Fundamental of Physics
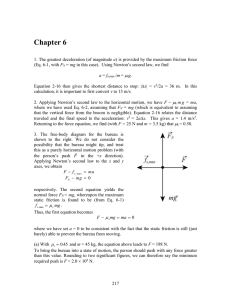
... representing the gravitational pull exerted by Earth, and an assumed-leftward f for the kinetic or static friction. We choose +x rightward and +y upward. We apply Newton’s second law to these axes: F f ma P FN mg 0 where F = 6.0 N and m = 2.5 kg is the mass of the block. (a) In this case, ...
... representing the gravitational pull exerted by Earth, and an assumed-leftward f for the kinetic or static friction. We choose +x rightward and +y upward. We apply Newton’s second law to these axes: F f ma P FN mg 0 where F = 6.0 N and m = 2.5 kg is the mass of the block. (a) In this case, ...
Inquiry version - Western Michigan University
... apply some “forces,” and record your actions in your notebook… [as in green] ”What kind of things are we doing as we apply forces?” Does anyone have a simple way to describe what we mean by force? [Through discussion, teacher leads students toward a simple generalization, defining FORCE as a PUSH or ...
... apply some “forces,” and record your actions in your notebook… [as in green] ”What kind of things are we doing as we apply forces?” Does anyone have a simple way to describe what we mean by force? [Through discussion, teacher leads students toward a simple generalization, defining FORCE as a PUSH or ...
master notes ch 4 (midterm prep)
... • An object at rest remains at rest, and an object in motion continues in motion with constant velocity (that is, constant speed in a straight line) unless the object experiences a net external force. • In other words, when the net external force on an object is zero, the object’s acceleration (or t ...
... • An object at rest remains at rest, and an object in motion continues in motion with constant velocity (that is, constant speed in a straight line) unless the object experiences a net external force. • In other words, when the net external force on an object is zero, the object’s acceleration (or t ...
How to enhance effectiveness of Direct Attack
... Really speaking some learned followers of Dr. Kano like Kiuzo Mifune in Japan and Koizumi in England already had some rotational ideas, but few people appreciated their words. To broaden the classical view biomechanics will use a very special field f experimentation. This field of experimentation is ...
... Really speaking some learned followers of Dr. Kano like Kiuzo Mifune in Japan and Koizumi in England already had some rotational ideas, but few people appreciated their words. To broaden the classical view biomechanics will use a very special field f experimentation. This field of experimentation is ...
A
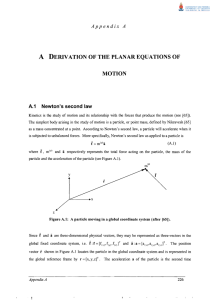
... For the purposes of analyzing a planar machining center it is required to derive the planar equations of motion. Consider Figure A3 showing an external force ( acting on the i-th particle of a system. For planar motion, the center of mass C of the system remains in the Gxy-plane, and coincides with ...
... For the purposes of analyzing a planar machining center it is required to derive the planar equations of motion. Consider Figure A3 showing an external force ( acting on the i-th particle of a system. For planar motion, the center of mass C of the system remains in the Gxy-plane, and coincides with ...
Relative Motion in Two Dimensions
... • When an object moves in a circle, the net force toward the center of the circle is called the centripetal force. • To analyze centripetal acceleration situations accurately, you must identify the agent of the force that causes the acceleration. Then you can apply Newton’s second law for the compon ...
... • When an object moves in a circle, the net force toward the center of the circle is called the centripetal force. • To analyze centripetal acceleration situations accurately, you must identify the agent of the force that causes the acceleration. Then you can apply Newton’s second law for the compon ...
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights
... solid cylinder, and a hollow cylinder. The spectators for the race demand that the race be fair, so you make sure that all of the objects have the same mass and radius and that they all start from rest. Then you let the three objects roll down a long ramp. Is there a way to predict which one will wi ...
... solid cylinder, and a hollow cylinder. The spectators for the race demand that the race be fair, so you make sure that all of the objects have the same mass and radius and that they all start from rest. Then you let the three objects roll down a long ramp. Is there a way to predict which one will wi ...
Basic Physics I – Selected Solved Problems from Cutnell &
... A tourist being chased by an angry bear is running in a straight line toward his car at a speed of 4.0 m/s. The car is a distance d away. The bear is 26 m behind the tourist and running at 6.0 m/s. The tourist reaches the car safely. What is the maximum possible value for d? REASONING In order for t ...
... A tourist being chased by an angry bear is running in a straight line toward his car at a speed of 4.0 m/s. The car is a distance d away. The bear is 26 m behind the tourist and running at 6.0 m/s. The tourist reaches the car safely. What is the maximum possible value for d? REASONING In order for t ...
Unit 4 Packet (Labs)
... 1. Measure and record the mass of the ball you plan to use in this experiment. 2. Connect the Motion Detector to the DIG/SONIC 1 channel of the interface. Place the Motion Detector on the floor and protect it by placing a wire basket over it. 3. Open the file “16 Energy of a Tossed Ball” from the Ph ...
... 1. Measure and record the mass of the ball you plan to use in this experiment. 2. Connect the Motion Detector to the DIG/SONIC 1 channel of the interface. Place the Motion Detector on the floor and protect it by placing a wire basket over it. 3. Open the file “16 Energy of a Tossed Ball” from the Ph ...
Textbook Practice Problems
... does mass impact the inertia of an object? Does a nickel have more inertial than a penny? (2E, 4D). Or have students explore the relationship between force and mass using “Active Physics – Sports”, p. S61 Does the amount of mass an object has affect its inertia? (2E, 4D). Show the video clip Dem ...
... does mass impact the inertia of an object? Does a nickel have more inertial than a penny? (2E, 4D). Or have students explore the relationship between force and mass using “Active Physics – Sports”, p. S61 Does the amount of mass an object has affect its inertia? (2E, 4D). Show the video clip Dem ...
Document
... Example : Two boxes and a pulley. Two boxes are connected by a cord running over a pulley. The coefficient of kinetic friction between box A and the table is 0.20. We ignore the mass of the cord and pulley and any friction in the pulley, which means we can assume that a force applied to one end of ...
... Example : Two boxes and a pulley. Two boxes are connected by a cord running over a pulley. The coefficient of kinetic friction between box A and the table is 0.20. We ignore the mass of the cord and pulley and any friction in the pulley, which means we can assume that a force applied to one end of ...
Static Friction
... object. The normal force is defined as the perpendicular component of the force exerted by the surface. In this case, the normal force is equal to the weight of the object. Once the box starts to slide, you must continue to exert a force to keep the object moving, or friction will slow it to a stop. ...
... object. The normal force is defined as the perpendicular component of the force exerted by the surface. In this case, the normal force is equal to the weight of the object. Once the box starts to slide, you must continue to exert a force to keep the object moving, or friction will slow it to a stop. ...