Motion & Forces
... be the difference between the two forces because they are in opposite directions. They are considered to be unbalanced forces. ...
... be the difference between the two forces because they are in opposite directions. They are considered to be unbalanced forces. ...
Chapter Review
... a. smaller than the force used to push the object that has less mass. b. larger than the force used to push the object that has less mass. c. the same as the force used to push the object that has less mass. d. equal to the object’s weight. Short Answer ...
... a. smaller than the force used to push the object that has less mass. b. larger than the force used to push the object that has less mass. c. the same as the force used to push the object that has less mass. d. equal to the object’s weight. Short Answer ...
Potential Energy - McMaster Physics and Astronomy
... if the collision lasts 0.1s, what was the average force ? if the force looks like below, what was the max force ? ...
... if the collision lasts 0.1s, what was the average force ? if the force looks like below, what was the max force ? ...
TEKS 5 - Pearson School
... Aristotle The ancient Greek scientist and philosopher Aristotle (384 B.C.E.–322 B.C.E.) made many scientific discoveries through careful observation and logical reasoning. He was not always correct. Aristotle incorrectly proposed that force is required to keep an object moving at constant speed. Thi ...
... Aristotle The ancient Greek scientist and philosopher Aristotle (384 B.C.E.–322 B.C.E.) made many scientific discoveries through careful observation and logical reasoning. He was not always correct. Aristotle incorrectly proposed that force is required to keep an object moving at constant speed. Thi ...
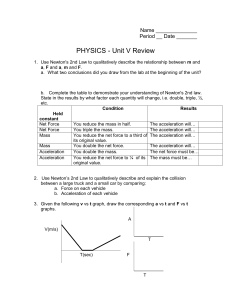
Unit V review
... You reduce the net force to ¼ of its The mass must be… original value. 2. Use Newton’s 2nd Law to qualitatively describe and explain the collision between a large truck and a small car by comparing: a. Force on each vehicle b. Acceleration of each vehicle 3. Given the following v vs t graph, draw th ...
... You reduce the net force to ¼ of its The mass must be… original value. 2. Use Newton’s 2nd Law to qualitatively describe and explain the collision between a large truck and a small car by comparing: a. Force on each vehicle b. Acceleration of each vehicle 3. Given the following v vs t graph, draw th ...
Newton’s Laws of Motion
... Inertia is the tendency of an object to resist changes in its velocity: whether in motion or motionless. ...
... Inertia is the tendency of an object to resist changes in its velocity: whether in motion or motionless. ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... Inertia is the tendency of an object to resist changes in its velocity: whether in motion or motionless. ...
... Inertia is the tendency of an object to resist changes in its velocity: whether in motion or motionless. ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion - Doral Academy Preparatory
... The size of the force on the air equals the size of the force on the bird; the direction of the force on the air (downwards) is opposite the direction of the force on the bird (upwards). Action-reaction force pairs make it possible for birds to fly. ...
... The size of the force on the air equals the size of the force on the bird; the direction of the force on the air (downwards) is opposite the direction of the force on the bird (upwards). Action-reaction force pairs make it possible for birds to fly. ...
Name
... 1. A net force F accelerates a mass m with an acceleration of a. If the same net force is applied to mass 2m, then the acceleration will be a. 4a b. 2a c. a/2 d. a/4 2. A 20-ton truck collides with a 1500 lb car and causes a lot of damage to the car. Since a lot of damage is done on the car, a. the ...
... 1. A net force F accelerates a mass m with an acceleration of a. If the same net force is applied to mass 2m, then the acceleration will be a. 4a b. 2a c. a/2 d. a/4 2. A 20-ton truck collides with a 1500 lb car and causes a lot of damage to the car. Since a lot of damage is done on the car, a. the ...
Second
... the weight Fg of an object, the magnitude of the force of gravity acting on it, if the acceleration a is the acceleration due to gravity, g = 9.8 m/s2. ...
... the weight Fg of an object, the magnitude of the force of gravity acting on it, if the acceleration a is the acceleration due to gravity, g = 9.8 m/s2. ...
+x - SeyedAhmad.com
... Example 4: What is the maximum acceleration for the 2-kg mass in the previous problem? (A = 12 cm, k = 400 N/m) The maximum acceleration occurs when the restoring force is a maximum; i.e., when the stretch or compression of the spring is largest. F = ma = -kx ...
... Example 4: What is the maximum acceleration for the 2-kg mass in the previous problem? (A = 12 cm, k = 400 N/m) The maximum acceleration occurs when the restoring force is a maximum; i.e., when the stretch or compression of the spring is largest. F = ma = -kx ...
Review – Circular Motion, Gravitation, and Kepler`s Laws Date
... 19. A spacecraft starts on Earth is moving to Mars. Which of the following is correct about the gravitational force on the spacecraft due to Earth’s attraction? A. The force becomes zero when the spacecraft is half way between the planets B. The force becomes zero when the spacecraft is closer to th ...
... 19. A spacecraft starts on Earth is moving to Mars. Which of the following is correct about the gravitational force on the spacecraft due to Earth’s attraction? A. The force becomes zero when the spacecraft is half way between the planets B. The force becomes zero when the spacecraft is closer to th ...