Part I
... must be an inward (Centripetal) force pointed towards the circle center so that the natural tendency of the object to move in a straight line (Newton’s 1st Law!) will be overcome. If the centripetal force goes to zero, the ball will fly off in a direction tangent to the circle ...
... must be an inward (Centripetal) force pointed towards the circle center so that the natural tendency of the object to move in a straight line (Newton’s 1st Law!) will be overcome. If the centripetal force goes to zero, the ball will fly off in a direction tangent to the circle ...
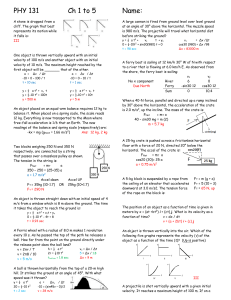
Chapter 3 Dynamics: Motion and Force 3.1 Homework # 19
... rear. Explain why the head of the victim seems to be thrown backward in this situation. Is it really? 04. When a golf ball is dropped to the pavement it bounces back up. Is a force needed to make it bounce back up? If so, what exerts the force? 05. A person wearing a cast on an arm or a leg experien ...
... rear. Explain why the head of the victim seems to be thrown backward in this situation. Is it really? 04. When a golf ball is dropped to the pavement it bounces back up. Is a force needed to make it bounce back up? If so, what exerts the force? 05. A person wearing a cast on an arm or a leg experien ...
document
... direction of the net force acting on it, there must be a net force toward the center of the circle. This force can be provided by any number of agents ...
... direction of the net force acting on it, there must be a net force toward the center of the circle. This force can be provided by any number of agents ...
sessn5
... Sometimes physicists like to write the above equation in a more compact form using the scalar (or dot) product. It is another way of saying include the cosine of the angle between the 2 vectors W = F.d Our more general equation for work has some more special cases. If the force and displacement vec ...
... Sometimes physicists like to write the above equation in a more compact form using the scalar (or dot) product. It is another way of saying include the cosine of the angle between the 2 vectors W = F.d Our more general equation for work has some more special cases. If the force and displacement vec ...
Luis Anchordoqui
... its arc so that the ball continues moving in a circle (b) Calculate the tension in the cord at the bottom of the arc, assuming the ball is moving at twice speed of part ...
... its arc so that the ball continues moving in a circle (b) Calculate the tension in the cord at the bottom of the arc, assuming the ball is moving at twice speed of part ...
1 - Vernon ISD
... 14. Inertia is a property of matter that is related to its mass, regardless of its motion. An object with a small mass has less inertia than an object with a large mass. Ball Z has the largest mass. Therefore, it has the most inertia. 15. Velocity is a vector quantity. This means that an object's ve ...
... 14. Inertia is a property of matter that is related to its mass, regardless of its motion. An object with a small mass has less inertia than an object with a large mass. Ball Z has the largest mass. Therefore, it has the most inertia. 15. Velocity is a vector quantity. This means that an object's ve ...
PHY131 E1
... it with a 10-N force. Rank the situations shown below according to the magnitude of the normal force exerted by the surface on the crate, least to greatest. ...
... it with a 10-N force. Rank the situations shown below according to the magnitude of the normal force exerted by the surface on the crate, least to greatest. ...
PowerPoint Lecture Chapter 6
... 1. Acts on materials that are in contact with each other 2. friction acts in opposite direction to oppose motion 3. friction mainly due to irregularities in the two surfaces. ...
... 1. Acts on materials that are in contact with each other 2. friction acts in opposite direction to oppose motion 3. friction mainly due to irregularities in the two surfaces. ...
Chapter 1
... that exerts a force on the ball. This force is the ball’s weight. • The earth’s gravity produces the ball’s weight. The weight points toward the earth’s center. • The ball’s weight causes it to ...
... that exerts a force on the ball. This force is the ball’s weight. • The earth’s gravity produces the ball’s weight. The weight points toward the earth’s center. • The ball’s weight causes it to ...
Combining Forces
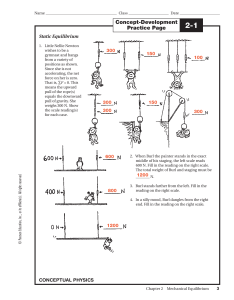
... • If the net force on an object is zero, the velocity of the object does not change. • If the net force is zero and the object is at rest, it remains at rest. • If the net force is zero and the object is moving, it continues to move in a straight line with constant speed. Newton’s Laws of Motion ...
... • If the net force on an object is zero, the velocity of the object does not change. • If the net force is zero and the object is at rest, it remains at rest. • If the net force is zero and the object is moving, it continues to move in a straight line with constant speed. Newton’s Laws of Motion ...