Momemtum/Impulse/ Conservation of Momentum
... Ft = mvf - mvi Ft = mvf – mvi t t F = mvf – mvi t ...
... Ft = mvf - mvi Ft = mvf – mvi t t F = mvf – mvi t ...
Question Bank
... 5. What are fundamental and derived units? Give examples 6. Distinguish between units and dimensions. Give examples. 7. Define principle of transmissibility. 8. A force vector F= 700i + 1500j is applied to a bolt. Determine the magnitude of the force and angle it forms with the horizontal. 9. A forc ...
... 5. What are fundamental and derived units? Give examples 6. Distinguish between units and dimensions. Give examples. 7. Define principle of transmissibility. 8. A force vector F= 700i + 1500j is applied to a bolt. Determine the magnitude of the force and angle it forms with the horizontal. 9. A forc ...
Chap04
... or water, the fluid exerts a drag force on the moving object in the direction opposite to its motion. A drag force is the force exerted by a fluid on the object moving through the fluid. This force is dependent on the motion of the object, the properties of the object, and the properties of the flui ...
... or water, the fluid exerts a drag force on the moving object in the direction opposite to its motion. A drag force is the force exerted by a fluid on the object moving through the fluid. This force is dependent on the motion of the object, the properties of the object, and the properties of the flui ...
Chapter Objectives
... 6. Find the velocity at different times for a freely falling object 7. Find the position at different times for a freely falling object 8. Find the time it takes an object dropped from rest to fall a given distance. Ch. 4 1. Describe the relation between net force and acceleration 2. Find the accele ...
... 6. Find the velocity at different times for a freely falling object 7. Find the position at different times for a freely falling object 8. Find the time it takes an object dropped from rest to fall a given distance. Ch. 4 1. Describe the relation between net force and acceleration 2. Find the accele ...
Classical mechanics
... An attractive feature of a course in classical mechanics is that it is a wonderful opportunity to learn to use many of the mathematical techniques needed in so many other branches of physics - vectors, vector calculus, differential equations, complex numbers, Taylor series, Fourier series, calculus ...
... An attractive feature of a course in classical mechanics is that it is a wonderful opportunity to learn to use many of the mathematical techniques needed in so many other branches of physics - vectors, vector calculus, differential equations, complex numbers, Taylor series, Fourier series, calculus ...
Interview Format - PhysicsEducation.net
... DEM: Now, if acceleration is constant, tell me what that tells you about force. STUDENT: It tells me that the force is going to be constant . . . If I want to keep my acceleration constant, it seems like I would need to keep my force constant. DEM: Now, on this one we’ve gone all the way around. At ...
... DEM: Now, if acceleration is constant, tell me what that tells you about force. STUDENT: It tells me that the force is going to be constant . . . If I want to keep my acceleration constant, it seems like I would need to keep my force constant. DEM: Now, on this one we’ve gone all the way around. At ...
Stacey Carpenter - University of Hawaii System
... acceleration, which Galileo had defined. Newton knew that a force was needed to accelerate an object. He experimented and found that acceleration is proportional to the force; the harder you push, the more the object accelerates. Push twice as hard, and the object accelerates twice as fast. aF He a ...
... acceleration, which Galileo had defined. Newton knew that a force was needed to accelerate an object. He experimented and found that acceleration is proportional to the force; the harder you push, the more the object accelerates. Push twice as hard, and the object accelerates twice as fast. aF He a ...
Forces - Lemon Bay High School
... Newton’s First Law • An object at rest remains at rest, and an object in motion continues in motion with constant velocity (that is, constant speed in a straight line) unless the object experiences a net external force. • In other words, when the net external force on an object is zero, the object’s ...
... Newton’s First Law • An object at rest remains at rest, and an object in motion continues in motion with constant velocity (that is, constant speed in a straight line) unless the object experiences a net external force. • In other words, when the net external force on an object is zero, the object’s ...
Document
... Newton’s first law is drawn from his concept of net force and Galileo’s concept of inertia. Essentially, Newton’s first law says that the velocity of an object will not change if there is no net force acting on it. v = 0 In his words... Every body continues in its state of rest, or of uniform mot ...
... Newton’s first law is drawn from his concept of net force and Galileo’s concept of inertia. Essentially, Newton’s first law says that the velocity of an object will not change if there is no net force acting on it. v = 0 In his words... Every body continues in its state of rest, or of uniform mot ...
Chap04-2014
... Force and Acceleration The formula, , tells you that if you double the force, you will double the object’s acceleration. If you apply the same force to several different objects, the one with the most mass will have the smallest acceleration and the one with the least mass will have the greatest acc ...
... Force and Acceleration The formula, , tells you that if you double the force, you will double the object’s acceleration. If you apply the same force to several different objects, the one with the most mass will have the smallest acceleration and the one with the least mass will have the greatest acc ...
newton`s laws
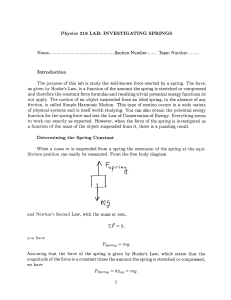
... supporting force exerted by the table. Since the book is at rest on the table, its acceleration is zero, so the net force on the book must be zero. Therefore, the magnitude of the support force must equal the magnitude of the book's weight, which is Fw =mg = (2)(9.8) =20 N. This means the normal for ...
... supporting force exerted by the table. Since the book is at rest on the table, its acceleration is zero, so the net force on the book must be zero. Therefore, the magnitude of the support force must equal the magnitude of the book's weight, which is Fw =mg = (2)(9.8) =20 N. This means the normal for ...
Lecture 1 - Basic Physics
... • Velocity: tangent to trajectory curve. • Speed: absolute value of velocity. ...
... • Velocity: tangent to trajectory curve. • Speed: absolute value of velocity. ...