torque
... a linear system, we can show the relationship between torque and angular momentum Angular momentum is defined as L = I ω ...
... a linear system, we can show the relationship between torque and angular momentum Angular momentum is defined as L = I ω ...
Name Reading Science – Newton`s Laws and Roller Coasters In
... The mass of your body and the coaster cars is constant while the amount of force changes due to changes in acceleration. The changes in acceleration are due mostly to friction. Newton’s third law of action-reaction, states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. This means th ...
... The mass of your body and the coaster cars is constant while the amount of force changes due to changes in acceleration. The changes in acceleration are due mostly to friction. Newton’s third law of action-reaction, states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. This means th ...
Action and Reaction on Different Masses
... Newton’s third law describes the relationship between two forces in an interaction. • One force is called the action force. • The other force is called the reaction force. • Neither force exists without the other. • They are equal in strength and opposite in direction. • They occur at the same time ...
... Newton’s third law describes the relationship between two forces in an interaction. • One force is called the action force. • The other force is called the reaction force. • Neither force exists without the other. • They are equal in strength and opposite in direction. • They occur at the same time ...
香港考試局
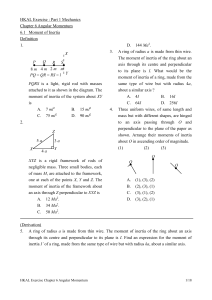
... Point masses of 3 kg and 5 kg are attached to the ends of an L-shaped light frame ABC, with AB vertical and BC horizontal. The frame is pivoted at and free to rotate about point B in a vertical plane. What is the initial angular acceleration of the system when released from rest ? A. 1.1 rad s-2 B. ...
... Point masses of 3 kg and 5 kg are attached to the ends of an L-shaped light frame ABC, with AB vertical and BC horizontal. The frame is pivoted at and free to rotate about point B in a vertical plane. What is the initial angular acceleration of the system when released from rest ? A. 1.1 rad s-2 B. ...
Lecture 1
... Mass: Property of a body of fluid that is a measure of its inertia or resistance to a change in motion. It’s also a measure of the quantity of fluid. Mass does not change with the body’s position, movement or alteration of its shape unless material is added or removed. Weight: Gravitational force ac ...
... Mass: Property of a body of fluid that is a measure of its inertia or resistance to a change in motion. It’s also a measure of the quantity of fluid. Mass does not change with the body’s position, movement or alteration of its shape unless material is added or removed. Weight: Gravitational force ac ...
force
... • The force of gravity from the Earth continuously pulls the moon in a nearly circular orbit around the Earth. • Centripetal force: center-directed force that continuously changes the direction of an object to make it move in a circle. – As an object moves in a continuous (constant) circular motion, ...
... • The force of gravity from the Earth continuously pulls the moon in a nearly circular orbit around the Earth. • Centripetal force: center-directed force that continuously changes the direction of an object to make it move in a circle. – As an object moves in a continuous (constant) circular motion, ...
Exam 2
... B) No, because the force and the displacement of the object are perpendicular. C) Yes, since a force acts and the object moves, and work is force times distance. D) Yes, since it takes energy to turn an object. 40) A 3.0-kg object moves to the right at 4.0 m/s. It collides head-on with a 6.0-kg obje ...
... B) No, because the force and the displacement of the object are perpendicular. C) Yes, since a force acts and the object moves, and work is force times distance. D) Yes, since it takes energy to turn an object. 40) A 3.0-kg object moves to the right at 4.0 m/s. It collides head-on with a 6.0-kg obje ...
Momentum and Impulse notes
... What does momentum and impulse have to do with each other? Momentum = mv If velocity changes, momentum changes, and acceleration (either + or –) occurs But we know: 1. for acceleration to occur, a force has to be applied. 2. If a given force is applied over a longer time, more acceleration occurs. ...
... What does momentum and impulse have to do with each other? Momentum = mv If velocity changes, momentum changes, and acceleration (either + or –) occurs But we know: 1. for acceleration to occur, a force has to be applied. 2. If a given force is applied over a longer time, more acceleration occurs. ...
RevfinQ2010AnsFa06
... table. Both have the same momentum, and you exert the same force to stop each. How do the time intervals to stop them compare? A: It takes less time to stop the little calculator. B: Both take the same time. C: It takes more time to stop the little calculator. Answer: F = p/t. Same F, same p for ...
... table. Both have the same momentum, and you exert the same force to stop each. How do the time intervals to stop them compare? A: It takes less time to stop the little calculator. B: Both take the same time. C: It takes more time to stop the little calculator. Answer: F = p/t. Same F, same p for ...