Moon Phases in Traditional Astrology
... “What each phase signifies and what kinds of Effects it has – We will append how the figures in question are also taken in relation to their effect-description and how they are fitting for a certain god.” 1 “The Conjunction, then, gives indications for reputation and power and kingly and sovereign d ...
... “What each phase signifies and what kinds of Effects it has – We will append how the figures in question are also taken in relation to their effect-description and how they are fitting for a certain god.” 1 “The Conjunction, then, gives indications for reputation and power and kingly and sovereign d ...
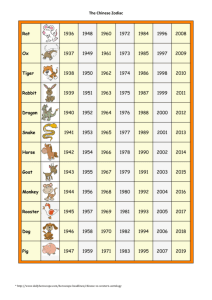
The Chinese Zodiac - Restaurant-East
... he summoned all the creatures on Earth to participate in a race. The first twelve species to cross the finish line were awarded signs in the Chinese zodiac. Consequently, the Rat got first p ...
... he summoned all the creatures on Earth to participate in a race. The first twelve species to cross the finish line were awarded signs in the Chinese zodiac. Consequently, the Rat got first p ...
Discovering The Universe for Yourself
... The Moon, Our Constant Companion • As the Moon moves through the sky, both its appearance and the time at which it rises and sets change with the cycle of Lunar Phases. ...
... The Moon, Our Constant Companion • As the Moon moves through the sky, both its appearance and the time at which it rises and sets change with the cycle of Lunar Phases. ...
JEOPARDY: Astronomy - Mr. Morrow`s Class
... 200 Q: Why do stars appear to move across the night sky? A: Stars do not move, but because Earth is rotating it looks like they move across the night sky from east to west. 300 Q: What is a constellation? A: a group of stars that form a pattern and are often named after animals, objects, or people. ...
... 200 Q: Why do stars appear to move across the night sky? A: Stars do not move, but because Earth is rotating it looks like they move across the night sky from east to west. 300 Q: What is a constellation? A: a group of stars that form a pattern and are often named after animals, objects, or people. ...
Exoplanets and Tides
... globe. There are continents sticking up, deep and shallow parts, etc. This complicates things, but tides can be reliably predicted. The Sun also raises tides. But it is at a much greater distance (400x as far away), so its tides are less important than the lunar tides, only about 1/3 as high. ...
... globe. There are continents sticking up, deep and shallow parts, etc. This complicates things, but tides can be reliably predicted. The Sun also raises tides. But it is at a much greater distance (400x as far away), so its tides are less important than the lunar tides, only about 1/3 as high. ...
January 2012 - Powerhouse Museum
... This star chart shows the stars and constellations visible in the night sky for Sydney, Melbourne, Canberra, Hobart and Adelaide for January 2012 at about 8.30 pm (summer time) and at about 7.30 pm (local standard time) for Perth and Brisbane. For Darwin and similar locations, the chart will still a ...
... This star chart shows the stars and constellations visible in the night sky for Sydney, Melbourne, Canberra, Hobart and Adelaide for January 2012 at about 8.30 pm (summer time) and at about 7.30 pm (local standard time) for Perth and Brisbane. For Darwin and similar locations, the chart will still a ...
June2016 - Celestial Insight
... and decision making. All this points towards a myriad of possible options from which we have to choose. Venus at superior conjunction holds they key to these decisions with our personal priorities about to alter course s we move towards her evening phase. There isn’t much in the way of fixed energy ...
... and decision making. All this points towards a myriad of possible options from which we have to choose. Venus at superior conjunction holds they key to these decisions with our personal priorities about to alter course s we move towards her evening phase. There isn’t much in the way of fixed energy ...
Earth, Moon, Sun Study Guide
... 9) Why does the moon appear to have different shapes? We can only see the part of the moon that is lit by the sun. Sometimes we can see the whole lit side (full moon), and other times we can half of the moon, or none of the moon. It depends on where the moon is in its revolution around the earth. 1 ...
... 9) Why does the moon appear to have different shapes? We can only see the part of the moon that is lit by the sun. Sometimes we can see the whole lit side (full moon), and other times we can half of the moon, or none of the moon. It depends on where the moon is in its revolution around the earth. 1 ...
Space Revision Answers File
... Dwarf Planets: Ceres, Pluto, and Eris 2. What are the four different types of galaxy shapes? Also define ‘galaxy’ The four different types of galaxy shapes are spiral, elliptical, lenticular, and irregular. A galaxy is a system of millions or billions of stars, together with gas and dust, held toget ...
