What you need to be able to do
... car would have to be slowing down. (b) The car would have to be moving at a constant speed (c) The car would have to be at rest. (d) The car could be going at any constant speed, including being at rest. ...
... car would have to be slowing down. (b) The car would have to be moving at a constant speed (c) The car would have to be at rest. (d) The car could be going at any constant speed, including being at rest. ...
Chapter 5: Forces in Equilibrium
... How does a table “know” how much normal force to supply to keep a book at rest? ...
... How does a table “know” how much normal force to supply to keep a book at rest? ...
F - learnphysics
... • Newton’s Second Law of Motion states that when a resultant force acts on an object of constant mass, the object will accelerate. The product of the mass and acceleration of the object is equal to the resultant force. In equation form, this is represened as F = ma • A resultant force is 1 N if the ...
... • Newton’s Second Law of Motion states that when a resultant force acts on an object of constant mass, the object will accelerate. The product of the mass and acceleration of the object is equal to the resultant force. In equation form, this is represened as F = ma • A resultant force is 1 N if the ...
Summary of Chapters 1-3 Equations of motion for a uniformly acclerating object
... the gravity force pulling the mass down the ramp? As you slowly put the mass on the ramp, the ramp compresses & stretches along the ramp as gravity tries to slide the mass down the ramp. When you let go, the ramp has stretched enough to push on the mass with EXACTLY the right amount of force up the ...
... the gravity force pulling the mass down the ramp? As you slowly put the mass on the ramp, the ramp compresses & stretches along the ramp as gravity tries to slide the mass down the ramp. When you let go, the ramp has stretched enough to push on the mass with EXACTLY the right amount of force up the ...
45 Newton`s Laws Introduction
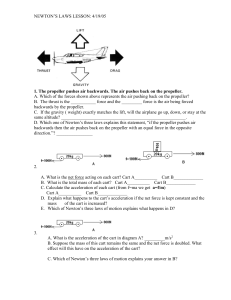
... 4. Refer to the diagram labeled “A”. If the cart is moving to the right at 3.0m/s, what will happen to the 10kg weight sitting on the top of the cart if the cart stops abruptly? 5. Look up Bernoulli’s Principle in your text. What is the significance of Bernoulli’s Principle with respect to an airpla ...
... 4. Refer to the diagram labeled “A”. If the cart is moving to the right at 3.0m/s, what will happen to the 10kg weight sitting on the top of the cart if the cart stops abruptly? 5. Look up Bernoulli’s Principle in your text. What is the significance of Bernoulli’s Principle with respect to an airpla ...
Chapter 5
... First you must know the magnitude of the decelerating force in order to find the magnitude of deceleration. This will then allow you to find the distance the cart will travel before it momentarily comes to a stop. Comment: If you place the x-axis of the coordinate system along the incline, you will ...
... First you must know the magnitude of the decelerating force in order to find the magnitude of deceleration. This will then allow you to find the distance the cart will travel before it momentarily comes to a stop. Comment: If you place the x-axis of the coordinate system along the incline, you will ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... • If the car were to abruptly stop and the seat belts were not being worn, then the passengers in motion would continue in motion. • Assuming a negligible amount of friction between the passengers and the seats, the passengers would likely be propelled from the car and be hurled into the air. • Once ...
... • If the car were to abruptly stop and the seat belts were not being worn, then the passengers in motion would continue in motion. • Assuming a negligible amount of friction between the passengers and the seats, the passengers would likely be propelled from the car and be hurled into the air. • Once ...
Sample 1103 Lab Report
... were placed atop it. The forces acting on the system were the gravitational force on the cart and objects atop it, and the normal force from the track opposing the cart’s weight. The net force on the system was zero. Thus there was no imbalance of forces, and no acceleration. One end of the string w ...
... were placed atop it. The forces acting on the system were the gravitational force on the cart and objects atop it, and the normal force from the track opposing the cart’s weight. The net force on the system was zero. Thus there was no imbalance of forces, and no acceleration. One end of the string w ...
Friction
... Objects on an incline will often stay put. There must be a force that holds the object in place. ...
... Objects on an incline will often stay put. There must be a force that holds the object in place. ...