FOLDS AND STRUCTURES DUE TO FOLDING
... Folding generally takes place in areas of sedimentary rocks that have been laid down in horizontal layers called strata. ...
... Folding generally takes place in areas of sedimentary rocks that have been laid down in horizontal layers called strata. ...
Geology of Arkansas Headwaters Recreation Area
... metamorphosed rock are also exposed in the horst walls below the sedimentary rock layers high on the horst walls – Significant glaciations have occurred to both horst walls to the north end of the valley and in the Sawatch alone to the south end • Where Lake Creek, Clear Creek, and Pine Creek end at ...
... metamorphosed rock are also exposed in the horst walls below the sedimentary rock layers high on the horst walls – Significant glaciations have occurred to both horst walls to the north end of the valley and in the Sawatch alone to the south end • Where Lake Creek, Clear Creek, and Pine Creek end at ...
Chapter 17 Mountain Building
... • Crustal thickening, uplift, and thrusting occurs as movement slows and subduction ceases • Marine sediments are thrust upward onto the new continent ...
... • Crustal thickening, uplift, and thrusting occurs as movement slows and subduction ceases • Marine sediments are thrust upward onto the new continent ...
Notes on Metamorphic Rocks and Deformation of Crust Mountains
... -__________________-the largest mountain systems are part of larger mountain belts (two major belts of the world- Eurasian-Melanesian belt and Circum-Pacific belt) 2.What results when oceanic and continental crust collide? -Volcanic mountains due to subduction of oceanic crust (ex. Cascades Mountain ...
... -__________________-the largest mountain systems are part of larger mountain belts (two major belts of the world- Eurasian-Melanesian belt and Circum-Pacific belt) 2.What results when oceanic and continental crust collide? -Volcanic mountains due to subduction of oceanic crust (ex. Cascades Mountain ...
Document
... on the western coast of Asia Minor, the region of the Great Theater looked out on a beautiful bay much like that at modern Izmir. The walkway led from the theater to the harbor. Years later, sediment carried by the river silted up the bay and the site is now landlocked. Agricultural practices in the ...
... on the western coast of Asia Minor, the region of the Great Theater looked out on a beautiful bay much like that at modern Izmir. The walkway led from the theater to the harbor. Years later, sediment carried by the river silted up the bay and the site is now landlocked. Agricultural practices in the ...
Geologic Trips, Sierra Nevada
... homogenous body of granite. Instead, it is made up of over one hundred individual plutons. Each pluton covers an area of from one to several hundred square miles and represents a separate intrusion of magma. Although most plutons are distinguished by their composition and age, plutons may have many ...
... homogenous body of granite. Instead, it is made up of over one hundred individual plutons. Each pluton covers an area of from one to several hundred square miles and represents a separate intrusion of magma. Although most plutons are distinguished by their composition and age, plutons may have many ...
Suggested Answers: Extension Questions
... minerals), and textures (tendency for minerals to align forming foliation). Also tendency for rocks to become harder/less porous as a result. Not Heat & Pressure – these are agents of change, not the changes themselves. ...
... minerals), and textures (tendency for minerals to align forming foliation). Also tendency for rocks to become harder/less porous as a result. Not Heat & Pressure – these are agents of change, not the changes themselves. ...
Unit 4 Chapter 11
... When mountains form they start to erode, when they erode they become lighter making the range appear to rise. It is called uplift due to the isostatic adjustment. Deposition and Isostasy Subsidence- It is the apparent sinking of the ocean floor due to the deposition of mud, sand and gravel flowing f ...
... When mountains form they start to erode, when they erode they become lighter making the range appear to rise. It is called uplift due to the isostatic adjustment. Deposition and Isostasy Subsidence- It is the apparent sinking of the ocean floor due to the deposition of mud, sand and gravel flowing f ...
GLS100labF10_FR_fieldtrip
... are a by-product of glaciation. Assume that the rocks exposed here at Forest River Park are approximately 400 million years old and were formed 2 miles (~10,560 feet) beneath the surface, as indicated by the mineralogy and texture of the large intrusions. The local sediments overlying the rock consi ...
... are a by-product of glaciation. Assume that the rocks exposed here at Forest River Park are approximately 400 million years old and were formed 2 miles (~10,560 feet) beneath the surface, as indicated by the mineralogy and texture of the large intrusions. The local sediments overlying the rock consi ...
geotime1
... of rock found IN another rock must be OLDER (formed first). • UNCONFORMITY : A gap in the rock record…caused by erosion of a rock surface and a new rock being fromed on the erosional surface. ...