... Dwarf Planets: Ceres, Pluto, and Eris 2. What are the four different types of galaxy shapes? Also define ‘galaxy’ The four different types of galaxy shapes are spiral, elliptical, lenticular, and irregular. A galaxy is a system of millions or billions of stars, together with gas and dust, held toget ...
The Moon and the Sun: 2003 version
... How has the Moon changed the last week? Is there a volunteer to draw what they saw on the board? What shape would you predict tonight? Does anyone know the name of this Moon phase? Why does this change occur? Did anyone observe the Moon at the same time each evening? Was the Moon always ...
... How has the Moon changed the last week? Is there a volunteer to draw what they saw on the board? What shape would you predict tonight? Does anyone know the name of this Moon phase? Why does this change occur? Did anyone observe the Moon at the same time each evening? Was the Moon always ...
Study Guide for Unit 4: Stars and Solar System
... we only see one side of the moon. It takes about 28 days for the Moon to make one complete rotation and revolution around the Earth. *The moons rotation and revolution around the Earth causes different moon phases. There are eight moon phases. *Waxing means the moon light we see is getting larger. T ...
... we only see one side of the moon. It takes about 28 days for the Moon to make one complete rotation and revolution around the Earth. *The moons rotation and revolution around the Earth causes different moon phases. There are eight moon phases. *Waxing means the moon light we see is getting larger. T ...
Astronomy - Learn Earth Science
... If an object is moving toward you, the waves get scrunched together and get (longer, shorter). If an object is moving away from you, the waves appear to spread out and get (longer, shorter). ...
... If an object is moving toward you, the waves get scrunched together and get (longer, shorter). If an object is moving away from you, the waves appear to spread out and get (longer, shorter). ...
Our Solar System Study Guide 4 grade standard to be tested: S4E2
... The solar system is made up of the Sun, planets, moons, and other objects that orbit the Sun. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun. We are able to see planets because light from the Sun reflects them. The Sun gives off light and heat. Both inner and outer planets orbit the Sun and are part of the so ...
... The solar system is made up of the Sun, planets, moons, and other objects that orbit the Sun. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun. We are able to see planets because light from the Sun reflects them. The Sun gives off light and heat. Both inner and outer planets orbit the Sun and are part of the so ...
Celestial Equator - University of Maryland Astronomy
... Summer occurs in your hemisphere when sunlight hits it more directly; winter occurs when the sunlight is less direct. Spring and fall are in between. AXIS TILT is the key to the seasons; without it, we would not have seasons on Earth! ...
... Summer occurs in your hemisphere when sunlight hits it more directly; winter occurs when the sunlight is less direct. Spring and fall are in between. AXIS TILT is the key to the seasons; without it, we would not have seasons on Earth! ...
The Moon - Tarotmoon Press
... come to the surface more than usual. Each full moon cycle you will experience in your lifetime is slightly different, and although the moon cycle creates a backdrop of energies based on the signs and phases it travels through, each person experiences them somewhat differently because of their own Mo ...
... come to the surface more than usual. Each full moon cycle you will experience in your lifetime is slightly different, and although the moon cycle creates a backdrop of energies based on the signs and phases it travels through, each person experiences them somewhat differently because of their own Mo ...
star chart - Ontario Science Centre
... During this full Moon, the Moon will be at its closest point in its orbit around Earth JULY 28 Southern Delta Aquariid meteor shower peaks; Not always the best to see from Canada but at least the Moon will set early this night AUG 10 * Second Supermoon of the year; This will be the largest full Moon ...
... During this full Moon, the Moon will be at its closest point in its orbit around Earth JULY 28 Southern Delta Aquariid meteor shower peaks; Not always the best to see from Canada but at least the Moon will set early this night AUG 10 * Second Supermoon of the year; This will be the largest full Moon ...
GAYNES SCHOOL SCHEME OF WORK – SCIENCE
... What is in the sky tonight? Show picture on tonight's night sky http://www.schoolsobservatory.org.uk/ What do you know? Sketch the solar system Is earth special? Day and night ...
... What is in the sky tonight? Show picture on tonight's night sky http://www.schoolsobservatory.org.uk/ What do you know? Sketch the solar system Is earth special? Day and night ...
Lecture
... In this picture of the Earth rising, what is the predominant direction of the sun in relation to the observer? 1) above the observer 2) below the observer 3) behind the observer 4) behind the Earth ...
