Resurection Plants and the Secrets of Eternal Leaf
... Most higher plants possess a phase in their life cycle in which tissues can survive desiccation. However, this is restricted to specialized tissues such as seeds and pollen. Resurrection plants are remarkable in that they can tolerate almost complete water loss in their vegetative tissues. The desic ...
... Most higher plants possess a phase in their life cycle in which tissues can survive desiccation. However, this is restricted to specialized tissues such as seeds and pollen. Resurrection plants are remarkable in that they can tolerate almost complete water loss in their vegetative tissues. The desic ...
Chapter 22 Plant Structure and Function
... tissues is ground tissue. Ground tissues consist of parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma cells and have diverse functions, including photosynthesis, storage, and support. Most of a plant consists of ground tissue. The ground tissue of leaves and green stems contains cells with numerous chloropl ...
... tissues is ground tissue. Ground tissues consist of parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma cells and have diverse functions, including photosynthesis, storage, and support. Most of a plant consists of ground tissue. The ground tissue of leaves and green stems contains cells with numerous chloropl ...
Stem
... evolved in many plants. – These shoots, which include stolons, rhizomes, tubers, and bulbs, are often mistaken for roots. – Stolons, such as the “runners” of strawberry plants, grow on the surface and enable a plant to colonize large areas asexually when a parent plant fragments into many smaller of ...
... evolved in many plants. – These shoots, which include stolons, rhizomes, tubers, and bulbs, are often mistaken for roots. – Stolons, such as the “runners” of strawberry plants, grow on the surface and enable a plant to colonize large areas asexually when a parent plant fragments into many smaller of ...
Plant intelligence
... Numerous biotic signals are sensed and modify the phenotype. These include the presence, absence and identity of neighbours, (Tremmel and Bazzaz 1993, 1995), cooperation, mutualism, disturbance, trampling, herbivory, parasitism and space (Callaway et al. 2003; references are listed in Turkington and ...
... Numerous biotic signals are sensed and modify the phenotype. These include the presence, absence and identity of neighbours, (Tremmel and Bazzaz 1993, 1995), cooperation, mutualism, disturbance, trampling, herbivory, parasitism and space (Callaway et al. 2003; references are listed in Turkington and ...
Roots
... which in turn are composed of different cell types • A tissue is a group of cells consisting of one or more cell types that together perform a specialized function • An organ consists of several types of tissues that together carry out particular functions ...
... which in turn are composed of different cell types • A tissue is a group of cells consisting of one or more cell types that together perform a specialized function • An organ consists of several types of tissues that together carry out particular functions ...
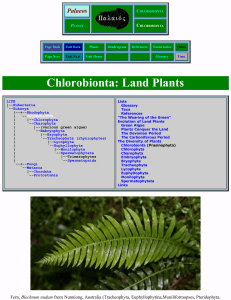
Palaeos Plants: Chlorobionta
... don't reveal much about the structures or nature of these plants. All we can say is that these plants were probably of a hepatophyte grade of evolution - small, non-vascular, and lacking morphological differentiation into roots, stems, and leaves, like modern mosses and liverworts. The first unambig ...
... don't reveal much about the structures or nature of these plants. All we can say is that these plants were probably of a hepatophyte grade of evolution - small, non-vascular, and lacking morphological differentiation into roots, stems, and leaves, like modern mosses and liverworts. The first unambig ...
22–2 Bryophytes
... Mosses have rhizoids, which are long cells that anchor them in the ground and absorb water and minerals from the soil. Water moves through rhizoids and into the rest of the ...
... Mosses have rhizoids, which are long cells that anchor them in the ground and absorb water and minerals from the soil. Water moves through rhizoids and into the rest of the ...
Did auxin play a crucial role in the evolution of
... 1988). The multicellular sporophyte of each land plant division can be said to exhibit a characteristic body plan that is based on such features as meristem organization, vascular tissue arrangement, positional relationships among vegetative organs and positional relationships of reproductive struct ...
... 1988). The multicellular sporophyte of each land plant division can be said to exhibit a characteristic body plan that is based on such features as meristem organization, vascular tissue arrangement, positional relationships among vegetative organs and positional relationships of reproductive struct ...