... of rock found IN another rock must be OLDER (formed first). • UNCONFORMITY : A gap in the rock record…caused by erosion of a rock surface and a new rock being fromed on the erosional surface. ...
Geology of the Kaimai Ranges
... took millions of years to form, most movement happened about 1-2 million years ago when the Kaimai volcanos on the east of the Hauraki Fault were uplifted (in places up to 4 kilometres higher than the west). As well as creating the mountain range, the faulting also tilted the Waiteariki Ignimbrite t ...
... took millions of years to form, most movement happened about 1-2 million years ago when the Kaimai volcanos on the east of the Hauraki Fault were uplifted (in places up to 4 kilometres higher than the west). As well as creating the mountain range, the faulting also tilted the Waiteariki Ignimbrite t ...
5.12 A interpret how land forms are the result of a combination of
... such as deltas, canyons, and sand dunes are the result of changes to Earth’s Surface by wind, water, and ice ...
... such as deltas, canyons, and sand dunes are the result of changes to Earth’s Surface by wind, water, and ice ...
MidTerm2001-for2002 - Department of Earth and Planetary
... a) This rock type appeared during the Archean and the early Proterozoic eons. Its presence suggests that the Earth's early atmosphere contained hardly any oxygen while parts of the oceans may have been oxygenated. b) This rock type is limited to the Archean eon and could not have formed if rivers ca ...
... a) This rock type appeared during the Archean and the early Proterozoic eons. Its presence suggests that the Earth's early atmosphere contained hardly any oxygen while parts of the oceans may have been oxygenated. b) This rock type is limited to the Archean eon and could not have formed if rivers ca ...
Document
... Active normal faulting produces a sharp surface break called a fault scarp. Repeated faulting may produce a great rock cliff hundreds of meters high. Erosion quickly modifies a fault scarp, but, because the fault plane extends hundreds of meters down into the bedrock, its effects persist for long sp ...
... Active normal faulting produces a sharp surface break called a fault scarp. Repeated faulting may produce a great rock cliff hundreds of meters high. Erosion quickly modifies a fault scarp, but, because the fault plane extends hundreds of meters down into the bedrock, its effects persist for long sp ...
California`s Mineral, Energy, and Soil Resources
... • Some of the features of the California landscape formed as the result of tectonic processes that took place deep beneath the surface • Wind, water, ice, and other agents of erosion at the surface carved other features of the landscape • Millions of years ago, the subduction of an oceanic plate ben ...
... • Some of the features of the California landscape formed as the result of tectonic processes that took place deep beneath the surface • Wind, water, ice, and other agents of erosion at the surface carved other features of the landscape • Millions of years ago, the subduction of an oceanic plate ben ...
13. Deformation and Mountain Building
... (1) This is where the oceanic crust is being subducted beneath the continent (2) The Andes are the best example (3) This was once a passive margin 200 Ma like the East Coast of North America (4) Subduction started when the Atlantic spreading ridge pushed the continents into the Pacific Plate and cau ...
... (1) This is where the oceanic crust is being subducted beneath the continent (2) The Andes are the best example (3) This was once a passive margin 200 Ma like the East Coast of North America (4) Subduction started when the Atlantic spreading ridge pushed the continents into the Pacific Plate and cau ...
California`s Mineral, Energy, and Soil Resources
... • Some of the features of the California landscape formed as the result of tectonic processes that took place deep beneath the surface • Wind, water, ice, and other agents of erosion at the surface carved other features of the landscape • Millions of years ago, the subduction of an oceanic plate ben ...
... • Some of the features of the California landscape formed as the result of tectonic processes that took place deep beneath the surface • Wind, water, ice, and other agents of erosion at the surface carved other features of the landscape • Millions of years ago, the subduction of an oceanic plate ben ...
THE ORIGIN OF THE APPALACHIAN MOUNTAINS
... a fragment of the original mountain structure as it was geologically constructed 300 million years ago. We must now look to the far side of the Atlantic Ocean to find the other fragments. So where are the other fragments and how did this long mountain chain come about? Over the last 50 years we have ...
