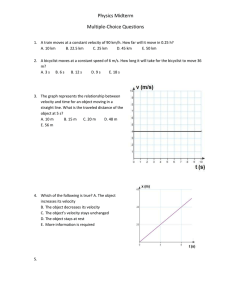
Skill Sheet 5.1 Isaac Newton
... the object has. The inertia of an object is related to its mass. You need more force to move or stop an object with a lot of mass or inertia than you need for an object with less mass or inertia. In Newton's second law, the acceleration of an object is directly related to the force on it, and invers ...
... the object has. The inertia of an object is related to its mass. You need more force to move or stop an object with a lot of mass or inertia than you need for an object with less mass or inertia. In Newton's second law, the acceleration of an object is directly related to the force on it, and invers ...
3 - CSUN.edu
... H. None of these choices can be suitably fill in this blank. 8. In a collision, an object experiences an impulse. This impulse can be determined by ____. Enter the two answers alphabetically with no commas or spaces between the letters. A. Multiplying the force on the object by the time over which t ...
... H. None of these choices can be suitably fill in this blank. 8. In a collision, an object experiences an impulse. This impulse can be determined by ____. Enter the two answers alphabetically with no commas or spaces between the letters. A. Multiplying the force on the object by the time over which t ...
Rooney AP Physics - Ch 7 Circular Motion and Gravitation
... labeling all the forces acting on the object(s) • Choose a coordinate system that has one axis perpendicular to the circular path and the other axis tangent to the circular path – The normal to the plane of motion is also often needed ...
... labeling all the forces acting on the object(s) • Choose a coordinate system that has one axis perpendicular to the circular path and the other axis tangent to the circular path – The normal to the plane of motion is also often needed ...
unit 2 universal gravitation and circular motion
... Satellites are objects that are projected into space They are at a constant height above the planet and are in uniform circular motion The force of gravity keeps the satellite in orbit around the earth (or any other planet) ...
... Satellites are objects that are projected into space They are at a constant height above the planet and are in uniform circular motion The force of gravity keeps the satellite in orbit around the earth (or any other planet) ...
Newton`s 1st Law of Motion
... 1. Recall that the First Law was basically in two parts: (1) objects at rest tend to stay that way. (2) object in uniform motion tend to stay that way. With this in mind, use the First Law to explain each: a. You stamp your boots to remove snow from them. b. You hang a rug on a line and beat it with ...
... 1. Recall that the First Law was basically in two parts: (1) objects at rest tend to stay that way. (2) object in uniform motion tend to stay that way. With this in mind, use the First Law to explain each: a. You stamp your boots to remove snow from them. b. You hang a rug on a line and beat it with ...
12.1 Forces
... the floor and object are bent slightly out of shape Rolling friction is is about 100 to 1000 times less than the force of static or sliding friction Ball bearings are often used to reduce friction in machines Friction is greatly reduced because it changes sliding friction to rolling friction T ...
... the floor and object are bent slightly out of shape Rolling friction is is about 100 to 1000 times less than the force of static or sliding friction Ball bearings are often used to reduce friction in machines Friction is greatly reduced because it changes sliding friction to rolling friction T ...
PhysCh7.78
... • Acceleration directed toward the center of a circular path • Although an object is moving at a constant speed, it can still have an acceleration. • Velocity is a vector, which has both magnitude and DIRECTION. • In circular motion, velocity is constantly changing direction. ...
... • Acceleration directed toward the center of a circular path • Although an object is moving at a constant speed, it can still have an acceleration. • Velocity is a vector, which has both magnitude and DIRECTION. • In circular motion, velocity is constantly changing direction. ...
Fall 1999 Test #1, version 1
... A candy bar of mass m rests on a tray of mass M that is on a horizontal frictionless surface. The coefficient of static friction between the candy bar and the upper surface of the tray is µs. A constant horizontal force F on the tray accelerates the tray and the candy bar to the right. (a) Draw a fr ...
... A candy bar of mass m rests on a tray of mass M that is on a horizontal frictionless surface. The coefficient of static friction between the candy bar and the upper surface of the tray is µs. A constant horizontal force F on the tray accelerates the tray and the candy bar to the right. (a) Draw a fr ...
Lecture 5 - McMaster Physics and Astronomy
... coefficient of static friction μs=0.50. What minimum force F is needed to pull the block? ...
... coefficient of static friction μs=0.50. What minimum force F is needed to pull the block? ...