Basic Learning Processes - Webcourses
... to the extent that the organism has been deprived (relative to its baseline frequency) of performing that behavior. Reward learning: Another term for positive reinforcement. (In reward learning, we learn from reinforcing consequences.) Some instructors strongly oppose the use of this term, but it is ...
... to the extent that the organism has been deprived (relative to its baseline frequency) of performing that behavior. Reward learning: Another term for positive reinforcement. (In reward learning, we learn from reinforcing consequences.) Some instructors strongly oppose the use of this term, but it is ...
An Analytical Evaluation of “Differential Negative Reinforcement of
... reinforcers are not highly contrived but rather resemble the actual reinforcer qualitatively. A natural reinforcer is functionally relevant to the learner. A more natural reinforcer is used to promote better generalization. It can help ensure that the contingency arranged for in the behavior change ...
... reinforcers are not highly contrived but rather resemble the actual reinforcer qualitatively. A natural reinforcer is functionally relevant to the learner. A more natural reinforcer is used to promote better generalization. It can help ensure that the contingency arranged for in the behavior change ...
Third Quarter Syllabus - International Training Center for Applied
... Applied Behavior Analysis is one of the most rapidly advancing areas of modern science. Applied behavior analysis (ABA) is the science of applying experimentally derived principles of behavior to improve socially significant behavior. ABA takes what we know about behavior and uses it to bring about ...
... Applied Behavior Analysis is one of the most rapidly advancing areas of modern science. Applied behavior analysis (ABA) is the science of applying experimentally derived principles of behavior to improve socially significant behavior. ABA takes what we know about behavior and uses it to bring about ...
SP ED 5022/6022-001 | Applied Behavior Analysis Powerpoint
... really that useful for us as classroom teachers to apply to, OK if I have a child acting out in my classroom, now what do I do? Biochemical explanations don't really help you all that much, because you as a teacher can't necessarily change a child's genetics or their biochemistry. So this has sort o ...
... really that useful for us as classroom teachers to apply to, OK if I have a child acting out in my classroom, now what do I do? Biochemical explanations don't really help you all that much, because you as a teacher can't necessarily change a child's genetics or their biochemistry. So this has sort o ...
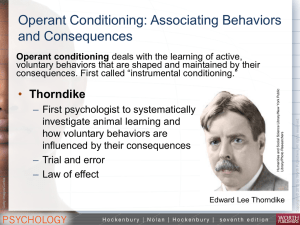
Operant Conditioning PP
... • Believed that internal factors like thoughts, emotions, and beliefs could not be used to explain behavior. • Instead said that new behaviors were actively chosen by the organism • Looked at “Operants” or active behaviors that are used on the environment to generate consequences • Developed the fun ...
... • Believed that internal factors like thoughts, emotions, and beliefs could not be used to explain behavior. • Instead said that new behaviors were actively chosen by the organism • Looked at “Operants” or active behaviors that are used on the environment to generate consequences • Developed the fun ...
Operant Conditioning
... presses or pecks to release a food or water reward, and a device that records these responses. • Shaping - procedure in which rewards, such as food, gradually guide an animal’s behavior toward a desired behavior. • Successive approximations - shaping method in which you reward responses that are eve ...
... presses or pecks to release a food or water reward, and a device that records these responses. • Shaping - procedure in which rewards, such as food, gradually guide an animal’s behavior toward a desired behavior. • Successive approximations - shaping method in which you reward responses that are eve ...
Operant Conditioning
... presses or pecks to release a food or water reward, and a device that records these responses. • Shaping - procedure in which rewards, such as food, gradually guide an animal’s behavior toward a desired behavior. • Successive approximations - shaping method in which you reward responses that are eve ...
... presses or pecks to release a food or water reward, and a device that records these responses. • Shaping - procedure in which rewards, such as food, gradually guide an animal’s behavior toward a desired behavior. • Successive approximations - shaping method in which you reward responses that are eve ...
