earned knowledge of several cryptographic algor ...
Crypto in data security
... • The science of codes and passwords • Need to prove the identity of the sender and the recipient • The message In the meantime • Should not change the content of the message to make sure ...
... • The science of codes and passwords • Need to prove the identity of the sender and the recipient • The message In the meantime • Should not change the content of the message to make sure ...
Bio-Block - Cartier Environmental Services Inc.
... Bio-Block Gives round the clock waste degradation treatment with a simple, easy to use system. Simply suspend the block into the treatment area, hanging the block just away from the higher flow areas. The block will dissolve over a 30-90 day as the wastewater flow washes over it. Higher flow rates w ...
... Bio-Block Gives round the clock waste degradation treatment with a simple, easy to use system. Simply suspend the block into the treatment area, hanging the block just away from the higher flow areas. The block will dissolve over a 30-90 day as the wastewater flow washes over it. Higher flow rates w ...
compatible-development-of
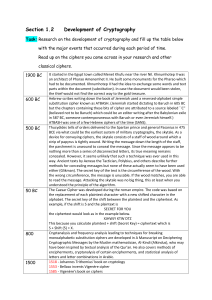
... sells information on KL-7 cipher machine. The Walker spy ring operates until 1985. 1974 - Horst Feistel develops Feistel network block cipher design. 1976 - the Data Encryption Standard was published as an official Federal Information Processing Standard (FIPS) for the United States. The Data Encryp ...
... sells information on KL-7 cipher machine. The Walker spy ring operates until 1985. 1974 - Horst Feistel develops Feistel network block cipher design. 1976 - the Data Encryption Standard was published as an official Federal Information Processing Standard (FIPS) for the United States. The Data Encryp ...