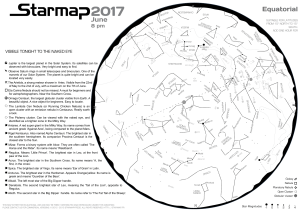
20 pm - Starmap
... Regulus. Means 'Little Prince'. The brightest star in Leo, at the front paw of the Lion. Acrux. The brightest star in the Southern Cross. Its name means 'A, the first, in the cross'. ...
... Regulus. Means 'Little Prince'. The brightest star in Leo, at the front paw of the Lion. Acrux. The brightest star in the Southern Cross. Its name means 'A, the first, in the cross'. ...
PC2491 Examples 2
... temperature of 100K. Estimate how large the cloud can be before it begins to collapse under its own gravity. ...
... temperature of 100K. Estimate how large the cloud can be before it begins to collapse under its own gravity. ...
Chapter 15 (Star Lives)
... B. only their temperatures. C. heliocentric parallax and density. D. measuring the sizes of eclipsing binary systems. 20. Once you know about the H-R diagram, you can determine a star's luminosity if you: A. know its “type” and measure its temperature. B. know its distance and mass. C. know its size ...
... B. only their temperatures. C. heliocentric parallax and density. D. measuring the sizes of eclipsing binary systems. 20. Once you know about the H-R diagram, you can determine a star's luminosity if you: A. know its “type” and measure its temperature. B. know its distance and mass. C. know its size ...
Bluffing your way in Astronomy: Taurus
... they will reveal over two hundred. The faint haze around the stars appears as a beautiful blue mist in photographs. Older astronomy books say this is a wispy remnant of the molecular cloud in which they were born. However astronomers now think the stars in the Pleiades are at least 100 million years ...
... they will reveal over two hundred. The faint haze around the stars appears as a beautiful blue mist in photographs. Older astronomy books say this is a wispy remnant of the molecular cloud in which they were born. However astronomers now think the stars in the Pleiades are at least 100 million years ...
STELLAR EVOLUTION
... undergo repeated novae explosions, or disintegrate as a supernova. Almost all evolutionary processes in stars take much longer than a human lifetime; we cannot watch a star evolve from birth to death. A few exceptions are supernova and nova explosions, which happen in hours and days. ...
... undergo repeated novae explosions, or disintegrate as a supernova. Almost all evolutionary processes in stars take much longer than a human lifetime; we cannot watch a star evolve from birth to death. A few exceptions are supernova and nova explosions, which happen in hours and days. ...
M13 – The Great Hercules Cluster
... The quiet, peaceful nights of winter have now been replaced by summer nights full of the sounds of life. Cicadas, crickets, whippoorwills and barred owls provide a symphony for our ears while the stars of summer provide a symphony for our eyes. Go outside on a warm June night and look up at the star ...
... The quiet, peaceful nights of winter have now been replaced by summer nights full of the sounds of life. Cicadas, crickets, whippoorwills and barred owls provide a symphony for our ears while the stars of summer provide a symphony for our eyes. Go outside on a warm June night and look up at the star ...
Powerpoint of lecture 1
... • Chemical composition similar for many stars … • … so Teff, L can be deduced • Variability: • some pulsating variables show period-luminosity relation ...
... • Chemical composition similar for many stars … • … so Teff, L can be deduced • Variability: • some pulsating variables show period-luminosity relation ...
DUPREE_SPLINTER
... Poster children for second parameter: NGC 362 & NGC 288 (Bellazzini et al. 2001; Catelan et al. 2001) ...
... Poster children for second parameter: NGC 362 & NGC 288 (Bellazzini et al. 2001; Catelan et al. 2001) ...
22 pm - Starmap
... Using binoculars, preferably with a tripod, will considerably enhance your star gazing experience. Many deep sky objects like galaxies and clusters will be within reach. Jupiter satellites and Saturn’s rings will also be visible. A spectacular experience for beginners in astronomy... Avoid the night ...
... Using binoculars, preferably with a tripod, will considerably enhance your star gazing experience. Many deep sky objects like galaxies and clusters will be within reach. Jupiter satellites and Saturn’s rings will also be visible. A spectacular experience for beginners in astronomy... Avoid the night ...
ppt
... positions as a function of epoch over all plates on which a star appears. New proper motions are calculated, and the process is iterated until it converges to the final proper motion values. Proper-motion uncertainties are determined from the scatter about the best-fit line. Typically, the reference ...
... positions as a function of epoch over all plates on which a star appears. New proper motions are calculated, and the process is iterated until it converges to the final proper motion values. Proper-motion uncertainties are determined from the scatter about the best-fit line. Typically, the reference ...
Document
... planet formation much more than the process of star formation Why: Clusters have radial scale of 1 pc, with distance between protostars of 0.24pc. Cores are observed to move at 0.1 km/s. During their formation time of 0.1 Myr, protostars move only 0.01 pc << 0.24 pc… ...
... planet formation much more than the process of star formation Why: Clusters have radial scale of 1 pc, with distance between protostars of 0.24pc. Cores are observed to move at 0.1 km/s. During their formation time of 0.1 Myr, protostars move only 0.01 pc << 0.24 pc… ...
Today`s Powerpoint
... Finally, fusion starts, stopping collapse: a star! Star reaches Main Sequence at end of Hayashi Track ...
... Finally, fusion starts, stopping collapse: a star! Star reaches Main Sequence at end of Hayashi Track ...
galctr
... L.Hartmann: Dynamic Star Formation From ages of associations in clouds, infer rapid onset of SF (<1Myr) after MC formation and rapid dispersal of cloud after SF (<5 Myr) Sco OB2: externally-driven sweep-up of gas into cloud (tcross ~100 Myr, ages <15 Myr) Can molecular material appear so quic ...
