Chapter 14 - Work and Power – Physical Science Study Guide What
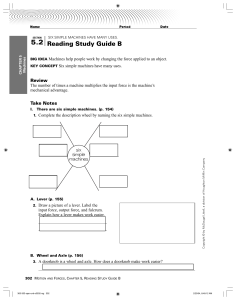
... 9. A machine is a device that can multiply __________. 10. When a machine does work it can not increase a force and _______________________. 11. How can a machine make work easier for you? 12. How can you make the work output of a machine greater than the work input? 13. The actual mechanical advant ...
... 9. A machine is a device that can multiply __________. 10. When a machine does work it can not increase a force and _______________________. 11. How can a machine make work easier for you? 12. How can you make the work output of a machine greater than the work input? 13. The actual mechanical advant ...
Artificial Intelligence in Machines
... Artificial intelligence has been the subject of optimism, but has also suffered setbacksand, today, has become an essential part of the technology industry, providing the heavy lifting for many of the most difficult problems in computer science. All research is highly technical and specialized, deep ...
... Artificial intelligence has been the subject of optimism, but has also suffered setbacksand, today, has become an essential part of the technology industry, providing the heavy lifting for many of the most difficult problems in computer science. All research is highly technical and specialized, deep ...
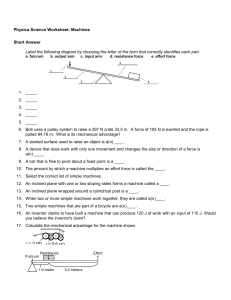
Physica Science Worksheet: Machines Short Answer Label the
... 7. A slanted surface used to raise an object is a(n) ____. 8. A device that does work with only one movement and changes the size or direction of a force is a(n) ____. 9. A bar that is free to pivot about a fixed point is a ____. 10. The amount by which a machine multiplies an effort force is called ...
... 7. A slanted surface used to raise an object is a(n) ____. 8. A device that does work with only one movement and changes the size or direction of a force is a(n) ____. 9. A bar that is free to pivot about a fixed point is a ____. 10. The amount by which a machine multiplies an effort force is called ...
12 Machine-repairmen problem
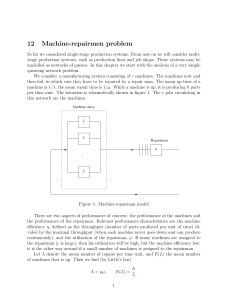
... So far we considered single-stage production systems. From now on we will consider multistage production systems, such as production lines and job shops. These systems may be modelled as networks of queues. In this chapter we start with the analysis of a very simple queueing network problem. We cons ...
... So far we considered single-stage production systems. From now on we will consider multistage production systems, such as production lines and job shops. These systems may be modelled as networks of queues. In this chapter we start with the analysis of a very simple queueing network problem. We cons ...
PSCh5GR - TeacherPage.com
... For an ideal machine, what is the relationship of the input work to the output work? ...
... For an ideal machine, what is the relationship of the input work to the output work? ...
Using Machines
... Conservation of energy states that energy can never be created or destroyed, therefore the machine can never create extra energy Machine can never give more energy then it receives ...
... Conservation of energy states that energy can never be created or destroyed, therefore the machine can never create extra energy Machine can never give more energy then it receives ...
Section 9.1
... 9.1 Using Machines The input includes everything you do to make the machine accomplish a task, like pushing on the bicycle pedals. The output is what the machine does for you, like going fast or climbing a steep hill. ...
... 9.1 Using Machines The input includes everything you do to make the machine accomplish a task, like pushing on the bicycle pedals. The output is what the machine does for you, like going fast or climbing a steep hill. ...
Artificial Inteligence
... • Transformation of data:-By using AI machines one can transfer interval data into ordinal data and ordinal data into categorical data. For e.g. we have data:45 7 9 43 1 We want to sort and give ranks to it. Sorted : 1 7 9 43 45 Ranked: 1 2 3 4 ...
... • Transformation of data:-By using AI machines one can transfer interval data into ordinal data and ordinal data into categorical data. For e.g. we have data:45 7 9 43 1 We want to sort and give ranks to it. Sorted : 1 7 9 43 45 Ranked: 1 2 3 4 ...
Self-replicating machine

A self-replicating machine is a type of autonomous robot that is capable of reproducing itself autonomously using raw materials found in the environment, thus exhibiting self-replication in a way analogous to that found in nature. The concept of self-replicating machines has been advanced and examined by Homer Jacobsen, Edward F. Moore, Freeman Dyson, John von Neumann and in more recent times by K. Eric Drexler in his book on nanotechnology, Engines of Creation and by Robert Freitas and Ralph Merkle in their review Kinematic Self-Replicating Machines which provided the first comprehensive analysis of the entire replicator design space. The future development of such technology is an integral part of several plans involving the mining of moons and asteroid belts for ore and other materials, the creation of lunar factories, and even the construction of solar power satellites in space. The possibly misnamed von Neumann probe is one theoretical example of such a machine. Von Neumann also worked on what he called the universal constructor, a self-replicating machine that would operate in a cellular automata environment.A self-replicating machine is an artificial self-replicating system that relies on conventional large-scale technology and automation. Certain idiosyncratic terms are occasionally found in the literature. For example, the term ""clanking replicator"" was once used by Drexler to distinguish macroscale replicating systems from the microscopic nanorobots or ""assemblers"" that nanotechnology may make possible, but the term is informal and is rarely used by others in popular or technical discussions. Replicators have also been called ""von Neumann machines"" after John von Neumann, who first rigorously studied the idea. However, the term ""von Neumann machine"" is less specific and also refers to a completely unrelated computer architecture that von Neumann proposed and so its use is discouraged where accuracy is important. Von Neumann himself used the term universal constructor to describe such self-replicating machines.Historians of machine tools, even before the numerical control era, sometimes figuratively said that machine tools were a unique class of machines because they have the ability to ""reproduce themselves"" by copying all of their parts. Implicit in these discussions is that a human would direct the cutting processes (later planning and programming the machines), and would then be assembling the parts. The same is true for RepRaps, which are another class of machines sometimes mentioned in reference to such non-autonomous ""self-replication"". In contrast, machines that are truly autonomously self-replicating (like biological machines) are the main subject discussed here.