PSYCHOLOGY Unit 3: Learning“Operant Conditioning”
... First, any behavior changes that result from punishment are often temporary. "Punished behavior is likely to reappear after the punitive consequences are withdrawn," Skinner explained in his book About Behaviorism. Perhaps the greatest drawback is the fact that punishment does not actually offer any ...
... First, any behavior changes that result from punishment are often temporary. "Punished behavior is likely to reappear after the punitive consequences are withdrawn," Skinner explained in his book About Behaviorism. Perhaps the greatest drawback is the fact that punishment does not actually offer any ...
Psychological Theories of Crime and Delinquency
... delinquency (Shoemaker). In essence, delinquent behavior is seen as the external manifestation of an internal disease (Shoemaker). Erikson expanded on this theory, explaining delinquency as an ‘‘identity crisis’’ created by inner turmoil (Siegel et al., 2006). As has been noted by many critics of ps ...
... delinquency (Shoemaker). In essence, delinquent behavior is seen as the external manifestation of an internal disease (Shoemaker). Erikson expanded on this theory, explaining delinquency as an ‘‘identity crisis’’ created by inner turmoil (Siegel et al., 2006). As has been noted by many critics of ps ...
B3-Utilizing-ABA-in - PATH International
... Automatic process that refers to the selective effects of CONSEQUENCE on behaviors. Includes: Reinforcement Punishment ...
... Automatic process that refers to the selective effects of CONSEQUENCE on behaviors. Includes: Reinforcement Punishment ...
AP Ch. 5 Operant
... called positive punishment – Punishment by removal: a situation in which an operant is followed by the removal or subtraction of a reinforcing stimulus; also called negative punishment ...
... called positive punishment – Punishment by removal: a situation in which an operant is followed by the removal or subtraction of a reinforcing stimulus; also called negative punishment ...
Operant Conditioning - PV
... Operant Conditioning • A type of learning in which behavior occurs more frequently if followed by reinforcement or occurs less frequently if followed by punishment. ...
... Operant Conditioning • A type of learning in which behavior occurs more frequently if followed by reinforcement or occurs less frequently if followed by punishment. ...
Operant Conditioning
... dog's responses of lifting its head higher and higher. Then, he simply set about shaping a jumping response by flashing the strobe (and simultaneously taking a picture), followed by giving a meat treat, each time the dog satisfied the criterion for reinforcement. The result of this process is shown ...
... dog's responses of lifting its head higher and higher. Then, he simply set about shaping a jumping response by flashing the strobe (and simultaneously taking a picture), followed by giving a meat treat, each time the dog satisfied the criterion for reinforcement. The result of this process is shown ...
Skinner`s Theory - BDoughertyAmSchool
... himself whether he could get more complex sorts of behaviors using this. He responded with the idea of shaping, or “the method of successive approximations.” Basically, it involved first reinforcing a behavior only vaguely similar to the one desired. Once that was established, you look out for varia ...
... himself whether he could get more complex sorts of behaviors using this. He responded with the idea of shaping, or “the method of successive approximations.” Basically, it involved first reinforcing a behavior only vaguely similar to the one desired. Once that was established, you look out for varia ...
1 Learning Classical Conditioning Classical conditioning terms
... ?Operant conditioning chamber ...
... ?Operant conditioning chamber ...
File - Coach Wilkinson`s AP Euro Site
... does not actually offer any information about more appropriate or desired behaviors. While subjects might be learning to not perform certain actions, they are not really learning anything about what they should be doing. Another thing to consider about punishment is that it can have unintended and u ...
... does not actually offer any information about more appropriate or desired behaviors. While subjects might be learning to not perform certain actions, they are not really learning anything about what they should be doing. Another thing to consider about punishment is that it can have unintended and u ...
Module 10 Presentation
... learning on aggressiveness in children • All three groups viewed a film of an adult punching and verbally abusing a ‘Bobo Doll’ – Group One: Adult was rewarded – Group Two: Adult was punished – Group Three: No consequences for the adult ...
... learning on aggressiveness in children • All three groups viewed a film of an adult punching and verbally abusing a ‘Bobo Doll’ – Group One: Adult was rewarded – Group Two: Adult was punished – Group Three: No consequences for the adult ...