... L.Hartmann: Dynamic Star Formation From ages of associations in clouds, infer rapid onset of SF (<1Myr) after MC formation and rapid dispersal of cloud after SF (<5 Myr) Sco OB2: externally-driven sweep-up of gas into cloud (tcross ~100 Myr, ages <15 Myr) Can molecular material appear so quic ...
mass of star
... Finally, fusion starts, stopping collapse: a star! Star reaches Main Sequence at end of Hayashi Track ...
... Finally, fusion starts, stopping collapse: a star! Star reaches Main Sequence at end of Hayashi Track ...
Scattering (and the blue sky)
... Emission and Absorption Spectra More accurately, a gas cloud is only opaque within spectral lines, while a star is opaque at all wavelengths. The brightness of each depends on the usual T4 relation. If, as is usually the case, the cloud is colder than the star (or the star’s atmosphere is colder th ...
... Emission and Absorption Spectra More accurately, a gas cloud is only opaque within spectral lines, while a star is opaque at all wavelengths. The brightness of each depends on the usual T4 relation. If, as is usually the case, the cloud is colder than the star (or the star’s atmosphere is colder th ...
ppt
... Cloud and star formation may have to be treated together Both magnetic and non-magnetic turbulence simulations are promising Observations of the large scale magnetic field strength are needed to ...
... Cloud and star formation may have to be treated together Both magnetic and non-magnetic turbulence simulations are promising Observations of the large scale magnetic field strength are needed to ...
The Interstellar Medium and Star Formation
... pebbles, then rocks, then boulders, then planetesimals, then planets. Some planets become massive enough to also accumulate Hydrogen and Helium gas. • However, during and after formation, it seems that some planets are able to migrate in their disks, drifting inwards to settle close to the star. We ...
... pebbles, then rocks, then boulders, then planetesimals, then planets. Some planets become massive enough to also accumulate Hydrogen and Helium gas. • However, during and after formation, it seems that some planets are able to migrate in their disks, drifting inwards to settle close to the star. We ...
Death of High Mass Stars
... Carbon fuses into higher mass elements. • Process continues as core runs out of fuel. • All fusion ends with silicon fusing into iron. ...
... Carbon fuses into higher mass elements. • Process continues as core runs out of fuel. • All fusion ends with silicon fusing into iron. ...
Ch 11c and 12 ( clusters 3-31-11)
... Star Clusters: Confirmation of Stellar Evolution: 1. What is special about star clusters? ...
... Star Clusters: Confirmation of Stellar Evolution: 1. What is special about star clusters? ...
Star Formation
... hot enough to produce nuclear fusion. • By then, the core is very dense, far denser than water, and the heat can’t get out easily or quickly, so collapse by now is very slow. • This new energy source provides pressure which stabilizes (after some wiggling around) the star against further collapse fo ...
... hot enough to produce nuclear fusion. • By then, the core is very dense, far denser than water, and the heat can’t get out easily or quickly, so collapse by now is very slow. • This new energy source provides pressure which stabilizes (after some wiggling around) the star against further collapse fo ...
Replenishing the ISM - Stockton University
... Interstellar Dust Grains Is there dust that we cannot see? Yes. Quite a bit in fact. ...
... Interstellar Dust Grains Is there dust that we cannot see? Yes. Quite a bit in fact. ...
ppt
... How can we test theories of star evolution? • Binaries help, because one can get mass so that theories can be tested • But stars change so slowly, it is impossible to test theories by watching just one star move through phases • Fortunately, there are 1011 stars in our Galaxy, all with a range of ma ...
... How can we test theories of star evolution? • Binaries help, because one can get mass so that theories can be tested • But stars change so slowly, it is impossible to test theories by watching just one star move through phases • Fortunately, there are 1011 stars in our Galaxy, all with a range of ma ...
Stars: Their Life and Afterlife
... not only tend to form close together in space, but also in time – and so, for massive stars, they will also die relatively close together in space and time. Superbubbles form from OB associations. OB associations are clusters of massive stars of spectral types – you guessed it – O and B. • O stars a ...
... not only tend to form close together in space, but also in time – and so, for massive stars, they will also die relatively close together in space and time. Superbubbles form from OB associations. OB associations are clusters of massive stars of spectral types – you guessed it – O and B. • O stars a ...
Open cluster

An open cluster, also known as galactic cluster, is a group of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way Galaxy, and many more are thought to exist. They are loosely bound by mutual gravitational attraction and become disrupted by close encounters with other clusters and clouds of gas as they orbit the galactic center, resulting in a migration to the main body of the galaxy as well as a loss of cluster members through internal close encounters. Open clusters generally survive for a few hundred million years, with the most massive ones surviving for a few billion years. In contrast, the more massive globular clusters of stars exert a stronger gravitational attraction on their members, and can survive for longer. Open clusters have been found only in spiral and irregular galaxies, in which active star formation is occurring.Young open clusters may still be contained within the molecular cloud from which they formed, illuminating it to create an H II region. Over time, radiation pressure from the cluster will disperse the molecular cloud. Typically, about 10% of the mass of a gas cloud will coalesce into stars before radiation pressure drives the rest of the gas away.Open clusters are key objects in the study of stellar evolution. Because the cluster members are of similar age and chemical composition, their properties (such as distance, age, metallicity and extinction) are more easily determined than they are for isolated stars. A number of open clusters, such as the Pleiades, Hyades or the Alpha Persei Cluster are visible with the naked eye. Some others, such as the Double Cluster, are barely perceptible without instruments, while many more can be seen using binoculars or telescopes. The Wild Duck Cluster, M11, is an example.