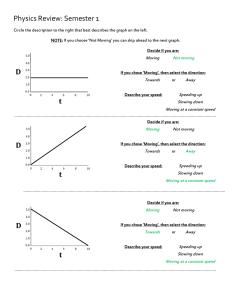
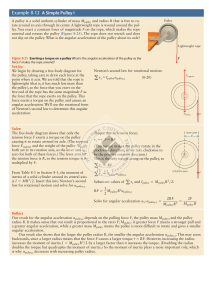
5-19-10 ap work energy power
... A father pulls his child in a little red wagon with constant speed. If the father pulls with a force of 16 N for 10.0 m, and the handle of the wagon is inclined at an angle of 60º above the horizontal, how much work does the father do on the wagon? ...
... A father pulls his child in a little red wagon with constant speed. If the father pulls with a force of 16 N for 10.0 m, and the handle of the wagon is inclined at an angle of 60º above the horizontal, how much work does the father do on the wagon? ...
Project1: Automation using Light Sensors
... excavators, and backhoes must not be overloaded because of their potential to overturn. Most stability calculations can be easily done by hand. For complex stability situations however, analysis software is usually used. For this experiment we will illustrate the concept of stability for a block und ...
... excavators, and backhoes must not be overloaded because of their potential to overturn. Most stability calculations can be easily done by hand. For complex stability situations however, analysis software is usually used. For this experiment we will illustrate the concept of stability for a block und ...
Horizontal Motion
... friction), then there are no forces acting on the x-axis. • If net force is zero, then acceleration is zero. • If acceleration is zero, then the object is either at rest or moving at constant velocity. • Since we know that the object is already in motion, the projectile must be moving at constant sp ...
... friction), then there are no forces acting on the x-axis. • If net force is zero, then acceleration is zero. • If acceleration is zero, then the object is either at rest or moving at constant velocity. • Since we know that the object is already in motion, the projectile must be moving at constant sp ...
Gravity and Free fall
... Weight and mass Legend says that about 1587, Galileo dropped two balls from the Leaning Tower of Pisa to see which would fall faster. Suppose the balls had masses of 1.0 kg and 10 kg. a. ...
... Weight and mass Legend says that about 1587, Galileo dropped two balls from the Leaning Tower of Pisa to see which would fall faster. Suppose the balls had masses of 1.0 kg and 10 kg. a. ...
Document
... An inertial reference frame is one in which Newton’s first law is valid. This excludes rotating and accelerating frames. How can we tell if we are in an inertial reference frame? By checking to see if Newton’s first law holds! Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... An inertial reference frame is one in which Newton’s first law is valid. This excludes rotating and accelerating frames. How can we tell if we are in an inertial reference frame? By checking to see if Newton’s first law holds! Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
205-wikarta-KULIAH I MEKTEK TI
... equations of equilibrium used to solve for the unknowns (usually forces or angles). ...
... equations of equilibrium used to solve for the unknowns (usually forces or angles). ...
Force of Friction When an object moves or attempts to move along
... is a force that opposes this movement called friction. A surface may seem smooth to us when we touch or look at them but as we look with microscopes even the most smooth surface is not truly smooth. As an object slides over another surface the ridges of the rough surface will contact and we believe ...
... is a force that opposes this movement called friction. A surface may seem smooth to us when we touch or look at them but as we look with microscopes even the most smooth surface is not truly smooth. As an object slides over another surface the ridges of the rough surface will contact and we believe ...
Newton`s 2nd Law - Issaquah Connect
... The same net force on twice the mass = half the acceleration The twice the net force on twice the mass = the same acceleration as before ...
... The same net force on twice the mass = half the acceleration The twice the net force on twice the mass = the same acceleration as before ...
force
... stretched spring upon any object that is attached to it. An object that compresses or stretches a spring is always acted upon by a force that restores the object to its rest or equilibrium position – directed toward equilibrium position. ...
... stretched spring upon any object that is attached to it. An object that compresses or stretches a spring is always acted upon by a force that restores the object to its rest or equilibrium position – directed toward equilibrium position. ...
AP Physics 1- Dynamics Practice Problems ANSWERS FACT
... block and the surface is µ=0.20. a). Is it possible for the block to be slowing down? If so, give a possible value of the magnitude of F1 that would allow the block to slow down. If not, explain why not with reference to Newton’s second law. b). In order to double the block’s initial speed to 10 m/s ...
... block and the surface is µ=0.20. a). Is it possible for the block to be slowing down? If so, give a possible value of the magnitude of F1 that would allow the block to slow down. If not, explain why not with reference to Newton’s second law. b). In order to double the block’s initial speed to 10 m/s ...
Multiple Choice
... 1988M3 The two uniform disks shown above have equal mass, and each can rotate on frictionless bearings about a fixed axis through its center. The smaller disk has a radius R and moment of inertia I about its axis. The larger disk has a radius 2R a. Determine the moment of inertia of the larger disk ...
... 1988M3 The two uniform disks shown above have equal mass, and each can rotate on frictionless bearings about a fixed axis through its center. The smaller disk has a radius R and moment of inertia I about its axis. The larger disk has a radius 2R a. Determine the moment of inertia of the larger disk ...
ConcepTest
... ConcepTest Work and Energy II A golfer making a putt gives the ball an initial velocity of v0, but he has badly misjudged the putt, and the ball only travels one-quarter of the distance to the hole. If the resistance force due to the grass is constant, what speed should he have given the ball (from ...
... ConcepTest Work and Energy II A golfer making a putt gives the ball an initial velocity of v0, but he has badly misjudged the putt, and the ball only travels one-quarter of the distance to the hole. If the resistance force due to the grass is constant, what speed should he have given the ball (from ...
Answer
... certain height , it begins to fall towards Earth’s surface under the influence of gravitational force. Such a motion of object is called free fall. 2. What do you mean by acceleration due to gravity? Answer When an object falls freely towards the surface of earth from a certain height, then its velo ...
... certain height , it begins to fall towards Earth’s surface under the influence of gravitational force. Such a motion of object is called free fall. 2. What do you mean by acceleration due to gravity? Answer When an object falls freely towards the surface of earth from a certain height, then its velo ...
2.05 AQA F = ma - extra questions
... Q3. The following data were obtained when two students performed an experiment to determine the acceleration of free fall. One student released a lump of lead the size of a tennis ball from a window in a tall building and the other measured the time for it to reach the ground. distance fallen by the ...
... Q3. The following data were obtained when two students performed an experiment to determine the acceleration of free fall. One student released a lump of lead the size of a tennis ball from a window in a tall building and the other measured the time for it to reach the ground. distance fallen by the ...