Microcytic Anemia
... • Review key aspects of history, physical and laboratory evaluation • Review a systematic approach to the differential diagnosis • http://www.anemia.org/professionals/ • http://www.anemia.org/patients/bonemarrow-basics/ ...
... • Review key aspects of history, physical and laboratory evaluation • Review a systematic approach to the differential diagnosis • http://www.anemia.org/professionals/ • http://www.anemia.org/patients/bonemarrow-basics/ ...
Antimicrobial resistance What is antimicrobial resistance?
... gonorrhoeae), involving even "last-line" oral cephalosporins, and is increasing in prevalence worldwide. Untreatable gonococcal infections would result in increased rates of illness and death, thus reversing the gains made in the control of this sexually transmitted infection. New resistance mechani ...
... gonorrhoeae), involving even "last-line" oral cephalosporins, and is increasing in prevalence worldwide. Untreatable gonococcal infections would result in increased rates of illness and death, thus reversing the gains made in the control of this sexually transmitted infection. New resistance mechani ...
Infectious Agent - Global Road Warrior
... have occurred among adventure travelers on river trips in Africa. Clinical Presentation Incubation period is typically 14–84 days for acute schistosomiasis (Katayama syndrome), but chronic infection can remain asymptomatic for years. Penetration of cercariae can be associated with a rash that develo ...
... have occurred among adventure travelers on river trips in Africa. Clinical Presentation Incubation period is typically 14–84 days for acute schistosomiasis (Katayama syndrome), but chronic infection can remain asymptomatic for years. Penetration of cercariae can be associated with a rash that develo ...
GRANT WOOD AEA
... or illness. These individuals may be at various stages in the infectious process—incubation; mildly infected without symptoms; or chronic carriers of an infectious agent such as the HIV and hepatitis viruses. In fact, the transmission of communicable diseases is more likely to occur from contact wit ...
... or illness. These individuals may be at various stages in the infectious process—incubation; mildly infected without symptoms; or chronic carriers of an infectious agent such as the HIV and hepatitis viruses. In fact, the transmission of communicable diseases is more likely to occur from contact wit ...
IOSR Journal of Mathematics (IOSR-JM)
... health. Acute and chronic respiratory diseases, especially pulmonary tuberculosis, malaria and HIV/AIDS are responsible for a large portion of mortality especially in developing countries [16]. Globally HIV/AIDS has killed more than 35 million people since it was first discovered in 1981 and almost ...
... health. Acute and chronic respiratory diseases, especially pulmonary tuberculosis, malaria and HIV/AIDS are responsible for a large portion of mortality especially in developing countries [16]. Globally HIV/AIDS has killed more than 35 million people since it was first discovered in 1981 and almost ...
Coccidia - Mountain View Vet Hospital
... poor without treatment and death may result. With treatment, however, the prognosis is good. Transmission or Cause: Transmission of coccidia begins when the immature coccidia, or oocysts, are passed in the feces from an infected dog or cat into the environment, where they can mature and be ingested ...
... poor without treatment and death may result. With treatment, however, the prognosis is good. Transmission or Cause: Transmission of coccidia begins when the immature coccidia, or oocysts, are passed in the feces from an infected dog or cat into the environment, where they can mature and be ingested ...
Unit 4 Student Summary Notes
... destroy host cells that become cancerous via the detection of new antigens (a molecular marker found on the surface of cells) by T lymphocytes. A group of white blood cells called leucocytes are the main cells involved in this process. They release cytokines into the blood stream to recruit large nu ...
... destroy host cells that become cancerous via the detection of new antigens (a molecular marker found on the surface of cells) by T lymphocytes. A group of white blood cells called leucocytes are the main cells involved in this process. They release cytokines into the blood stream to recruit large nu ...
The effects of maternal helminth and malaria infections on mother
... increase viral loads in the placenta [6]. Placental malaria can also damage the placenta which may facilitate transplacental passage of HIV to the fetus. Yet the few epidemiological studies that have examined the association of placental malaria with the risk of MTCT have produced conflicting result ...