The Psychology of Learning and Behavior
... known for his studies of reflex behavior. He was born in Ryazan', and educated at the University of Saint Petersburg and at the Military Medical Academy, St. Petersburg; from 1884 to 1886 he studied in Breslau (now Wroclaw, Poland) and Leipzig, Germany. Before the Russian Revolution he served as dir ...
... known for his studies of reflex behavior. He was born in Ryazan', and educated at the University of Saint Petersburg and at the Military Medical Academy, St. Petersburg; from 1884 to 1886 he studied in Breslau (now Wroclaw, Poland) and Leipzig, Germany. Before the Russian Revolution he served as dir ...
I Have a Dream: My Hopeful Future for Behavior Analysis
... man and animal alike, do adjust themselves to their environment by means of hereditary and habit equipments. These adjustments may be very adequate or they may be so inadequate that the organism barely maintains its existence; secondly, that certain stimuli lead the organisms to make the responses. ...
... man and animal alike, do adjust themselves to their environment by means of hereditary and habit equipments. These adjustments may be very adequate or they may be so inadequate that the organism barely maintains its existence; secondly, that certain stimuli lead the organisms to make the responses. ...
LCog paper 1
... sexually capable teens to abstain? Who decides these issues? What about vocations? Can we use operant conditioning to develop a desire for positive social contribution that will be maintained outside of the operant setting? As it becomes less obvious what positive behaviors to shape, it should also ...
... sexually capable teens to abstain? Who decides these issues? What about vocations? Can we use operant conditioning to develop a desire for positive social contribution that will be maintained outside of the operant setting? As it becomes less obvious what positive behaviors to shape, it should also ...
Unit 6 Learning Classical Conditioning Please keep in mind that
... Primary Reinforcer: an innately reinforcing stimulus, such as one that satisfies a biological need (e.g., food or water). Secondary (or Conditioned) Reinforcer: a stimulus that gains it reinforcing power through its association with a primary reinforcer (e.g., money). **Remember: Immediate reinforce ...
... Primary Reinforcer: an innately reinforcing stimulus, such as one that satisfies a biological need (e.g., food or water). Secondary (or Conditioned) Reinforcer: a stimulus that gains it reinforcing power through its association with a primary reinforcer (e.g., money). **Remember: Immediate reinforce ...
Study Guide - DocShare.tips
... • Conditioning somatic (voluntary) behavior versus autonomic (involuntary) behaviors. Somatic is easier to donation then autonomic. • Deprivation level: learning is faster and stronger when learned is deprive of rewards. • Competing rewards: conditioning is a slow and weak if other behaviors are als ...
... • Conditioning somatic (voluntary) behavior versus autonomic (involuntary) behaviors. Somatic is easier to donation then autonomic. • Deprivation level: learning is faster and stronger when learned is deprive of rewards. • Competing rewards: conditioning is a slow and weak if other behaviors are als ...
EXPLORING PSYCHOLOGY (7th Edition in Modules) David Myers
... attaching 3 parts. After he gets his parts attached, he gets some free time before the next car moves down the line. 18. Brittany is a telemarketer trying to sell life insurance. After so many calls, someone will eventually buy. ...
... attaching 3 parts. After he gets his parts attached, he gets some free time before the next car moves down the line. 18. Brittany is a telemarketer trying to sell life insurance. After so many calls, someone will eventually buy. ...
MyersExpPsych7e_IM_Module 19 Garber edits
... 6. Madison spanks her son if she has to ask him three times to clean up his room. 7. Emily has a spelling test every Friday. She usually does well and gets a star sticker. 8. Steve’s a big gambling man. He plays the slot machines all day hoping for a big win. 9. Snakes get hungry at certain times of ...
... 6. Madison spanks her son if she has to ask him three times to clean up his room. 7. Emily has a spelling test every Friday. She usually does well and gets a star sticker. 8. Steve’s a big gambling man. He plays the slot machines all day hoping for a big win. 9. Snakes get hungry at certain times of ...