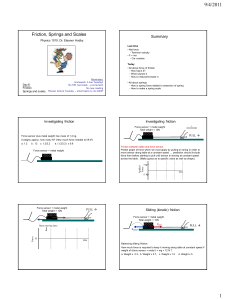
Momentum and Impulse
... (8 True/False Questions) 1. Impulses are normally smaller when bouncing takes place. 2. If a net force acts on an object, the object's momentum will change. 3. Momentum is defined as an object's mass times its velocity. 4. If the net external force acting on a system is zero, then the total momentum ...
... (8 True/False Questions) 1. Impulses are normally smaller when bouncing takes place. 2. If a net force acts on an object, the object's momentum will change. 3. Momentum is defined as an object's mass times its velocity. 4. If the net external force acting on a system is zero, then the total momentum ...
forces and motion notes
... always exerted by one object on another object. This rule is true for action and reaction forces. However, action and reaction forces in a pair do not act on the same object. ...
... always exerted by one object on another object. This rule is true for action and reaction forces. However, action and reaction forces in a pair do not act on the same object. ...
Wednesday, July 14, 2004
... A one piece cylinder is shaped as in the figure with core section protruding from the larger drum. The cylinder is free to rotate around the central axis shown in the picture. A rope wrapped around the drum whose radius is R1 exerts force F1 to the right on the cylinder, and another force exerts F2 ...
... A one piece cylinder is shaped as in the figure with core section protruding from the larger drum. The cylinder is free to rotate around the central axis shown in the picture. A rope wrapped around the drum whose radius is R1 exerts force F1 to the right on the cylinder, and another force exerts F2 ...
Acceleration Testing Handout
... apply to measuring and analyzing the motion dynamics of amusement rides? • ASTM F2137, Standard practice for Measuring the Dynamic Characteristics of Amusement Rides and Devices – This entire standard applies to the acquisition of quality, repeatable, documented test data measuring the motion dy ...
... apply to measuring and analyzing the motion dynamics of amusement rides? • ASTM F2137, Standard practice for Measuring the Dynamic Characteristics of Amusement Rides and Devices – This entire standard applies to the acquisition of quality, repeatable, documented test data measuring the motion dy ...
Force - Kuropas 7-4 science
... In summary! If the effects of the forces don't cancel each other, if one force is stronger than others, the forces are unbalanced forces. Unbalanced forces cause a change in motion; speed and/or direction. • When two forces act in the same direction on an object, the net force is equal to the sum o ...
... In summary! If the effects of the forces don't cancel each other, if one force is stronger than others, the forces are unbalanced forces. Unbalanced forces cause a change in motion; speed and/or direction. • When two forces act in the same direction on an object, the net force is equal to the sum o ...
Part II
... • The roller coaster’s path is nearly circular at the minimum or maximum points on the track. • When at the top, there is a maximum speed at which the coaster will not leave the top of the track. ...
... • The roller coaster’s path is nearly circular at the minimum or maximum points on the track. • When at the top, there is a maximum speed at which the coaster will not leave the top of the track. ...
Steps to Solving Newtons Laws Problems.
... 12.) A book weighing 20. newtons slides at a constant velocity down a ramp inclined at 30.° to the horizontal as shown in the diagram. What is the force of friction between the book and the ramp? 1) 10. N up the ramp 2) 17 N up the ramp 3) 10. N down the ramp 4) 17 N down the ramp ...
... 12.) A book weighing 20. newtons slides at a constant velocity down a ramp inclined at 30.° to the horizontal as shown in the diagram. What is the force of friction between the book and the ramp? 1) 10. N up the ramp 2) 17 N up the ramp 3) 10. N down the ramp 4) 17 N down the ramp ...
4.1 Resistance in Mechanical Systems
... In Section 1.1 you learned that the motion of a body in equilibrium is described by Newton’s first law of motion: Every object will remain at rest, or will continue to move in a straight line with constant speed4 unless the object is acted on by a net force. ...
... In Section 1.1 you learned that the motion of a body in equilibrium is described by Newton’s first law of motion: Every object will remain at rest, or will continue to move in a straight line with constant speed4 unless the object is acted on by a net force. ...
Honors Physics Unit 4 Notes
... object is zero. • Objects that are either at rest or moving with constant velocity are said to be in equilibrium. • Newton’s first law describes objects in equilibrium. Tip: To determine whether a body is in equilibrium, find the net force. If the net force is zero, the body is in equilibrium. If th ...
... object is zero. • Objects that are either at rest or moving with constant velocity are said to be in equilibrium. • Newton’s first law describes objects in equilibrium. Tip: To determine whether a body is in equilibrium, find the net force. If the net force is zero, the body is in equilibrium. If th ...