... increase viral loads in the placenta [6]. Placental malaria can also damage the placenta which may facilitate transplacental passage of HIV to the fetus. Yet the few epidemiological studies that have examined the association of placental malaria with the risk of MTCT have produced conflicting result ...
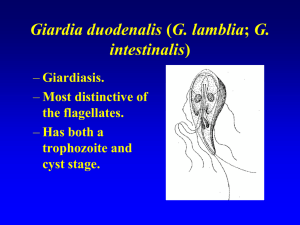
AH2.5 Parasitism
... e.g. tapeworm lacks digestive system because it absorbs digested food from animal’s intestine ...
... e.g. tapeworm lacks digestive system because it absorbs digested food from animal’s intestine ...
Topics Covered IMMUNITY TO PARASITIC AND FUNGAL
... • Direct killing of schistosome larvae by IFN-! activated M" • ADCC killing of schistosome larvae by eosinophils and Ab IgE – Eosinophils use FcR to bind IgE coated larvae – Esosinophils degranulate and release ROI and other toxins that kill over 24 ...
... • Direct killing of schistosome larvae by IFN-! activated M" • ADCC killing of schistosome larvae by eosinophils and Ab IgE – Eosinophils use FcR to bind IgE coated larvae – Esosinophils degranulate and release ROI and other toxins that kill over 24 ...
06 05 10 Hepatitis C look back press release
... Hepatitis C is a blood borne virus infection. The virus is spread when blood from an infected person gets into the bloodstream of another. Today, injecting drug use is the most common way to acquire hepatitis C virus infection. Individuals who inject drugs acquire their infections when they share co ...
... Hepatitis C is a blood borne virus infection. The virus is spread when blood from an infected person gets into the bloodstream of another. Today, injecting drug use is the most common way to acquire hepatitis C virus infection. Individuals who inject drugs acquire their infections when they share co ...
Bacillary Dysentery (shigellosis)
... fever, abdominal pain, diarrhea, tenesmus , stool mixed with mucus blood, & pus. even companied with shock and toxic encepholopthy. ...
... fever, abdominal pain, diarrhea, tenesmus , stool mixed with mucus blood, & pus. even companied with shock and toxic encepholopthy. ...
MENINGITIS+Mala..
... a. Bactericidal inhibit DNA synthesis b. Excellent tissue and CNS penetration. c. Acetylated with liver Renal. d. Toxicity : Hepatitis / P. ...
... a. Bactericidal inhibit DNA synthesis b. Excellent tissue and CNS penetration. c. Acetylated with liver Renal. d. Toxicity : Hepatitis / P. ...
58 Facts About Blood Donation
... 28. 2.7 pints: the average whole blood and red blood cell transfusion. 29. Children being treated for cancer, premature infants and children having heart surgery need blood and platelets from donors of all types, especially type O. 30. Anemic patients need blood transfusions to increase their red bl ...
... 28. 2.7 pints: the average whole blood and red blood cell transfusion. 29. Children being treated for cancer, premature infants and children having heart surgery need blood and platelets from donors of all types, especially type O. 30. Anemic patients need blood transfusions to increase their red bl ...
Case 1: A four-month-old boy with bilateral arm swelling
... enteric fever include fever and constitutional symptoms, such as headache, malaise, anorexia, lethargy, abdominal pain and tenderness. Hepatomegaly, splenomegaly, diarrhea and mental status changes can also occur. Constipation may occur early in the illness. Young children may present with a nonspec ...
... enteric fever include fever and constitutional symptoms, such as headache, malaise, anorexia, lethargy, abdominal pain and tenderness. Hepatomegaly, splenomegaly, diarrhea and mental status changes can also occur. Constipation may occur early in the illness. Young children may present with a nonspec ...
TNM HistologyGuts
... Blood flows into the spleen via the splenic artery which then branches into trabecular arteries. As an individual trabecular artery emerges from the connective tissue, it is then known as the artery of the white pulp (central artery) which is surrounded by the PALS. The blood vessel continues into a ...
... Blood flows into the spleen via the splenic artery which then branches into trabecular arteries. As an individual trabecular artery emerges from the connective tissue, it is then known as the artery of the white pulp (central artery) which is surrounded by the PALS. The blood vessel continues into a ...
