block 2 - Council of Europe
... caused by forces extraneous to him”, or in other words, “the probability of occurrence, within a specific period of time in a given area, of a potentially damaging natural phenomena” (Table 1-I). Technologic hazards are “major man-made accidents, that is, the initiating event in a disaster arises fr ...
... caused by forces extraneous to him”, or in other words, “the probability of occurrence, within a specific period of time in a given area, of a potentially damaging natural phenomena” (Table 1-I). Technologic hazards are “major man-made accidents, that is, the initiating event in a disaster arises fr ...
Study of age factor of concrete upto 180 days
... in large quantities by the iron and steel industry in India. These operate at a temperature of about 1500 degree centigrade and are fed with a carefully controlled mixture of iron – ore, coke and limestone. The iron ore is reduced to iron and remaining materials from slag that floats on top of the i ...
... in large quantities by the iron and steel industry in India. These operate at a temperature of about 1500 degree centigrade and are fed with a carefully controlled mixture of iron – ore, coke and limestone. The iron ore is reduced to iron and remaining materials from slag that floats on top of the i ...
Evaluation of Residual Strength Properties of Steel Fiber Reinforced
... advantages than can be attained with fiber addition, a there is limited information regarding the quantitative influence and relative importance of fiber parameters such as amount, aspect ratio and fiber type. In general, the addition of fibers has added a further dimension to the study of fatigue i ...
... advantages than can be attained with fiber addition, a there is limited information regarding the quantitative influence and relative importance of fiber parameters such as amount, aspect ratio and fiber type. In general, the addition of fibers has added a further dimension to the study of fatigue i ...
Overview of Geologic Structures
... Earthquakes: fault rupture and offset is most common cause of earthquakes and seismic activity; related to brittle deformation and "elastic rebound" of rock material immediately following rupture (a) ...
... Earthquakes: fault rupture and offset is most common cause of earthquakes and seismic activity; related to brittle deformation and "elastic rebound" of rock material immediately following rupture (a) ...
Arsenic in Ground Water in the Cow Island Area, Louisiana
... Water quality in and around the towns of Cow Island and Forked Island, Louisiana has been a major issue in recent years. Intense media attention in occurred in 2004, when the Louisiana Department of Environmental Quality (LDEQ) conducted tests of total arsenic (As) content in groundwater from 21 dom ...
... Water quality in and around the towns of Cow Island and Forked Island, Louisiana has been a major issue in recent years. Intense media attention in occurred in 2004, when the Louisiana Department of Environmental Quality (LDEQ) conducted tests of total arsenic (As) content in groundwater from 21 dom ...
Landslides in weathered granitic rocks in Japan and Malaysia
... the ground surface when a slope inclines some 40 degrees. The extent of disintegration seems to abruptly change at the base of a loosened zone, probably due to the fact that creep and widening, as well as neoformation of microcracks, occurs interconnectedly. In other words, the increase of microcrac ...
... the ground surface when a slope inclines some 40 degrees. The extent of disintegration seems to abruptly change at the base of a loosened zone, probably due to the fact that creep and widening, as well as neoformation of microcracks, occurs interconnectedly. In other words, the increase of microcrac ...
JOUR
... 1. Several correlations were produced to simulate the effect of shear force and oil / water ratio on the emulsion stability factors. By using these correlations, these factors can be calculated to determine the stability degree or condition of the emulsion. 2. An excellent improvement in electric st ...
... 1. Several correlations were produced to simulate the effect of shear force and oil / water ratio on the emulsion stability factors. By using these correlations, these factors can be calculated to determine the stability degree or condition of the emulsion. 2. An excellent improvement in electric st ...
Soluble rocks - British Geological Survey
... Monitoring and measurement The British Geological Survey is compiling and maintaining a national database of karst features that currently holds information for about half of the country. This dataset was founded on, and has improved on, information that was initially gathered for a database of natu ...
... Monitoring and measurement The British Geological Survey is compiling and maintaining a national database of karst features that currently holds information for about half of the country. This dataset was founded on, and has improved on, information that was initially gathered for a database of natu ...
IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE)
... Many buildings (having number of stories range between 7-13 storey) has been studied according to scheduled investigations. It has been found that the major reasons of these failure are duo to poor concreting, slab excessive deflection, excessive cracks in beams, foundation settlement, insufficient ...
