HOW TO USE A VOM
... All VOM are battery powered. When you turn them on, you should see activity on the digital display. If the batter is low, you may get an indicator, or just no display. In either case, replace the battery before testing. Referring to the first picture, notice that there are three (3) jacks for the te ...
... All VOM are battery powered. When you turn them on, you should see activity on the digital display. If the batter is low, you may get an indicator, or just no display. In either case, replace the battery before testing. Referring to the first picture, notice that there are three (3) jacks for the te ...
FST3126MX Datasheet - Mouser Electronics
... Other inputs at VCC or GND Note 4: Typical values are at VCC = 5.0V and T A = +25°C Note 5: Measured by the voltage drop between A and B pins at the indicated current through the switch. On resistance is determined by the lower of the voltages on the two (A or B) pins. ...
... Other inputs at VCC or GND Note 4: Typical values are at VCC = 5.0V and T A = +25°C Note 5: Measured by the voltage drop between A and B pins at the indicated current through the switch. On resistance is determined by the lower of the voltages on the two (A or B) pins. ...
5 Experiment - Characteristics of Bipolar Junction Transistors
... Q1: What are the approximate collector-emitter voltages at the transition between the saturation and active regions? 2. Build circuit shown in Figure 1. Set VCC to 5 V using a DC voltage supply. For VIN, use a function generator to create a low frequency (<10 Hz) square wave. Use a T-junction to att ...
... Q1: What are the approximate collector-emitter voltages at the transition between the saturation and active regions? 2. Build circuit shown in Figure 1. Set VCC to 5 V using a DC voltage supply. For VIN, use a function generator to create a low frequency (<10 Hz) square wave. Use a T-junction to att ...
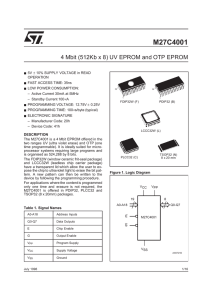
M27C4001 - EECS Instructional Support Group Home Page
... a. the lowest possible memory power dissipation, b. complete assurance that output bus contention will not occur. ...
... a. the lowest possible memory power dissipation, b. complete assurance that output bus contention will not occur. ...
A Forward-Body-Bias Tuned 450MHz Gm-C 3rd-Order Low
... devices isolates the drains and sources from the bulk, allowing the transistor body to be used as a back-gate, hence enabling significant threshold voltage (Vt) shifts. Low-Vt devices in this technology are implemented as 'flip-well' transistors, where the Nand PMOS lay above n- and p-wells respecti ...
... devices isolates the drains and sources from the bulk, allowing the transistor body to be used as a back-gate, hence enabling significant threshold voltage (Vt) shifts. Low-Vt devices in this technology are implemented as 'flip-well' transistors, where the Nand PMOS lay above n- and p-wells respecti ...
TDA2050 - STMicroelectronics
... Short-circuit protection The TDA2050 has an original circuit which limits the current of the output transistors. The maximum output current is a function of the collector emitter voltage, hence the output transistors work within their safe operating area. This function can therefore be considered as ...
... Short-circuit protection The TDA2050 has an original circuit which limits the current of the output transistors. The maximum output current is a function of the collector emitter voltage, hence the output transistors work within their safe operating area. This function can therefore be considered as ...
PDF
... • Motivation for low-power video decoders • Low-power techniques – pipelining and parallelism – independent voltage/clock domains – efficient memory accessing ...
... • Motivation for low-power video decoders • Low-power techniques – pipelining and parallelism – independent voltage/clock domains – efficient memory accessing ...
Section E. Power Supply Unit
... Allow adequate venUlatlon above and below the rack. In some applications tnvolvtng high duty cycles. additional dump resistors may be needed as described earlier in this chapter. ...
... Allow adequate venUlatlon above and below the rack. In some applications tnvolvtng high duty cycles. additional dump resistors may be needed as described earlier in this chapter. ...
IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE) e-ISSN: 2278-1676,p-ISSN: 2320-3331,
... Since LDR has large resistance when dark and a low resistance when brightly lit, thus if R2 is much larger than R1 , Vout is large because most of the voltage are across R2 Thus when intruder’s shadow is cast on the LDR , there is increase in the LDR’s resistance bringing about increase base current ...
... Since LDR has large resistance when dark and a low resistance when brightly lit, thus if R2 is much larger than R1 , Vout is large because most of the voltage are across R2 Thus when intruder’s shadow is cast on the LDR , there is increase in the LDR’s resistance bringing about increase base current ...
UNIT II
... lower than that at the load • The reflection coefficient and standing-wave ratio both have larger magnitudes at the load • Computer programs and Smith Charts are available to calculate losses and mismatches in transmission lines ...
... lower than that at the load • The reflection coefficient and standing-wave ratio both have larger magnitudes at the load • Computer programs and Smith Charts are available to calculate losses and mismatches in transmission lines ...
to view the course outline.
... Simple Inputs: Programming a water detection system. Simple Outputs: Programming a beeping alarm for water leaks. ...
... Simple Inputs: Programming a water detection system. Simple Outputs: Programming a beeping alarm for water leaks. ...
transformers trm-8, -12, -24, -358
... No-load state current: maks. 36 mA AC (U=230 V AC, f=50 Hz) No-load state secondary voltage: 3,9 V AC or 6,3 V AC or 9,8 V AC No-load state secondary voltage tolerance: ±5 % Rated secondary current: 5 A AC or 3 A AC or 1.88 A AC Rated secondary voltage: 3 V AC or 5 V AC or 8 V AC Rated secondary vol ...
... No-load state current: maks. 36 mA AC (U=230 V AC, f=50 Hz) No-load state secondary voltage: 3,9 V AC or 6,3 V AC or 9,8 V AC No-load state secondary voltage tolerance: ±5 % Rated secondary current: 5 A AC or 3 A AC or 1.88 A AC Rated secondary voltage: 3 V AC or 5 V AC or 8 V AC Rated secondary vol ...
Power Electronics
... Motor load must always be connected as continuous operation of the softstart with no load may cause overheating of the motor and softstart. It is recommended that the softstart is protected by superfast semiconductor fuses rated as per the current rating of the softstart or motor. However, standard ...
... Motor load must always be connected as continuous operation of the softstart with no load may cause overheating of the motor and softstart. It is recommended that the softstart is protected by superfast semiconductor fuses rated as per the current rating of the softstart or motor. However, standard ...
AVR120-6 - ElectricalManuals.net
... adjustments above and below this level should cause the light bulb to go off and on. ...
... adjustments above and below this level should cause the light bulb to go off and on. ...
Homework 6
... of the device. These circuits are often referred to as "voltage regulators", and in this problem we’ll explore how to build the simplest form of such a voltage regulator. (a) The first problem we may have had to solve to realize such a voltage regulator is to figure out how to build a reference tha ...
... of the device. These circuits are often referred to as "voltage regulators", and in this problem we’ll explore how to build the simplest form of such a voltage regulator. (a) The first problem we may have had to solve to realize such a voltage regulator is to figure out how to build a reference tha ...
DAC715 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... +VCC to COMMON ...................................................................... 0V, +17V –VCC to COMMON ...................................................................... 0V, –17V +VCC to –VCC ................................................................................................. ...
... +VCC to COMMON ...................................................................... 0V, +17V –VCC to COMMON ...................................................................... 0V, –17V +VCC to –VCC ................................................................................................. ...