... a fragment of the original mountain structure as it was geologically constructed 300 million years ago. We must now look to the far side of the Atlantic Ocean to find the other fragments. So where are the other fragments and how did this long mountain chain come about? Over the last 50 years we have ...
k11 Subdivisions of Precambrian time < Great Lakes - e
... Rocks older than the Cambrian are not widely exposed in Europe where the geologic column was devised. There, Precambrian rocks either are apparently unfossiliferous sedimentary strata called Eocambrian or, where they underlie fossiliferous strata nonconformably, are schists and gneisses, much fold-c ...
... Rocks older than the Cambrian are not widely exposed in Europe where the geologic column was devised. There, Precambrian rocks either are apparently unfossiliferous sedimentary strata called Eocambrian or, where they underlie fossiliferous strata nonconformably, are schists and gneisses, much fold-c ...
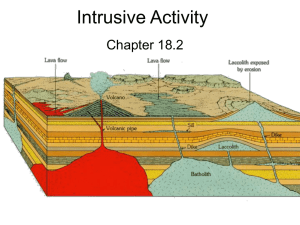
Intrusive Activity
... B. Magma can also cause blocks of rock to break off and sink into the magma, where the rocks may eventually melt. C. Magma can melt the rock into which it intrudes. ...
... B. Magma can also cause blocks of rock to break off and sink into the magma, where the rocks may eventually melt. C. Magma can melt the rock into which it intrudes. ...
GEOL-1403-McMahon
... Fold and fault belts including Trust faults – Detachment faults Fold and Trust Belts = crustal shortening and crustal thickening Example: The Alps are made of rock units that once covered an ocean floor of 500 km compressed into current width of 200 km. ...
... Fold and fault belts including Trust faults – Detachment faults Fold and Trust Belts = crustal shortening and crustal thickening Example: The Alps are made of rock units that once covered an ocean floor of 500 km compressed into current width of 200 km. ...
Virginia-Physical
... occurred before the formation of the Appalachian Mountains. The Piedmont is underlain by metamorphic rocks of various origins that were folded during the Paleozoic as the North American and African plates converged. Later, in the Mesozoic, it was affected by rifting as Pangaea broke apart and the ...
... occurred before the formation of the Appalachian Mountains. The Piedmont is underlain by metamorphic rocks of various origins that were folded during the Paleozoic as the North American and African plates converged. Later, in the Mesozoic, it was affected by rifting as Pangaea broke apart and the ...
Geology of the Death Valley area
The exposed geology of the Death Valley area presents a diverse and complex set of at least 23 formations of sedimentary units, two major gaps in the geologic record called unconformities, and at least one distinct set of related formations geologists call a group. The oldest rocks in the area that now includes Death Valley National Park are extensively metamorphosed by intense heat and pressure and are at least 1700 million years old. These rocks were intruded by a mass of granite 1400 Ma (million years ago) and later uplifted and exposed to nearly 500 million years of erosion.Marine deposition occurred 1200 to 800 Ma, creating thick sequences of conglomerate, mudstone, and carbonate rock topped by stromatolites, and possibly glacial deposits from the hypothesized Snowball Earth event. Rifting thinned huge roughly linear parts of the supercontinent Rodinia enough to allow sea water to invade and divide its landmass into component continents separated by narrow straits. A passive margin developed on the edges of these new seas in the Death Valley region. Carbonate banks formed on this part of the two margins only to be subsided as the continental crust thinned until it broke, giving birth to a new ocean basin. An accretion wedge of clastic sediment then started to accumulate at the base of the submerged precipice, entombing the region's first known fossils of complex life. These sandy mudflats gave way about 550 Ma to a carbonate platform which lasted for the next 300 million years of Paleozoic time.The passive margin switched to active margin in the early-to-mid Mesozoic when the Farallon Plate under the Pacific Ocean started to dive below the North American Plate, creating a subduction zone; volcanoes and uplifting mountains were created as a result. Erosion over many millions of years created a relatively featureless plain. Stretching of the crust under western North America started around 16 Ma and is thought to be caused by upwelling from the subducted spreading-zone of the Farallon Plate. This process continues into the present and is thought to be responsible for creating the Basin and Range province. By 2 to 3 million years ago this province had spread to the Death Valley area, ripping it apart and creating Death Valley, Panamint Valley and surrounding ranges. These valleys partially filled with sediment and, during colder periods during the current ice age, with lakes. Lake Manly was the largest of these lakes; it filled Death Valley during each glacial period from 240,000 years ago to 10,000 years ago. By 10,500 years ago these lakes were increasingly cut off from glacial melt from the Sierra Nevada, starving them of water and concentrating salts and minerals. The desert environment seen today developed after these lakes dried up.