File - Tissue sampling, processing and staining
... Urogenital protozoa e.g. Trichomonas vaginalis Blood and tissue protozoa e.g. Toxoplasma gondii, Plasmodium falciparum ...
... Urogenital protozoa e.g. Trichomonas vaginalis Blood and tissue protozoa e.g. Toxoplasma gondii, Plasmodium falciparum ...
Diagnosing the Tropical Traveller
... with risk-taking behaviour and with conditions encountered. The initial focus must be on ruling out conditions which are progressive, transmissible and treatable. It may be necessary to alert public health authorities or infectious diseases units early with a view to containment. Doctors seeing retu ...
... with risk-taking behaviour and with conditions encountered. The initial focus must be on ruling out conditions which are progressive, transmissible and treatable. It may be necessary to alert public health authorities or infectious diseases units early with a view to containment. Doctors seeing retu ...
Provisional PDF
... Visceral leishmaniasis (also called ‘kala-azar’) caused by Leishmania donovani was once prevalent in 17 provinces, municipalities and autonomous regions, especially in the rural areas north of the Yangtze River. As a result of effective control measures, including powerful drug treatments with penta ...
... Visceral leishmaniasis (also called ‘kala-azar’) caused by Leishmania donovani was once prevalent in 17 provinces, municipalities and autonomous regions, especially in the rural areas north of the Yangtze River. As a result of effective control measures, including powerful drug treatments with penta ...
Sixteen-year-old Parental Consent Form
... The Blood Center is the primary supplier of blood, blood components and plasma derivatives to local hospitals throughout South Louisiana and parts of the Mississippi Gulf Coast. Each day, The Blood Center must collect 300 - 350 pints of blood in order to maintain a stable area blood supply. Because ...
... The Blood Center is the primary supplier of blood, blood components and plasma derivatives to local hospitals throughout South Louisiana and parts of the Mississippi Gulf Coast. Each day, The Blood Center must collect 300 - 350 pints of blood in order to maintain a stable area blood supply. Because ...
Common Childhood Illnesses - Haldimand
... throat secretions of an infected person. • The virus can pass from an infected pregnant woman to her ...
... throat secretions of an infected person. • The virus can pass from an infected pregnant woman to her ...
Blood Transfusion ok320 KB
... • Severity of symptoms • Cause of anemia • Rapidity of anemia or symptoms • Co-morbidities and the age of the patient • Can we treat the anemia without transfusion? And • Is there enough time to wait for the response of such a treatment ? ...
... • Severity of symptoms • Cause of anemia • Rapidity of anemia or symptoms • Co-morbidities and the age of the patient • Can we treat the anemia without transfusion? And • Is there enough time to wait for the response of such a treatment ? ...
ICOPA.Prog
... MALARIA EXPERIMENTAL MODELS OF MALARIA PATHOGENESIS B Keynote: Louis Schofield, Australia. Invited: 1753 Magdalena Plebanski, Australia. T cell and DC subsets involved in natural and vaccine induced malaria specific immunity: a story of mice and men. 483 Srabasti Chakravorty, UK. Co-Operation Betwee ...
... MALARIA EXPERIMENTAL MODELS OF MALARIA PATHOGENESIS B Keynote: Louis Schofield, Australia. Invited: 1753 Magdalena Plebanski, Australia. T cell and DC subsets involved in natural and vaccine induced malaria specific immunity: a story of mice and men. 483 Srabasti Chakravorty, UK. Co-Operation Betwee ...
Plasmodium falciparum

Plasmodium falciparum is a protozoan parasite, one of the species of Plasmodium that cause malaria in humans. It is transmitted by the female Anopheles mosquito. Malaria caused by this species (also called malignant or falciparum malaria) is the most dangerous form of malaria, with the highest rates of complications and mortality. As of the latest World Health Organization report in 2014, there were 198 million cases of malaria worldwide in 2013, with an estimated death of 584,000. It is much more prevalent in sub-Saharan Africa than in many other regions of the world; in most African countries, over 75% of cases were due to P. falciparum, whereas in most other countries with malaria transmission, other, less virulent plasmodial species predominate. Almost every malarial death is caused by P. falciparum.