... Many buildings (having number of stories range between 7-13 storey) has been studied according to scheduled investigations. It has been found that the major reasons of these failure are duo to poor concreting, slab excessive deflection, excessive cracks in beams, foundation settlement, insufficient ...
Soluble rocks
... Monitoring and measurement The British Geological Survey is compiling and maintaining a national database of karst features that currently holds information for about half of the country. This dataset was founded on, and has improved on, information that was initially gathered for a database of natu ...
... Monitoring and measurement The British Geological Survey is compiling and maintaining a national database of karst features that currently holds information for about half of the country. This dataset was founded on, and has improved on, information that was initially gathered for a database of natu ...
custom material model for simulation of frp strenghtened reinforced
... extensive damages in the structural members. Many of the old shear wall buildings are at risk of suffering damages from a major earthquake mostly due to their insufficient inplane stiffness, flexural and shear strengths and ductility. Various methods and techniques of seismic strengthening and repai ...
... extensive damages in the structural members. Many of the old shear wall buildings are at risk of suffering damages from a major earthquake mostly due to their insufficient inplane stiffness, flexural and shear strengths and ductility. Various methods and techniques of seismic strengthening and repai ...
12 THE HILLSIDE ORDINANCE
... Street Access Requires that lots fronting on a Substandard Hillside Limited Street must have at least one-half of the width of the street(s) dedicated for the full frontage of the lot or for a lesser frontage as determined by the City Engineer. Relief from this requirement may be provided by Section ...
... Street Access Requires that lots fronting on a Substandard Hillside Limited Street must have at least one-half of the width of the street(s) dedicated for the full frontage of the lot or for a lesser frontage as determined by the City Engineer. Relief from this requirement may be provided by Section ...
2.2.3 Water content
... disintegration of these rocks when subject to change in water content. This nondurable behavior of these rocks is responsible for numerous slope instability problems, underground excavation problems and embankment failures. Water content has been demonstrated to have a marked influence on the streng ...
... disintegration of these rocks when subject to change in water content. This nondurable behavior of these rocks is responsible for numerous slope instability problems, underground excavation problems and embankment failures. Water content has been demonstrated to have a marked influence on the streng ...
مسرد جيولوجيا جامعة ايوا iowa
... bedding plane Surface separating layers of sedimentary rocks and deposits. Each bedding plane marks termination of one deposit and beginning of another of different character, such as a surface separating a sandstone bed from an overlying mudstone bed. Rock tends to breaks or separate, readily ...
... bedding plane Surface separating layers of sedimentary rocks and deposits. Each bedding plane marks termination of one deposit and beginning of another of different character, such as a surface separating a sandstone bed from an overlying mudstone bed. Rock tends to breaks or separate, readily ...
2. Fault mechanics: some basic aspects
... (fig. 12). High fluid pressures (caused by rapid burial of impermeable strata, thermal water pressuring and dehydration reactions occurring during burial and metamorphism) reduce drastically the stress needed to generate rock fracturing and formation of faults, since it supports part of the normal s ...
... (fig. 12). High fluid pressures (caused by rapid burial of impermeable strata, thermal water pressuring and dehydration reactions occurring during burial and metamorphism) reduce drastically the stress needed to generate rock fracturing and formation of faults, since it supports part of the normal s ...
pdf. - Dorset Geologists` Association
... between the outfall of the River Axe at Seaton, Devon and Lyme Regis, Dorset comprises a 100 to 800 m wide coastal zone of coalescing landslides. This is the largest active landslide complex in Britain and includes examples of all the principal types of mass movement including rotational failures, m ...
... between the outfall of the River Axe at Seaton, Devon and Lyme Regis, Dorset comprises a 100 to 800 m wide coastal zone of coalescing landslides. This is the largest active landslide complex in Britain and includes examples of all the principal types of mass movement including rotational failures, m ...
INTRODUCTION: (Importance to a Civil Engineer): The earlier
... 4. Boring, drilling and excavation to provide confirmation of the previous results, and quantitative detail, at critical points on the site; and 5. Testing of soils and rocks to assess their suitability, particularly their mechanical properties (soil mechanics and rock mechanics), either in situ or ...
... 4. Boring, drilling and excavation to provide confirmation of the previous results, and quantitative detail, at critical points on the site; and 5. Testing of soils and rocks to assess their suitability, particularly their mechanical properties (soil mechanics and rock mechanics), either in situ or ...
