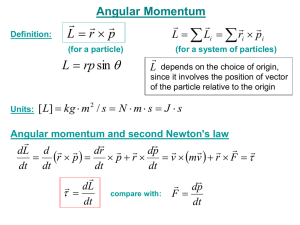
Physics 207: Lecture 2 Notes
... MP Problem Set 2 due tonight(!) MP Problem Set 3 due next week Physics 207: Lecture 5, Pg 1 ...
... MP Problem Set 2 due tonight(!) MP Problem Set 3 due next week Physics 207: Lecture 5, Pg 1 ...
Section 3 Forces Conservation of Momentum
... account for changes in the motion of objects. Using what you have learned, explain what happens in the following situation. An ice skater holding a basketball is standing on the surface of a frozen pond. The skater throws the ball forward. At the same time, the skater slides on the ice in the opposi ...
... account for changes in the motion of objects. Using what you have learned, explain what happens in the following situation. An ice skater holding a basketball is standing on the surface of a frozen pond. The skater throws the ball forward. At the same time, the skater slides on the ice in the opposi ...
12.3 Powerpoint
... account for changes in the motion of objects. Using what you have learned, explain what happens in the following situation. An ice skater holding a basketball is standing on the surface of a frozen pond. The skater throws the ball forward. At the same time, the skater slides on the ice in the opposi ...
... account for changes in the motion of objects. Using what you have learned, explain what happens in the following situation. An ice skater holding a basketball is standing on the surface of a frozen pond. The skater throws the ball forward. At the same time, the skater slides on the ice in the opposi ...
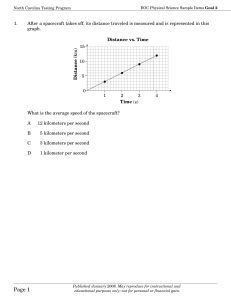
Page 1 - NC Department of Public Instruction
... A car starts from rest and accelerates uniformly at 1.7 m/s/s. How long will it take the car to reach a speed of 34 m/s? A ...
... A car starts from rest and accelerates uniformly at 1.7 m/s/s. How long will it take the car to reach a speed of 34 m/s? A ...
Simple Harmonic Motion
... ceiling almost to the floor and that its period is 15.5 s. (a) How tall is the tower? (b) If this pendulum is taken to the Moon, where the free-fall acceleration is 1.67 m/s2, what is the period there? 9. A simple 2.00-m-long pendulum oscillates at a location where g = 9.80 m/s2. How many complete o ...
... ceiling almost to the floor and that its period is 15.5 s. (a) How tall is the tower? (b) If this pendulum is taken to the Moon, where the free-fall acceleration is 1.67 m/s2, what is the period there? 9. A simple 2.00-m-long pendulum oscillates at a location where g = 9.80 m/s2. How many complete o ...
Name: Gravity Notes In a car accident, a seat belt helps prevent
... How do we know? THE MOON PULLS THE OCEAN AND CAUSES TIDES ...
... How do we know? THE MOON PULLS THE OCEAN AND CAUSES TIDES ...
Dynamics
... 1) What overcomes your inertia as the car accelerates? You can feel the car seat pushing against your back to move you forward. 2) What happens as you turn a corner? Your body tries to keep moving in a straight line, while the car turns the corner. You feel as if you are being pushed into the side ...
... 1) What overcomes your inertia as the car accelerates? You can feel the car seat pushing against your back to move you forward. 2) What happens as you turn a corner? Your body tries to keep moving in a straight line, while the car turns the corner. You feel as if you are being pushed into the side ...
Exam 2 solutions - BYU Physics and Astronomy
... Record your answers for problems 1-28 on the bubble sheet. You may write on this exam booklet, and are strongly encouraged to do so. I strongly encourage you to mark your answers in this test booklet. You will get this test booklet back (but only if you write your CID at the top of the first p ...
... Record your answers for problems 1-28 on the bubble sheet. You may write on this exam booklet, and are strongly encouraged to do so. I strongly encourage you to mark your answers in this test booklet. You will get this test booklet back (but only if you write your CID at the top of the first p ...
Physics 2414, Spring 2005 Group Exercise 10, Apr 28, 2005 ns
... (b) Write down the x-component of eqn. (6) and thus get an expression relating Nh and Ff . +Nh + 0+0 − Ff + 0 = 0 Nh = Ff ...
... (b) Write down the x-component of eqn. (6) and thus get an expression relating Nh and Ff . +Nh + 0+0 − Ff + 0 = 0 Nh = Ff ...
Physics 2414 Group Exercise 12 Solutions Solutions Equilibrium of
... (b) Write down the x-component of eqn. (6) and thus get an expression relating Nh and Ff . +Nh + 0+0 − Ff + 0 = 0 Nh = Ff ...
... (b) Write down the x-component of eqn. (6) and thus get an expression relating Nh and Ff . +Nh + 0+0 − Ff + 0 = 0 Nh = Ff ...
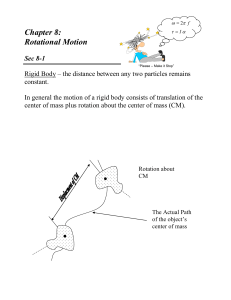
Chapter 8: Rotational Motion
... How to “think” about Torque 1. Torque must be specified about a pivot point 2. Torque is a product quantity made up of distance and force. 3. Torque causes angular acceleration, , in the same way that forces cause linear accelerations. 4. The Moment of Inertia, I, is a measure of resistance to rota ...
... How to “think” about Torque 1. Torque must be specified about a pivot point 2. Torque is a product quantity made up of distance and force. 3. Torque causes angular acceleration, , in the same way that forces cause linear accelerations. 4. The Moment of Inertia, I, is a measure of resistance to rota ...
Physics Ch. 7 Rotational Motion
... force that maintains circular motion is necessary for circular motion. If the force vanishes, then the object will travel in a straight line path tangent to the circle. Notice that the force is always at a right angle to the direction of motion. Fig. 7-11 shows the direction the ball follows i ...
... force that maintains circular motion is necessary for circular motion. If the force vanishes, then the object will travel in a straight line path tangent to the circle. Notice that the force is always at a right angle to the direction of motion. Fig. 7-11 shows the direction the ball follows i ...
Year 11 Biomechanics
... ‘A body continues in its state of rest or uniform motion unless an unbalanced force acts upon it.’ In other words, a body will remain at rest or in motion unless acted upon by a force. In order to get a body moving, a force must overcome the body’s tendency to remain at rest or inertia. The amount o ...
... ‘A body continues in its state of rest or uniform motion unless an unbalanced force acts upon it.’ In other words, a body will remain at rest or in motion unless acted upon by a force. In order to get a body moving, a force must overcome the body’s tendency to remain at rest or inertia. The amount o ...
Free Body Diagrams
... Aim: What are the different types of Friction? LO: Relate friction to the normal force LO: Calculate friction for different surface combinations LO: AGENDA Do Now - Worksheet Notes Worksheet HW# Due ...
... Aim: What are the different types of Friction? LO: Relate friction to the normal force LO: Calculate friction for different surface combinations LO: AGENDA Do Now - Worksheet Notes Worksheet HW# Due ...
f - Edublogs
... Your “apparent weight” is found by taking your REAL weight, mg, and adding the term ma, where “a” is your acceleration Apparent weight = mg + ma ...
... Your “apparent weight” is found by taking your REAL weight, mg, and adding the term ma, where “a” is your acceleration Apparent weight = mg + ma ...