Motion on a Curve
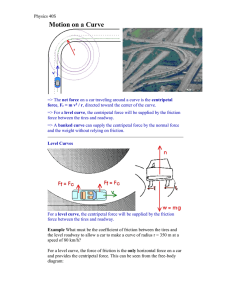
... vertically downward. The road surface exerts an upward normal reaction F on the car. The vertical component of the reaction must balance the downward weight of the car, so Fcos = mg The horizontal component of the reaction, Fsin, acts towards the centre of curvature of mv 2 the road. This componen ...
... vertically downward. The road surface exerts an upward normal reaction F on the car. The vertical component of the reaction must balance the downward weight of the car, so Fcos = mg The horizontal component of the reaction, Fsin, acts towards the centre of curvature of mv 2 the road. This componen ...
Planning Guide Conceptual Physics Third Edition
... Answer. Kepler was not aware of the law of inertia, or at least didn't apply it to this situation. The cannonball at rest in the cannon has the same speed as the earth's surface at that point. Its firing speed is relative to the moving earth, so there would be practically no difference in range whet ...
... Answer. Kepler was not aware of the law of inertia, or at least didn't apply it to this situation. The cannonball at rest in the cannon has the same speed as the earth's surface at that point. Its firing speed is relative to the moving earth, so there would be practically no difference in range whet ...
Notes on Newton`s Laws of Motion
... Newton’s Second Law of Motion • “The acceleration of an object is equal to the net force acting on it divided by the object’s mass” • Acceleration = net force/mass, or a = F/m • Mass is the amount of matter in an object and stays constant • Weight is the force of gravity on an object and can change ...
... Newton’s Second Law of Motion • “The acceleration of an object is equal to the net force acting on it divided by the object’s mass” • Acceleration = net force/mass, or a = F/m • Mass is the amount of matter in an object and stays constant • Weight is the force of gravity on an object and can change ...
008 Newton`s Second Law Explored
... Kinetics are the Cause • Kinetics cause Kinematics (not vice versa) • Kinematics such as velocity describe the motion. • Kinetics such as force, tell us what produced the motion. • E.g., A force acting on a mass produces an acceleration, which results in a change in velocity, and thus a change in di ...
... Kinetics are the Cause • Kinetics cause Kinematics (not vice versa) • Kinematics such as velocity describe the motion. • Kinetics such as force, tell us what produced the motion. • E.g., A force acting on a mass produces an acceleration, which results in a change in velocity, and thus a change in di ...
During a relay race, runner A runs a certain distance due north and
... 25. A car is rounding a circular curve of radius r on a banked turn. As the drawing indicates, there are two forces acting on the car, its weight mg and the normal force FN exerted on it by the road. Which force, or force component, provides the centripetal force that keeps the car moving on the ci ...
... 25. A car is rounding a circular curve of radius r on a banked turn. As the drawing indicates, there are two forces acting on the car, its weight mg and the normal force FN exerted on it by the road. Which force, or force component, provides the centripetal force that keeps the car moving on the ci ...
ConcepTest 4.1a Newton`s First Law I 1) there is a net force but the
... a1. The same force acts on a different mass m2 giving acceleration a2 = 2a1. If m1 and m2 are glued together and the same force F acts on this combination, what is the resulting acceleration? ...
... a1. The same force acts on a different mass m2 giving acceleration a2 = 2a1. If m1 and m2 are glued together and the same force F acts on this combination, what is the resulting acceleration? ...
Presentation - ScienceScene
... walking, swimming, jumping, rocket motion, objects resting on a table, tug-world of- war. Realcontexts: Changing the direction--changing the direction of a billiard ball, bus turning a corner; changing the speed--car speeding up, a rolling ball slowing down, magnets changing the motion of objects, w ...
... walking, swimming, jumping, rocket motion, objects resting on a table, tug-world of- war. Realcontexts: Changing the direction--changing the direction of a billiard ball, bus turning a corner; changing the speed--car speeding up, a rolling ball slowing down, magnets changing the motion of objects, w ...
Chapter 5
... A civil engineer wishes to redesign the curved roadway in Interactive Example 5.7 in such a way that a car will not have to rely on friction to round the curve without skidding. In other words, a car moving at the designated speed can negotiate the curve even when the road is covered with ice. Such ...
... A civil engineer wishes to redesign the curved roadway in Interactive Example 5.7 in such a way that a car will not have to rely on friction to round the curve without skidding. In other words, a car moving at the designated speed can negotiate the curve even when the road is covered with ice. Such ...
Apparent weight - University of Toronto Physics
... The gravitational effect of other astronomical bodies. Other astronomical bodies, particularly the sun and the moon, exert a very small gravitational force on objects at the earth's surface, depending on their relative positions. This causes the net gravitational force to vary by a small amount, and ...
... The gravitational effect of other astronomical bodies. Other astronomical bodies, particularly the sun and the moon, exert a very small gravitational force on objects at the earth's surface, depending on their relative positions. This causes the net gravitational force to vary by a small amount, and ...
Powerpoint revew chap4 no solutions
... This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching their courses and assessing student learning. Dissemination or sale of any part of this work (including on the World Wide Web) will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permit ...
... This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching their courses and assessing student learning. Dissemination or sale of any part of this work (including on the World Wide Web) will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permit ...
Physics 1710 Chapter 5: Laws of Motion—I
... • Newton’s Laws of Motion are: Acceleration (or deceleration) occurs if and ...
... • Newton’s Laws of Motion are: Acceleration (or deceleration) occurs if and ...
Set 4 - UCF Physics
... acceleration, we infer that there is no unbalanced force on that object. If you see a car moving at a constant speed on a level, straight highway, you infer that the frictional forces balance the driving forces. What is the net force acting on an airplane in level flight flying at 500 mph due east? ...
... acceleration, we infer that there is no unbalanced force on that object. If you see a car moving at a constant speed on a level, straight highway, you infer that the frictional forces balance the driving forces. What is the net force acting on an airplane in level flight flying at 500 mph due east? ...