GEOG 123B Lec. #5
... unconsolidated sediment and weathered rock forms the parent material from which soil evolves. When rock is broken and disintegrated without any chemical alteration, the process is called physical weathering or mechanical weathering. By breaking up rock, physical weathering greatly increases the surf ...
... unconsolidated sediment and weathered rock forms the parent material from which soil evolves. When rock is broken and disintegrated without any chemical alteration, the process is called physical weathering or mechanical weathering. By breaking up rock, physical weathering greatly increases the surf ...
Structure Foundation Considerations
... - Evaluation of construction methods - dry, slurry, and casing methods where applicable. - If casing will be required, can casing be pulled as shaft is concerted (this can result in significant cost savings on very large diameter shafts). - If artesian water was encountered in explorations, have des ...
... - Evaluation of construction methods - dry, slurry, and casing methods where applicable. - If casing will be required, can casing be pulled as shaft is concerted (this can result in significant cost savings on very large diameter shafts). - If artesian water was encountered in explorations, have des ...
Design of Soil and water conservation structures
... Structure can be designed either to retain or discharge runoff. They can also be designed so that part of the runoff is retained but the excess, during heavy storms, is discharged. In the higher rainfall areas(e.g. over 1,250 mm per annum), where crops are rarely short of water, or where there is a ...
... Structure can be designed either to retain or discharge runoff. They can also be designed so that part of the runoff is retained but the excess, during heavy storms, is discharged. In the higher rainfall areas(e.g. over 1,250 mm per annum), where crops are rarely short of water, or where there is a ...
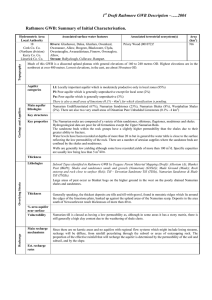
Rathmore GWB: Summary of Initial
... The topography of this body is mainly upland, with ground level rising from about 50 metres OD to the highest elevations. Of 400 metres OD on the catchment boundary. The groundwater body is comprised of rocks with low transmissivity and storativity, although localised zones of enhanced permeability ...
... The topography of this body is mainly upland, with ground level rising from about 50 metres OD to the highest elevations. Of 400 metres OD on the catchment boundary. The groundwater body is comprised of rocks with low transmissivity and storativity, although localised zones of enhanced permeability ...
Section 2 - Earthworks
... The supplementary reports should cover the following factors: a) Connections with the Comprehensive Report b) Design and construction requirements for special items such as road subgrades and retaining walls ...
... The supplementary reports should cover the following factors: a) Connections with the Comprehensive Report b) Design and construction requirements for special items such as road subgrades and retaining walls ...
analysis_assignment_1 - abuad lms
... beams as the equations do not become more complicated as the number of unknowns increases. The equations remain easy to derive no matter how many degrees of indeterminacy there are in the structure. b. This method provides a base of knowledge that is needed to perform the matrix-stiffness method, wh ...
... beams as the equations do not become more complicated as the number of unknowns increases. The equations remain easy to derive no matter how many degrees of indeterminacy there are in the structure. b. This method provides a base of knowledge that is needed to perform the matrix-stiffness method, wh ...
Landslide mitigation

Landslide mitigation refers to construction and other man-made activities on slopes with the goal of lessening the effect of landslides. Landslides can be triggered by many, sometimes concomitant causes. In addition to shallow erosion or reduction of shear strength caused by seasonal rainfall, landslides may be triggered by anthropic activities, such as adding excessive weight above the slope, digging at mid-slope or at the foot of the slope. Often, individual phenomena join together to generate instability over time, which often does not allow a reconstruction of the evolution of a particular landslide. Therefore, landslide hazard mitigation measures are not generally classified according to the phenomena that might cause a landslide. Instead, they are classified by the sort of slope stabilization method used: Geometric methods, in which the geometry of the hillside is changed (in general the slope); Hydrogeological methods, in which an attempt is made to lower the groundwater level or to reduce the water content of the material Chemical and mechanical methods, in which attempts are made to increase the shear strength of the unstable mass or to introduce active external forces (e.g. anchors, rock or ground nailing) or passive (e.g. structural wells, piles or reinforced ground) to counteract the destabilizing forces.Each of these methods varies somewhat with the type of material that makes up the slope.