Galaxy Images - Institute of Physics
... shows a bulge of starlight partially blocked by a rim of dust, as this spiral galaxy is being observed edge on. That same rim of dust appears bright in Spitzer's infrared image, which also reveals that Sombrero's central bulge of stars. ...
... shows a bulge of starlight partially blocked by a rim of dust, as this spiral galaxy is being observed edge on. That same rim of dust appears bright in Spitzer's infrared image, which also reveals that Sombrero's central bulge of stars. ...
talk
... Baryonic fraction for NGC 3741 (within the extent of the gas disk) ~ 0.18 ► comparable to other galaxies with less extended HI disk No evidence for baryon loss (measured within the extent of gas disk) in faint dwarf galaxies (contradiction to simulations of galaxy formation !) To reconcile rot ...
... Baryonic fraction for NGC 3741 (within the extent of the gas disk) ~ 0.18 ► comparable to other galaxies with less extended HI disk No evidence for baryon loss (measured within the extent of gas disk) in faint dwarf galaxies (contradiction to simulations of galaxy formation !) To reconcile rot ...
What Globular Clusters Teach Us About Oleg Gnedin
... • In the first two days of this meeting, we talked about matching galaxies to halos, in the full range from faint galaxies to massive galaxy clusters • While the distribution of dark matter is approximately self-similar on different mass scales, the baryon physics is not: Inside galaxies, the gas ha ...
... • In the first two days of this meeting, we talked about matching galaxies to halos, in the full range from faint galaxies to massive galaxy clusters • While the distribution of dark matter is approximately self-similar on different mass scales, the baryon physics is not: Inside galaxies, the gas ha ...
Document
... into4L* galaxies since z=1. “ While red galaxy mergers have been
observed, such mergers do not produce rapid growth of 4L* red galaxy stellar
masses between z=1 and the present day.”
...
... into
Galaxies - University of Iowa Astrophysics
... Why are Cepheid variable stars useful in determining distances? A) They all have the same distance. B) Their luminosity can be determined from their pulsation period. C) They all have the same luminosity. D) They all have the same radius. ...
... Why are Cepheid variable stars useful in determining distances? A) They all have the same distance. B) Their luminosity can be determined from their pulsation period. C) They all have the same luminosity. D) They all have the same radius. ...
Perseus ... Nuclear Emission and Outbursts from SMBHs in Normal Galaxies
... Cavities and shocks in the hot X-ray gas in galaxies and clusters provide a fossil record of AGN activity Hot X-ray atmospheres often provide the primary evidence of AGN activity •Observe outburst frequency - common >50% clusters (Dunn,Fabian)>30% galaxies ...
... Cavities and shocks in the hot X-ray gas in galaxies and clusters provide a fossil record of AGN activity Hot X-ray atmospheres often provide the primary evidence of AGN activity •Observe outburst frequency - common >50% clusters (Dunn,Fabian)>30% galaxies ...
How to kill a galaxy - University of Waterloo
... Build larger bulges in dense environments Consume available gas in rapid starburst Present in all environments, but more so at higher densities Establish red sequence in clusters at early times ...
... Build larger bulges in dense environments Consume available gas in rapid starburst Present in all environments, but more so at higher densities Establish red sequence in clusters at early times ...
Disk Galaxies and problem 3
... This is observationally seen in grand-design spirals, such as M51. The tidal arms are also easily produced in numerical simulations, see Fig. 7. • Bar spiral arms. A rotating bar at the centre of galaxies can also induce spiral arms that can last for a long time. This may be another way to form gran ...
... This is observationally seen in grand-design spirals, such as M51. The tidal arms are also easily produced in numerical simulations, see Fig. 7. • Bar spiral arms. A rotating bar at the centre of galaxies can also induce spiral arms that can last for a long time. This may be another way to form gran ...
SXDS Highlights : Subaru / FOCAS Spectroscopy
... surface brightnesses inferred from the size-luminosity relation is 2.9mag, and 1.7mag brighter than z=0 and z=1 disk galaxies, respectively. Surface stellar mass densities inferred from the size-stellar mass relation is 36 times larger than z=0-1 disk galaxies shown with thick solid line. ...
... surface brightnesses inferred from the size-luminosity relation is 2.9mag, and 1.7mag brighter than z=0 and z=1 disk galaxies, respectively. Surface stellar mass densities inferred from the size-stellar mass relation is 36 times larger than z=0-1 disk galaxies shown with thick solid line. ...
