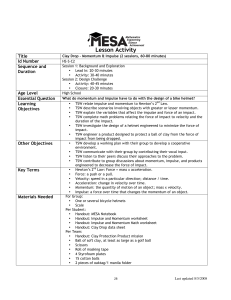
Q: How does a lever work? - National Science Teachers Association
... Let’s apply this to a lever, shown in Figure 3, page 60. This lever is a ruler, using a pencil as a fulcrum. Feel free to get your own ruler and pencil to play along and experience the operation of a lever. This lever is being used to lift a rock. ...
... Let’s apply this to a lever, shown in Figure 3, page 60. This lever is a ruler, using a pencil as a fulcrum. Feel free to get your own ruler and pencil to play along and experience the operation of a lever. This lever is being used to lift a rock. ...
Chapter 15 Problems
... spring force balances the force of gravity acting on the jumper? Note that this point is taken as the origin in our mathematical description of simple harmonic oscillation. (d) What is the angular frequency of the oscillation? (e) What time interval is ...
... spring force balances the force of gravity acting on the jumper? Note that this point is taken as the origin in our mathematical description of simple harmonic oscillation. (d) What is the angular frequency of the oscillation? (e) What time interval is ...
A
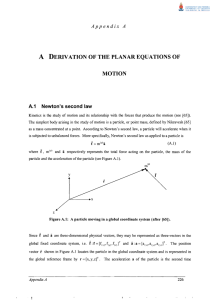
... The simplest body arising in the study of motion is a particle, or point mass, defined by Nikravesh [65] as a mass concentrated at a point. According to Newton's second law, a particle will accelerate when it is subjected to unbalanced forces. More specifically, Newton's second law as applied to a p ...
... The simplest body arising in the study of motion is a particle, or point mass, defined by Nikravesh [65] as a mass concentrated at a point. According to Newton's second law, a particle will accelerate when it is subjected to unbalanced forces. More specifically, Newton's second law as applied to a p ...
Types of Friction - AustinMeehanAcademy3
... Weight is related to mass, but they are not the same. ◦Weight changes when gravitational force changes. Mass: the amount of matter in an object. ◦The amount of mass in an object does not change. This can get confusing… because weight and mass are “constant” on Earth, the terms weight and mass are of ...
... Weight is related to mass, but they are not the same. ◦Weight changes when gravitational force changes. Mass: the amount of matter in an object. ◦The amount of mass in an object does not change. This can get confusing… because weight and mass are “constant” on Earth, the terms weight and mass are of ...
FREE Sample Here
... 17. A heavy object and a light object are dropped from rest at the same time in a vacuum. The heavier object will reach the ground A. before the lighter object. B. at the same time as the lighter object. C. after the lighter object. D. It depends on the shape of the object. ...
... 17. A heavy object and a light object are dropped from rest at the same time in a vacuum. The heavier object will reach the ground A. before the lighter object. B. at the same time as the lighter object. C. after the lighter object. D. It depends on the shape of the object. ...
Dynamics: Newton`s Laws of Motion
... of rest, or of uniform velocity in a straight line, as long as no net force acts on it. First Law – (Common) An object at rest remains at rest, and a object in motion, remains in motion unless acted upon by an outside force. ...
... of rest, or of uniform velocity in a straight line, as long as no net force acts on it. First Law – (Common) An object at rest remains at rest, and a object in motion, remains in motion unless acted upon by an outside force. ...
Newton`s Third Law, Momentum, Center of Mass
... Floor pushes forward on You (explains how a person walks) Road pushes forward on Tires (explains how a car moves) Gas pushes forward on Rocket (explains how a jet moves) Table pushes up on Book Moon pulls up on Earth Nail pulls right on Magnet ...
... Floor pushes forward on You (explains how a person walks) Road pushes forward on Tires (explains how a car moves) Gas pushes forward on Rocket (explains how a jet moves) Table pushes up on Book Moon pulls up on Earth Nail pulls right on Magnet ...
Rotational Motion
... rotational velocity of 5 rev/s about a vertical axis. The rotational inertia of the wheel is 2 kg·m2 about its center and the rotational inertia of the student and wheel and platform about the rotational axis of the platform is 6 kg·m2. What is the initial angular momentum of the system? a) ...
... rotational velocity of 5 rev/s about a vertical axis. The rotational inertia of the wheel is 2 kg·m2 about its center and the rotational inertia of the student and wheel and platform about the rotational axis of the platform is 6 kg·m2. What is the initial angular momentum of the system? a) ...
AP Physics – Friction
... The value of the coefficients depends on the two surfaces in contact with one another. These values are found by experiment. Useful tables can sometimes be found that have the different coefficient values for common materials worked out and ready for use by the enterprising physicist. ...
... The value of the coefficients depends on the two surfaces in contact with one another. These values are found by experiment. Useful tables can sometimes be found that have the different coefficient values for common materials worked out and ready for use by the enterprising physicist. ...
SHM - Red Hook Central Schools
... w = 2pf. = 0.4 p Hz =1.26 rad/s. • t = 10.66 s • x = 0.03 cos (1.26 x 10.66) = 0.019 m • You must use radians on calculator. ...
... w = 2pf. = 0.4 p Hz =1.26 rad/s. • t = 10.66 s • x = 0.03 cos (1.26 x 10.66) = 0.019 m • You must use radians on calculator. ...