... In this picture of the Earth rising, what is the predominant direction of the sun in relation to the observer? 1) above the observer 2) below the observer 3) behind the observer 4) behind the Earth ...
BENCHMARK 4 STUDY GUIDE
... Tides are the result of the Moon’s gravitational attraction on the oceans on the Earth in addition to the gravitational pull on the Earth itself. Any location will experience two high tides and two low tides in a 24 hr period due to the Earth’s rotation on its axis and the positioning of the Moon. S ...
... Tides are the result of the Moon’s gravitational attraction on the oceans on the Earth in addition to the gravitational pull on the Earth itself. Any location will experience two high tides and two low tides in a 24 hr period due to the Earth’s rotation on its axis and the positioning of the Moon. S ...
5.3 Most objects in the solar system are in a regular and predictable
... 4. The moon is a rocky object that revolves around the earth in a circular path called an orbit. The amount of time it takes for the moon to revolve once around the earth is about 29 days and is called a “lunar month.” 5. Half of the moon is always illuminated by the sun. Phases of the moon occur be ...
... 4. The moon is a rocky object that revolves around the earth in a circular path called an orbit. The amount of time it takes for the moon to revolve once around the earth is about 29 days and is called a “lunar month.” 5. Half of the moon is always illuminated by the sun. Phases of the moon occur be ...
Exam #1 Review
... 15. Describe the motions of the planets in the Solar System. 16. Explain how retrograde motion occurs and discuss the importance of viewing angle or ...
... 15. Describe the motions of the planets in the Solar System. 16. Explain how retrograde motion occurs and discuss the importance of viewing angle or ...
July 2013 - Joliet Junior College
... On July 5th, Earth will be at its farthest from the sun for the year - 94.5 million miles. In January, we are 91.4 million miles from the sun. Because we are farther from the sun in July, we move a little slower in our orbit - about 2,200 miles per hour slower than in January. Now that we are past t ...
... On July 5th, Earth will be at its farthest from the sun for the year - 94.5 million miles. In January, we are 91.4 million miles from the sun. Because we are farther from the sun in July, we move a little slower in our orbit - about 2,200 miles per hour slower than in January. Now that we are past t ...
Unit Plan
... 8. What would be the altitude-azimuth coordinates for an object that is located at the zenith? 9. Why do modern astronomers continue to use the celestial sphere when they know that stars are not all at the same distance? 10. Draw a sketch of the celestial sphere and label the celestial poles, the ce ...
... 8. What would be the altitude-azimuth coordinates for an object that is located at the zenith? 9. Why do modern astronomers continue to use the celestial sphere when they know that stars are not all at the same distance? 10. Draw a sketch of the celestial sphere and label the celestial poles, the ce ...
Slide 1
... •The moon is a rock object that revolves around the earth in a circular path called an orbit. •The amount of time it takes for the moon to revolve once around the earth is about 29 days and is called a “lunar month”. •Half of the moon is always illuminated by the sun. •Phases of the moon occur becau ...
... •The moon is a rock object that revolves around the earth in a circular path called an orbit. •The amount of time it takes for the moon to revolve once around the earth is about 29 days and is called a “lunar month”. •Half of the moon is always illuminated by the sun. •Phases of the moon occur becau ...
solar-sy - WordPress.com
... The reason for the seasons is not how close the earth is to the sun but the tilt of the earth. When the northern Hemisphere is tilted away from the sun (indirect sun light –spread out) it is our winter and when the northern hemisphere is tilted toward the sun (direct sunlight – more focused) it is o ...
... The reason for the seasons is not how close the earth is to the sun but the tilt of the earth. When the northern Hemisphere is tilted away from the sun (indirect sun light –spread out) it is our winter and when the northern hemisphere is tilted toward the sun (direct sunlight – more focused) it is o ...
Lunar effect
.jpg?width=300)
The term lunar effect refers to the belief that there is correlation between specific stages of the Earth's lunar cycle and behavior in animals (including humans), that cannot simply be explained by variation in light levels. A considerable number of studies have examined the belief: by the late 1980s, there were at least 40 published studies on the purported lunar-lunacy connection, and at least 20 published studies on the purported lunar-birthrate connection. Several extensive literature reviews and meta-analyses have found no correlation between the lunar cycle and human biology or behavior. One study with incomplete control for age and sex of a small sample indicates a possible connection between sleep quality and lunar phases, but a subsequent analysis conducted with a larger sample size and better experimental controls did not replicate the findings. The Moon, however, does influence the behavior of several animals.