Dark Energy and Cosmic Sound
... Measuring accurate distances is a key way to study the acceleration of the Universe and the properties of dark energy. In the last 4 years, astronomers have detected this acoustic signature in the clustering of galaxies. Important tool to study cosmological composition. Several new surveys being ini ...
... Measuring accurate distances is a key way to study the acceleration of the Universe and the properties of dark energy. In the last 4 years, astronomers have detected this acoustic signature in the clustering of galaxies. Important tool to study cosmological composition. Several new surveys being ini ...
Lecture 16
... Galaxies around quasars sometimes appear disturbed by collisions These may be AGN which are being fueled by gas funneled into the center of galaxies in these collisions. These events were much more frequent when galaxies were closer together, thus Quasars were much more common in the past. ...
... Galaxies around quasars sometimes appear disturbed by collisions These may be AGN which are being fueled by gas funneled into the center of galaxies in these collisions. These events were much more frequent when galaxies were closer together, thus Quasars were much more common in the past. ...
Curriculum Vitae - Centre for Astrophysics and Supercomputing
... • April 2014: Conference The formation and growth of galaxies in the young Universe, Obergurgl, Austria (invited talk) • March 2014: ESO conference: Gas and Stars in Galaxies: A multiwavelength 3D Perspective, Garching, Germany (invited talk) • July 2013: EWASS 2013 Session: Starburst Galaxies Now a ...
... • April 2014: Conference The formation and growth of galaxies in the young Universe, Obergurgl, Austria (invited talk) • March 2014: ESO conference: Gas and Stars in Galaxies: A multiwavelength 3D Perspective, Garching, Germany (invited talk) • July 2013: EWASS 2013 Session: Starburst Galaxies Now a ...
Stars, Galaxies and Black Holes
... • Did you know that a Black Hole is a Star that has died? QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. ...
... • Did you know that a Black Hole is a Star that has died? QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. ...
The Milky Way is on a collision course with its neighbor, the
... characteristics of galaxy interactions is the appearance of long streams of stars and gas that stretch from one or both of the participant galaxies. These features are typically referred to as “tidal tails,” and result from the powerful gravitational forces at work between merging galaxies. As the t ...
... characteristics of galaxy interactions is the appearance of long streams of stars and gas that stretch from one or both of the participant galaxies. These features are typically referred to as “tidal tails,” and result from the powerful gravitational forces at work between merging galaxies. As the t ...
Stars, Galaxies and Nebulae
... a photograph of the center of the Swan Nebula, or M17, a hotbed of newly born stars wrapped in colorful blankets of glowing gas and cradled in an enormous cold, dark ...
... a photograph of the center of the Swan Nebula, or M17, a hotbed of newly born stars wrapped in colorful blankets of glowing gas and cradled in an enormous cold, dark ...
Chapter 15.3 Galaxy Evolution
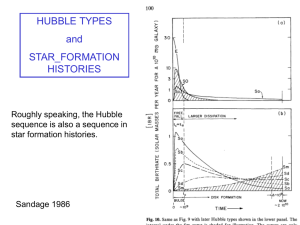
... clouds in about 1 billion year. - Protogalactic clouds then collapse to form disk galaxies. - The difference of galaxies come from two sources: 1. The initial conditions of the protogalactic clouds are different, either the spin or the density, which results in different type of galaxies. 2. Later ...
... clouds in about 1 billion year. - Protogalactic clouds then collapse to form disk galaxies. - The difference of galaxies come from two sources: 1. The initial conditions of the protogalactic clouds are different, either the spin or the density, which results in different type of galaxies. 2. Later ...
Announcements
... Presentations will be next Monday May 1 at 3:20pm. A written paper is also due at the same time. Exam 4 is after the presentations •Last exam will cover from Chapter 9 ...
... Presentations will be next Monday May 1 at 3:20pm. A written paper is also due at the same time. Exam 4 is after the presentations •Last exam will cover from Chapter 9 ...
Milky Way Galaxy
... Wave sources that move away cause waves to stretch. Wave sources that move closer cause waves to compress. Sound changes pitch. ...
... Wave sources that move away cause waves to stretch. Wave sources that move closer cause waves to compress. Sound changes pitch. ...
Here
... Effect of Seeing One important aspect in the study of the surface brightness of galaxies is the characterization of their surface brightness profiles, that is the dependence of the surface brightness upon the projected distance to the center of the galaxy. However, turbulence in the upper atmospher ...
... Effect of Seeing One important aspect in the study of the surface brightness of galaxies is the characterization of their surface brightness profiles, that is the dependence of the surface brightness upon the projected distance to the center of the galaxy. However, turbulence in the upper atmospher ...
