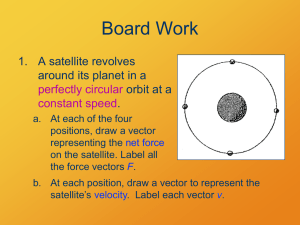
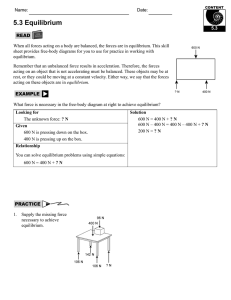
Newton`s Second Law of Motion
... As stated, Newton’s first law of motion governs the properties of inertia that an object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion remain in motion in the absence of an external force. However, it is observed that an object that tends to move comes to rest at a certain point as well as objects t ...
... As stated, Newton’s first law of motion governs the properties of inertia that an object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion remain in motion in the absence of an external force. However, it is observed that an object that tends to move comes to rest at a certain point as well as objects t ...
Gravity and Orbits Talk
... Consequence of Gravity: Orbits • The Force of Gravity keeps objects in Orbit • Without Gravity: Moon would move in straight line at constant speed (at 1000 m/s) – Newton’s First Law – It would move away from the Earth ...
... Consequence of Gravity: Orbits • The Force of Gravity keeps objects in Orbit • Without Gravity: Moon would move in straight line at constant speed (at 1000 m/s) – Newton’s First Law – It would move away from the Earth ...
Force in Mechanical Systems
... • If the forces are acting in the same direction – ADD to get the total force (resultant) on the body ...
... • If the forces are acting in the same direction – ADD to get the total force (resultant) on the body ...
Chapter 8 Accelerated Circular Motion continued
... other particle. A particle is a piece of matter, small enough in size to be regarded as a mathematical point. The force that each exerts on the other is directed along the line joining the particles. ...
... other particle. A particle is a piece of matter, small enough in size to be regarded as a mathematical point. The force that each exerts on the other is directed along the line joining the particles. ...
File jeopardy_review_ch_4
... Choose a category. You will be given the answer. You must give the correct question. Click to begin. ...
... Choose a category. You will be given the answer. You must give the correct question. Click to begin. ...
Chapter-05
... To identify all forces acting on an object, ask yourself the following: 1. What objects are “touching” the given object? These are contact forces. 2. What objects exert a force through “action at a distance” such as a gravitational, electrostatic, or magnetic force? These are action-at-a-distance fo ...
... To identify all forces acting on an object, ask yourself the following: 1. What objects are “touching” the given object? These are contact forces. 2. What objects exert a force through “action at a distance” such as a gravitational, electrostatic, or magnetic force? These are action-at-a-distance fo ...
Physics 131 Review Translational Kinematics: Position ( ): location relative to an origin
... acceleration in the x-direction, the velocity in that direction is constant. • At any given height, the speed of the ball is the same. Forces Newton's Laws: 1st: An object in motion or an object at rest will remain in motion or at rest if no net force acts on the object. 2nd: Net force is related t ...
... acceleration in the x-direction, the velocity in that direction is constant. • At any given height, the speed of the ball is the same. Forces Newton's Laws: 1st: An object in motion or an object at rest will remain in motion or at rest if no net force acts on the object. 2nd: Net force is related t ...
Ch.2 Linear Motion
... Its velocity or state of rest changes. The object accelerates. 25. If no net force acts on an object, what is necessarily zero (a) Velocity (b) Acceleration Acceleration is necessarily zero if no net force acts on an object. 26. If you hang from a clothesline when is the tension in the line greater, ...
... Its velocity or state of rest changes. The object accelerates. 25. If no net force acts on an object, what is necessarily zero (a) Velocity (b) Acceleration Acceleration is necessarily zero if no net force acts on an object. 26. If you hang from a clothesline when is the tension in the line greater, ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... watch it slide to a rest position. The book comes to a rest because of the presence of a force that force being the force of friction which brings the book to a rest position. ...
... watch it slide to a rest position. The book comes to a rest because of the presence of a force that force being the force of friction which brings the book to a rest position. ...
Ch. 8. Energy
... Its velocity or state of rest changes. The object accelerates. 25. If no net force acts on an object, what is necessarily zero (a) Velocity (b) Acceleration Acceleration is necessarily zero if no net force acts on an object. 26. If you hang from a clothesline when is the tension in the line greater, ...
... Its velocity or state of rest changes. The object accelerates. 25. If no net force acts on an object, what is necessarily zero (a) Velocity (b) Acceleration Acceleration is necessarily zero if no net force acts on an object. 26. If you hang from a clothesline when is the tension in the line greater, ...
Newton`s 3 rd Law of Motion
... 2. The teams who answers correctly win the point value of the question. 3. If a team answers a daily double incorrectly, then that team will lose the number of points they bid, and any other team can “ring in” by raising their hand and answer at that point. Let’s 4. There are two daily doubles avail ...
... 2. The teams who answers correctly win the point value of the question. 3. If a team answers a daily double incorrectly, then that team will lose the number of points they bid, and any other team can “ring in” by raising their hand and answer at that point. Let’s 4. There are two daily doubles avail ...
Lecture04
... 4-1: Three students can all pull on the ring (see sketch) with identical forces of magnitude F, but in different directions with respect to the +x axis. One of them pulls along the +x axis with force F1 as shown. What should the other two angles be to minimize the magnitude of the ring’s acceleratio ...
... 4-1: Three students can all pull on the ring (see sketch) with identical forces of magnitude F, but in different directions with respect to the +x axis. One of them pulls along the +x axis with force F1 as shown. What should the other two angles be to minimize the magnitude of the ring’s acceleratio ...
What is a Force?
... Gravity is the force that ALL objects in the UNIVERSE exert on each other... Newton said that gravitational force depends on 2 things: ...
... Gravity is the force that ALL objects in the UNIVERSE exert on each other... Newton said that gravitational force depends on 2 things: ...
L23_gravity
... Saturn accelerates 1/100th as much as Earth. Saturn accelerates 1/10th as much as Earth. Their accelerations are about the same. Saturn accelerates 10 times as much as Earth. Saturn accelerates 100 times as much as Earth. ...
... Saturn accelerates 1/100th as much as Earth. Saturn accelerates 1/10th as much as Earth. Their accelerations are about the same. Saturn accelerates 10 times as much as Earth. Saturn accelerates 100 times as much as Earth. ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Newton`s Laws of
... Objects in motion tend to stay in motion and objects at rest tend to stay at rest unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. Newton’s Second Law: Force equals mass times acceleration (F = ma). Newton’s Third Law: For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. ...
... Objects in motion tend to stay in motion and objects at rest tend to stay at rest unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. Newton’s Second Law: Force equals mass times acceleration (F = ma). Newton’s Third Law: For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. ...