Document
... A body moving in the positive x direction passes the origin at time t = 0. Between t = 0 and t = 1 second, the body has a constant speed of 24 meters per second. At t = 1 second, the body is given a constant acceleration of 6 meters per second squared in the negative x direction. The position x of t ...
... A body moving in the positive x direction passes the origin at time t = 0. Between t = 0 and t = 1 second, the body has a constant speed of 24 meters per second. At t = 1 second, the body is given a constant acceleration of 6 meters per second squared in the negative x direction. The position x of t ...
Slide 1
... The rpm stands for revolutions per minute, and it is an angular velocity measurement. ...
... The rpm stands for revolutions per minute, and it is an angular velocity measurement. ...
Earth`s Moon
... the surface of the Earth below, we may hit a town far away. If we were to load the cannon with more gun powder and fire it HORIZONTALLY to the surface of the Earth below, we may even hit a different country far away. Let’s say we were to load the cannon with just enough gun powder and fire it HO ...
... the surface of the Earth below, we may hit a town far away. If we were to load the cannon with more gun powder and fire it HORIZONTALLY to the surface of the Earth below, we may even hit a different country far away. Let’s say we were to load the cannon with just enough gun powder and fire it HO ...
Standard EPS Shell Presentation
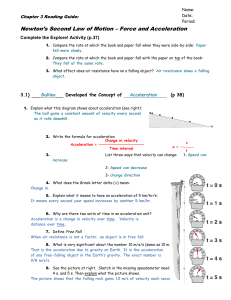
... 6.2 Newton’s second law Newton’s first law tells us that motion cannot change without a net force. According to Newton’s second law, the amount of acceleration depends on both the force and the mass. ...
... 6.2 Newton’s second law Newton’s first law tells us that motion cannot change without a net force. According to Newton’s second law, the amount of acceleration depends on both the force and the mass. ...
lec06
... reference system for measuring position and time that is not accelerating. If we wish to use Newton’s Second Law in an accelerating reference frame, we need to add extra terms to the equation that can be considered as forces operating on every object that we track using the accelerating reference fr ...
... reference system for measuring position and time that is not accelerating. If we wish to use Newton’s Second Law in an accelerating reference frame, we need to add extra terms to the equation that can be considered as forces operating on every object that we track using the accelerating reference fr ...
Slide 1
... Violent motion, on the other hand, was imposed motion. • It was the result of forces that pushed or pulled. • The important thing about defining violent motion was that it had an external cause. • Violent motion was imparted to objects. • Objects in their natural resting places could not move by the ...
... Violent motion, on the other hand, was imposed motion. • It was the result of forces that pushed or pulled. • The important thing about defining violent motion was that it had an external cause. • Violent motion was imparted to objects. • Objects in their natural resting places could not move by the ...
Newton`s Universal Law of Gravitation “The Apple and the Moon
... In 1798, Henry Cavendish devised an experiment to determine the value of G. Instead of involving the gravitational force exerted by the earth, he measured the gravitational attraction between two known masses in his lab. Measuring this force was difficult because it was exceedingly small (about 10–9 ...
... In 1798, Henry Cavendish devised an experiment to determine the value of G. Instead of involving the gravitational force exerted by the earth, he measured the gravitational attraction between two known masses in his lab. Measuring this force was difficult because it was exceedingly small (about 10–9 ...
Physics 2414, Spring 2005 Group Exercise 7, Mar 31, 2005
... (d) If the frictional force acting on the mass while sliding down the ~ f | = 173.2 Newtons, calculate the work done by the incline is |F frictional force in going from point ‘1’ to point ‘2’. Thus calculate ...
... (d) If the frictional force acting on the mass while sliding down the ~ f | = 173.2 Newtons, calculate the work done by the incline is |F frictional force in going from point ‘1’ to point ‘2’. Thus calculate ...