Rotation curves for galaxies: student activity
... We can weigh a spiral galaxy by measuring the gravitational effects of the galaxy's mass on the orbits of objects in its disk. Even beyond the point in the disk at which starlight fades into the blackness of intergalactic space, we can still see radio waves from atomic hydrogen gas. We can therefore ...
... We can weigh a spiral galaxy by measuring the gravitational effects of the galaxy's mass on the orbits of objects in its disk. Even beyond the point in the disk at which starlight fades into the blackness of intergalactic space, we can still see radio waves from atomic hydrogen gas. We can therefore ...
Elliptical galaxies
... •If the isophotes are not circularly symmetric, then the galaxy cannot be spherically symmetric, but it can still be axisymmetric. •In general the line of sight will be inclined at an angle with respect to the equatorial plane of an axisymmetric galaxy. •In that case, there are infinite de-projected ...
... •If the isophotes are not circularly symmetric, then the galaxy cannot be spherically symmetric, but it can still be axisymmetric. •In general the line of sight will be inclined at an angle with respect to the equatorial plane of an axisymmetric galaxy. •In that case, there are infinite de-projected ...
Practical cosmology with the Local Volume galaxies
... around us exceeds 1.5 - 2.0 times the global luminosity density (Karachentsev et al. 2004). Almost the same excess is also seen in the local HI mass density (Zwaan et al. 2003). About 2/3 of the LV galaxies belong to the known virialized groups like the LG. Because the average virial mass-to-luminos ...
... around us exceeds 1.5 - 2.0 times the global luminosity density (Karachentsev et al. 2004). Almost the same excess is also seen in the local HI mass density (Zwaan et al. 2003). About 2/3 of the LV galaxies belong to the known virialized groups like the LG. Because the average virial mass-to-luminos ...
Magellanic Irregular Galaxies and Chemical Evolution of
... properties of the galaxies. Moreover such gradients can easily be built by slow radial motion, even of the order of 1-10 km/s (Mayor and Vigroux, 1981, Astron. & Astrophys., 98, 1). In galaxies such as Irregulars or blue compact ones, the total mass is much smaller than in spirals for example, the r ...
... properties of the galaxies. Moreover such gradients can easily be built by slow radial motion, even of the order of 1-10 km/s (Mayor and Vigroux, 1981, Astron. & Astrophys., 98, 1). In galaxies such as Irregulars or blue compact ones, the total mass is much smaller than in spirals for example, the r ...
Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies

The Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies is a catalog of peculiar galaxies produced by Halton Arp. A total of 338 galaxies are presented in the atlas, which was originally published in 1966 by the California Institute of Technology.The primary goal of the catalog was to present photographs of examples of the different kinds of peculiar structures found among nearby galaxies. Arp realized that the reason why galaxies formed into spiral or elliptical shapes was not well understood. He perceived peculiar galaxies as small ""experiments"" that astronomers could use to understand the physical processes that distort spiral or elliptical galaxies. With this atlas, astronomers had a sample of peculiar galaxies that they could study in more detail. The atlas does not present a complete overview of every peculiar galaxy in the sky but instead provides examples of the different phenomena as observed in nearby galaxies.Because little was known at the time of publication about the physical processes that caused the different shapes, the galaxies in the atlas are sorted based on their appearance. Objects 1–101 are individual peculiar spiral galaxies or spiral galaxies that apparently have small companions. Objects 102–145 are elliptical and elliptical-like galaxies. Individual or groups of galaxies with neither elliptical nor spiral shapes are listed as objects 146–268. Objects 269–327 are double galaxies. Finally, objects that simply do not fit into any of the above categories are listed as objects 332–338. Most objects are best known by their other designations, but a few galaxies are best known by their Arp numbers (such as Arp 220).Today, the physical processes that lead to the peculiarities seen in the Arp atlas are now well understood. A large number of the objects are interacting galaxies, including M51 (Arp 85), Arp 220, and the Antennae Galaxies (NGC 4038/NGC 4039, or Arp 244). A few of the galaxies are simply dwarf galaxies that do not have enough mass to produce enough gravity to allow the galaxies to form any cohesive structure. NGC 1569 (Arp 210) is an example of one of the dwarf galaxies in the atlas. A few other galaxies are radio galaxies. These objects contain active galactic nuclei that produce powerful jets of gas called radio jets. The atlas includes the nearby radio galaxies M87 (Arp 152) and Centaurus A (Arp 153).