Conifers: The Backbone of the Winter Landscape
... The term conifer refers to plants that reproduce through the formation of cones, which are the female reproductive part of the plant. The needles of conifers are actually modified leaves that allow the plants to carry out photosynthesis, even in the winter. Because they are able to produce enough fo ...
... The term conifer refers to plants that reproduce through the formation of cones, which are the female reproductive part of the plant. The needles of conifers are actually modified leaves that allow the plants to carry out photosynthesis, even in the winter. Because they are able to produce enough fo ...
Article Transcriptomic Evidence for the Evolution
... Alternation of generations, in which the haploid and diploid stages of the life cycle are each represented by multicellular forms that differ in their morphology, is a defining feature of the land plants (embryophytes). Anciently derived lineages of embryophytes grow predominately in the haploid gam ...
... Alternation of generations, in which the haploid and diploid stages of the life cycle are each represented by multicellular forms that differ in their morphology, is a defining feature of the land plants (embryophytes). Anciently derived lineages of embryophytes grow predominately in the haploid gam ...
Modifications of roots
... herbaceous and woody perennial plants, and typically involves structural modifications of the stem, although any horizontal, underground part of a plant (whether stem or a root) can contribute to vegetative reproduction of a plant. And, in a few species (such as Kalanchoë), leaves are involved in ve ...
... herbaceous and woody perennial plants, and typically involves structural modifications of the stem, although any horizontal, underground part of a plant (whether stem or a root) can contribute to vegetative reproduction of a plant. And, in a few species (such as Kalanchoë), leaves are involved in ve ...
PURPLE LOOSESTRIFE (Lythrum salicaria L.)
... matching loss of wildlife, including several bird species that will not nest in loosestrife infestations. Purple loosestrife is also known to impede water flow, and may even result in the desiccation of wetland habitats. ...
... matching loss of wildlife, including several bird species that will not nest in loosestrife infestations. Purple loosestrife is also known to impede water flow, and may even result in the desiccation of wetland habitats. ...
22–2 Bryophytes
... Mosses have rhizoids, which are long cells that anchor them in the ground and absorb water and minerals from the soil. Water moves through rhizoids and into the rest of the ...
... Mosses have rhizoids, which are long cells that anchor them in the ground and absorb water and minerals from the soil. Water moves through rhizoids and into the rest of the ...
Roots, Stems, and Leaves
... such as those of the Victoria water lily, can be more than two meters in diameter. Other leaves, such as duckweed, are measured in millimeters. Some plants produce different forms of leaves on the same plant. A blade of grass is joined directly to the stem, but in other leaves, a stalk joins the lea ...
... such as those of the Victoria water lily, can be more than two meters in diameter. Other leaves, such as duckweed, are measured in millimeters. Some plants produce different forms of leaves on the same plant. A blade of grass is joined directly to the stem, but in other leaves, a stalk joins the lea ...
Plants living on fungi: a short review of mycoheterotrophy by Vincent
... plants through a special organ, the haustorium. There are approximately 350 species of holoparasitic plants. Arguably the most famous of all parasitic plants is Rafflesia arnoldii from rain forest in Sumatra and Borneo. The flower of R. arnoldii may be over 100 centimetres in diameter, and weigh up ...
... plants through a special organ, the haustorium. There are approximately 350 species of holoparasitic plants. Arguably the most famous of all parasitic plants is Rafflesia arnoldii from rain forest in Sumatra and Borneo. The flower of R. arnoldii may be over 100 centimetres in diameter, and weigh up ...
Bryophyte Ecology Glossary
... alluvium: deposit of clay, silt, sand, and gravel left by flowing water in river valley or delta, usually as fertile soil alpestrine: subalpine; growing to the tree line alpine: habitat above treeline of mountain alternation of generations: alternating cycle of sporophyte (2n) and gametophyte (1n) g ...
