Momentum
... sled to speed it up. The longer the you push the sled the greater the velocity and the greater the momentum you give it so time is also a factor. – Or think about the airbags in your car. They give you more time to slow down so less force is applied to your body. ...
... sled to speed it up. The longer the you push the sled the greater the velocity and the greater the momentum you give it so time is also a factor. – Or think about the airbags in your car. They give you more time to slow down so less force is applied to your body. ...
Rocket Science and Technology, 4363 Motor Ave
... The total contribution from an image vortex is N I N I , just as in the case of an external vortex. Add all four vortex terms, and multiply by 2 (to account for both fin panels) to the total first stage interference normal force. The remaining issue is the center of pressure of the vortex normal; ...
... The total contribution from an image vortex is N I N I , just as in the case of an external vortex. Add all four vortex terms, and multiply by 2 (to account for both fin panels) to the total first stage interference normal force. The remaining issue is the center of pressure of the vortex normal; ...
Universal force-motion equations and solar system implementation
... e. Generally, planets have one or more natural satellites. Those satellites also all revolve almost around the planets' equator planes. f. All celestial bodies revolve around the superior one, commonly in the same direction with its (superior’s) rotation, g. All celestial bodies, by some means or ot ...
... e. Generally, planets have one or more natural satellites. Those satellites also all revolve almost around the planets' equator planes. f. All celestial bodies revolve around the superior one, commonly in the same direction with its (superior’s) rotation, g. All celestial bodies, by some means or ot ...
College Physics (Etkina) Chapter 2 Newtonian Mechanics 2.1
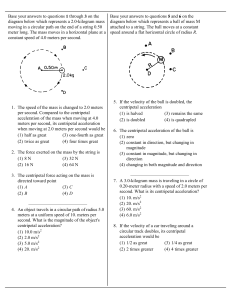
... acceleration. The magnitude of the force that the cart exerts on the horse A) is zero newtons. B) equal to the magnitude of . C) less than the magnitude of . D) greater than the magnitude of . E) cannot be determined without knowing the mass of the horse. Answer: B Var: 1 24) An object of weight W i ...
... acceleration. The magnitude of the force that the cart exerts on the horse A) is zero newtons. B) equal to the magnitude of . C) less than the magnitude of . D) greater than the magnitude of . E) cannot be determined without knowing the mass of the horse. Answer: B Var: 1 24) An object of weight W i ...
Newtons Review
... i. An object which is moving rightward has a rightward force acting upon it. Answer: False An object which is accelerating rightward must have a rightward force and a rightward net force acting upon it. But an object which is merely moving rightward does not necessarily have a rightward force upon i ...
... i. An object which is moving rightward has a rightward force acting upon it. Answer: False An object which is accelerating rightward must have a rightward force and a rightward net force acting upon it. But an object which is merely moving rightward does not necessarily have a rightward force upon i ...
Chapter 1
... Keep it going: It usually requires very little force to keep a trailer going—just enough to overcome the friction between the wheels and the axles. (You can coast on a bicycle for a long way.) Newton’s first law says that an object will continue to move in a straight line at constant speed unless it ...
... Keep it going: It usually requires very little force to keep a trailer going—just enough to overcome the friction between the wheels and the axles. (You can coast on a bicycle for a long way.) Newton’s first law says that an object will continue to move in a straight line at constant speed unless it ...
The Lagrangian Method vs
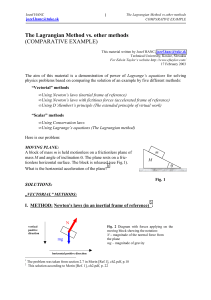
... 1) This principle uses the concept of the virtual displacement, which means, not actual small displacement, but it involves a possible, but purely mathematical experiment, so it can be applied in a certain definite time (even if such a displacement would involve physically infinite velocities). At t ...
... 1) This principle uses the concept of the virtual displacement, which means, not actual small displacement, but it involves a possible, but purely mathematical experiment, so it can be applied in a certain definite time (even if such a displacement would involve physically infinite velocities). At t ...
Generation of Gravitational Force
... i.e. Radio Frequency communication. But the motors or generators are based on magnetic induction principle. The electrostatic force is not used in motors and generators. If both electric and magnetic forces will be used in an Electro-mechanical system, then it will correlate with gravitational force ...
... i.e. Radio Frequency communication. But the motors or generators are based on magnetic induction principle. The electrostatic force is not used in motors and generators. If both electric and magnetic forces will be used in an Electro-mechanical system, then it will correlate with gravitational force ...
Physical Science
... starting point, at a velocity slower than the motion from 0 to 3 seconds. From 13 to 15 seconds the object is not moving relative to the starting point. From 15 to 21 seconds the object is accelerating (speeding up) as it moves away from the starting point. You do NOT need to construct or analyze v ...
... starting point, at a velocity slower than the motion from 0 to 3 seconds. From 13 to 15 seconds the object is not moving relative to the starting point. From 15 to 21 seconds the object is accelerating (speeding up) as it moves away from the starting point. You do NOT need to construct or analyze v ...
PS-5
... ○ Students should understand that the velocity of the object above is changing because the direction is changing. The speed of the object remains constant. Because the velocity of the object is changing, it is accelerating; Students need only say that the object is accelerating because the direc ...
... ○ Students should understand that the velocity of the object above is changing because the direction is changing. The speed of the object remains constant. Because the velocity of the object is changing, it is accelerating; Students need only say that the object is accelerating because the direc ...