Constant 1g acceleration
... Space Travel Under Constant 1g Acceleration The basic principle behind every high-thrust interplanetary space probe is to accelerate briefly, and then coast, following an elliptical, parabolic, or mildly hyperbolic solar trajectory to your destination, using gravity assists whenever possible. But th ...
... Space Travel Under Constant 1g Acceleration The basic principle behind every high-thrust interplanetary space probe is to accelerate briefly, and then coast, following an elliptical, parabolic, or mildly hyperbolic solar trajectory to your destination, using gravity assists whenever possible. But th ...
title of video - Discovery Education
... An afterburner is a pipe that is added to the back of a plane into which fuel can be dumped and ignited, giving a fighter jet an extra boost of speed. Because they expend fuel at a much higher rate than normal flight, afterburners are used sparingly, in such situations as takeoff from an aircraft ca ...
... An afterburner is a pipe that is added to the back of a plane into which fuel can be dumped and ignited, giving a fighter jet an extra boost of speed. Because they expend fuel at a much higher rate than normal flight, afterburners are used sparingly, in such situations as takeoff from an aircraft ca ...
θ θ θ θ θ θ - Physicshelpline
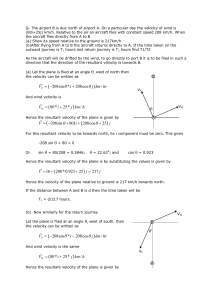
... V 208sin 80 i 208cos 25 j For this resultant velocity to be towards south, its i component must be zero. This gives -208 sin + 80 = 0 Or ...
... V 208sin 80 i 208cos 25 j For this resultant velocity to be towards south, its i component must be zero. This gives -208 sin + 80 = 0 Or ...
Four Forces of Flight
... force of gravity, and the amount of thrust produced by the engine must be greater than the drag force created by air resistance. Wing shapes that provide lift and have the proper angle of attack (the angle at which a wing meets the flow of air) can then help an airplane overcome gravity. Research ha ...
... force of gravity, and the amount of thrust produced by the engine must be greater than the drag force created by air resistance. Wing shapes that provide lift and have the proper angle of attack (the angle at which a wing meets the flow of air) can then help an airplane overcome gravity. Research ha ...
Semi Plenary 2
... Computationally efficient deterministic method for pruning infeasible solutions with polynomial time and space complexity Allows effective visualisation of high dimensional search space Identifies launch windows which can be optimised ...
... Computationally efficient deterministic method for pruning infeasible solutions with polynomial time and space complexity Allows effective visualisation of high dimensional search space Identifies launch windows which can be optimised ...
Reentry Vehicles and Orbital Mechanics Subcommittee
... flight performance of vehicles that orbit planets or reenter planetary atmospheres. Orbital mechanics involves the motion of spacecraft, such as rockets and satellites, and includes interplanetary transfers and orbital maneuvers. Orbital mechanics is used by mission planners to design propulsive man ...
... flight performance of vehicles that orbit planets or reenter planetary atmospheres. Orbital mechanics involves the motion of spacecraft, such as rockets and satellites, and includes interplanetary transfers and orbital maneuvers. Orbital mechanics is used by mission planners to design propulsive man ...
presentation
... into a lower energy elliptical orbit whereupon it will meet up with pre-deposited station and then return to its maximal point on the Venus Orbital path. This method of slowing down is most notably used for the orbital entry of satellites around large bodies ...
... into a lower energy elliptical orbit whereupon it will meet up with pre-deposited station and then return to its maximal point on the Venus Orbital path. This method of slowing down is most notably used for the orbital entry of satellites around large bodies ...
Flight dynamics (spacecraft)
Spacecraft flight dynamics is the science of space vehicle performance, stability, and control. It requires analysis of the six degrees of freedom of the vehicle's flight, which are similar to those of aircraft: translation in three dimensional axes; and its orientation about the vehicle's center of mass in these axes, known as pitch, roll and yaw, with respect to a defined frame of reference.Dynamics is the modeling of the changing position and orientation of a vehicle, in response to external forces acting on the body. For a spacecraft, these forces are of three types: propulsive force (usually provided by the vehicle's engine thrust); gravitational force exerted by the Earth or other celestial bodies; and aerodynamic lift and drag (when flying in the atmosphere of the Earth or other body, such as Mars or Venus). The vehicle's attitude must be taken into account because of its effect on the aerodynamic and propulsive forces. There are other reasons, unrelated to flight dynamics, for controlling the vehicle's attitude in non-powered flight (e.g., thermal control, solar power generation, communications, or astronomical observation).The principles of flight dynamics are normally used to control a spacecraft by means of an inertial navigation system in conjunction with an attitude control system. Together, they create a subsystem of the spacecraft bus often called ADCS.