... alluvium: deposit of clay, silt, sand, and gravel left by flowing water in river valley or delta, usually as fertile soil alpestrine: subalpine; growing to the tree line alpine: habitat above treeline of mountain alternation of generations: alternating cycle of sporophyte (2n) and gametophyte (1n) g ...
A Physiologically Explicit Morphospace for Tracheid
... 1967), morphospaces have been used to characterize morphological variation within and among fossil taxa. Two kinds of morphospaces have predominated: theoretical spaces that take shape from general rules or equations of form, and empirical spaces, which are derived from specimen measurements and hav ...
... 1967), morphospaces have been used to characterize morphological variation within and among fossil taxa. Two kinds of morphospaces have predominated: theoretical spaces that take shape from general rules or equations of form, and empirical spaces, which are derived from specimen measurements and hav ...
Unit 3.1 Stems
... functions: Stems produce leaves, branches, and flowers; stems hold leaves up to the sun; and stems transport substances throughout the plant. Stems make up an essential part of the water and mineral transport systems of the plant. Xylem and phloem form continuous tubes from the roots through the ste ...
... functions: Stems produce leaves, branches, and flowers; stems hold leaves up to the sun; and stems transport substances throughout the plant. Stems make up an essential part of the water and mineral transport systems of the plant. Xylem and phloem form continuous tubes from the roots through the ste ...
File
... these experiments, is that an asymmetrical distribution of auxin moving down from the coleoptile tip causes cells on the darker side to elongate faster than cells on the brighter side. However, studies of phototropism by organs other than grass coleoptiles provide little support for this idea. ○ The ...
... these experiments, is that an asymmetrical distribution of auxin moving down from the coleoptile tip causes cells on the darker side to elongate faster than cells on the brighter side. However, studies of phototropism by organs other than grass coleoptiles provide little support for this idea. ○ The ...
25 | SEEDLESS PLANTS - Open Textbooks Project
... Even when parts of a plant are close to a source of water, the aerial structures are likely to dry out. Water also provides buoyancy to organisms. On land, plants need to develop structural support in a medium that does not give the same lift as water. The organism is also subject to bombardment by ...
... Even when parts of a plant are close to a source of water, the aerial structures are likely to dry out. Water also provides buoyancy to organisms. On land, plants need to develop structural support in a medium that does not give the same lift as water. The organism is also subject to bombardment by ...
seedless plants
... on land may have opened the way to its colonization by plants • Systematists are currently debating the boundaries of the plant kingdom • Some biologists think the plant kingdom should be expanded to include some or all green algae • Until this debate is resolved, we will retain the embryophyte defi ...
... on land may have opened the way to its colonization by plants • Systematists are currently debating the boundaries of the plant kingdom • Some biologists think the plant kingdom should be expanded to include some or all green algae • Until this debate is resolved, we will retain the embryophyte defi ...
Chapter 29 PowerPoint
... Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
... Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
Chapter 39 – Plant Responses to Internal and External Signals
... The mechanism by which a signal promotes a new developmental course may depend on the activation of positive transcription factors (proteins that increase transcription of specific genes) or negative transcription factors (proteins that decrease ...
... The mechanism by which a signal promotes a new developmental course may depend on the activation of positive transcription factors (proteins that increase transcription of specific genes) or negative transcription factors (proteins that decrease ...
gametophyte
... Lycophytes (club mosses and their relatives) Monilophytes (ferns and their relatives) ...
... Lycophytes (club mosses and their relatives) Monilophytes (ferns and their relatives) ...
Embryophyte

The Embryophyta are the most familiar subkingdom of green plants that form vegetation on earth. Living embryophytes include hornworts, liverworts, mosses, ferns, lycophytes, gymnosperms and flowering plants, and emerged from Charophyte green algae. The Embryophyta are informally called land plants because they live primarily in terrestrial habitats, while the related green algae are primarily aquatic. All are complex multicellular eukaryotes with specialized reproductive organs. The name derives from their innovative characteristic of nurturing the young embryo sporophyte during the early stages of its multicellular development within the tissues of the parent gametophyte. With very few exceptions, embryophytes obtain their energy by photosynthesis, that is by using the energy of sunlight to synthesize their food from carbon dioxide and water.