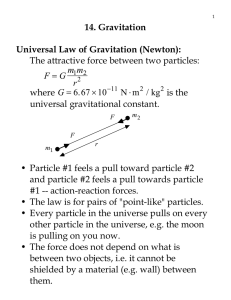
14. Gravitation Universal Law of Gravitation (Newton): G
... 14. Gravitation Universal Law of Gravitation (Newton): The attractive force between two particles: mm F = G 12 2 r where G = 6.67 × 10 −11 N ⋅ m 2 / kg 2 is the universal gravitational constant. F ...
... 14. Gravitation Universal Law of Gravitation (Newton): The attractive force between two particles: mm F = G 12 2 r where G = 6.67 × 10 −11 N ⋅ m 2 / kg 2 is the universal gravitational constant. F ...
Chapter 4: Newton`s Laws of Motion
... In some circumstances when objects that are in physical contact are moving as one unit (both have the same acceleration) it is acceptable, and in fact useful, to draw a composite force diagram for the objects. In this case the forces exerted on one object by the other do not appear on the diagram be ...
... In some circumstances when objects that are in physical contact are moving as one unit (both have the same acceleration) it is acceptable, and in fact useful, to draw a composite force diagram for the objects. In this case the forces exerted on one object by the other do not appear on the diagram be ...
Force
... – Contact forces exist when two objects are in contact with one another. – Long-range (FIELD) forces act over distances without a need for direct contact. Electromagnetic forces and gravity are long-range forces. ...
... – Contact forces exist when two objects are in contact with one another. – Long-range (FIELD) forces act over distances without a need for direct contact. Electromagnetic forces and gravity are long-range forces. ...
FORCE & MOTION
... EXAMPLE You and your friend are on opposites sides of the door again. Only this time the door starts to close. This is because the force you are exerting on the door is greater than the force your friend is exerting to try to keep the door open. The Net Force is the difference between the force tha ...
... EXAMPLE You and your friend are on opposites sides of the door again. Only this time the door starts to close. This is because the force you are exerting on the door is greater than the force your friend is exerting to try to keep the door open. The Net Force is the difference between the force tha ...
Practice_Exercise
... proportional to the net force acting on it. If the net B) 2 force is multiplied by some factor and the mass is C) 1/4 held constant the acceleration will be multiplied by D) 4 the same factor. Doubling the net force will double the acceleration. The acceleration is inversely proportional to the obje ...
... proportional to the net force acting on it. If the net B) 2 force is multiplied by some factor and the mass is C) 1/4 held constant the acceleration will be multiplied by D) 4 the same factor. Doubling the net force will double the acceleration. The acceleration is inversely proportional to the obje ...
force - Cloudfront.net
... • The force that opposes the sliding motion of two surfaces that are touching each other. • Depends on 2 factors: • 1. The kinds of surfaces • 2. The force pressing the surfaces ...
... • The force that opposes the sliding motion of two surfaces that are touching each other. • Depends on 2 factors: • 1. The kinds of surfaces • 2. The force pressing the surfaces ...
Name:______KEY_ Quiz Study Guide Topics included on this quiz
... 2.) Explain how objects on earth do not “violate” Newton’s Law of Inertia? Why don’t objects in motion stay in motion on earth? (Hint: What forces are acting on them?) ...
... 2.) Explain how objects on earth do not “violate” Newton’s Law of Inertia? Why don’t objects in motion stay in motion on earth? (Hint: What forces are acting on them?) ...
Name Newton`s Laws, Weight, Friction Practice Test 1. Use the
... e. What normal force would act on that object if it were dropped off a cliff on the moon? f. What net force would act on that object if it were dropped off a cliff on the moon? (ignore air resistance) g. What acceleration would act on that object if it were dropped off a cliff on the moon? (ignore a ...
... e. What normal force would act on that object if it were dropped off a cliff on the moon? f. What net force would act on that object if it were dropped off a cliff on the moon? (ignore air resistance) g. What acceleration would act on that object if it were dropped off a cliff on the moon? (ignore a ...
Section 4.1 Force and Motion
... the moving ball and the stationary object continues as it was. Newton’s First Law of Motion – also called the Law of Inertia. The law states the following: “An object at rest will stay at rest, an object in motion will stay in motion, unless acted on by an outside force.” Or the old book version is ...
... the moving ball and the stationary object continues as it was. Newton’s First Law of Motion – also called the Law of Inertia. The law states the following: “An object at rest will stay at rest, an object in motion will stay in motion, unless acted on by an outside force.” Or the old book version is ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... Consider the propulsion of a fish through the water. A fish uses its fins to push water backwards. In turn, the water reacts by pushing the fish forwards, propelling the fish through the water. The size of the force on the water equals the size of the force on the fish; the direction of the force on ...
... Consider the propulsion of a fish through the water. A fish uses its fins to push water backwards. In turn, the water reacts by pushing the fish forwards, propelling the fish through the water. The size of the force on the water equals the size of the force on the fish; the direction of the force on ...
Gravity and Motion All objects fall with the same acceleration Galileo
... objects will land at the same time when they are dropped at the same time from the same height. Acceleration due to gravity is the same for all objects All objects accelerate toward Earth at a rate of 9.8 m/s/s. ...
... objects will land at the same time when they are dropped at the same time from the same height. Acceleration due to gravity is the same for all objects All objects accelerate toward Earth at a rate of 9.8 m/s/s. ...