there are different types of forces
... Earths gravity pulling on your mass. On the Moon your weight would be ...
... Earths gravity pulling on your mass. On the Moon your weight would be ...
Physics 106P: Lecture 1 Notes
... To describe the response of an object to a given impulse we need the concept of linear momentum: ...
... To describe the response of an object to a given impulse we need the concept of linear momentum: ...
PS03H - willisworldbio
... • Objects in the shuttle seem to be floating because they are all falling with the same ______________. ...
... • Objects in the shuttle seem to be floating because they are all falling with the same ______________. ...
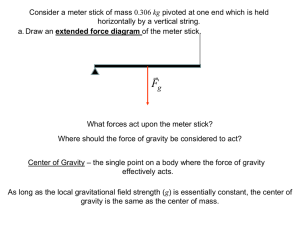
Static Equilibrium (print version)
... Where should the force of gravity be considered to act? Center of Gravity – the single point on a body where the force of gravity effectively acts. As long as the local gravitational field strength (g) is essentially constant, the center of gravity is the same as the center of mass. ...
... Where should the force of gravity be considered to act? Center of Gravity – the single point on a body where the force of gravity effectively acts. As long as the local gravitational field strength (g) is essentially constant, the center of gravity is the same as the center of mass. ...
Experiment 5: Newton`s Second Law
... This analysis assumes a frictionless environment. For simplicity, Ff will be counterbalanced by a small mass, mf , hanged from one end of the system. When the weight of mf is equal to the force of friction (mf g = Ff ), the system will be in equilibrium. ΣF = 0 N ...
... This analysis assumes a frictionless environment. For simplicity, Ff will be counterbalanced by a small mass, mf , hanged from one end of the system. When the weight of mf is equal to the force of friction (mf g = Ff ), the system will be in equilibrium. ΣF = 0 N ...
lecture03
... Equal to its weight Less than its weight but more than zero Depends on the speed of the puck Zero ...
... Equal to its weight Less than its weight but more than zero Depends on the speed of the puck Zero ...
Chap. 7 Conceptual Modules Giancoli
... magnitude acts on a 130-g pebble. How does the rate of change of the boulder’s momentum compare to the rate of change of the pebble’s momentum? ...
... magnitude acts on a 130-g pebble. How does the rate of change of the boulder’s momentum compare to the rate of change of the pebble’s momentum? ...
Centripetal Force - Northern Illinois University
... This experiment uses a vertical shaft that can freely rotate to spin a massive bob of mass m. The bob hangs by two strings from a horizontal bar with a counterweight on the other side. The counterweight helps the shaft rotate evenly. A spring can connect the bob to the shaft and provides a force to ...
... This experiment uses a vertical shaft that can freely rotate to spin a massive bob of mass m. The bob hangs by two strings from a horizontal bar with a counterweight on the other side. The counterweight helps the shaft rotate evenly. A spring can connect the bob to the shaft and provides a force to ...
to see a detailed table of contents outlining all chapter lessons in
... 18.4 Kinetic Energy of a Rigid Body in Three Dimensions 18.5 Motion of a Rigid Body in Three Dimensions 18.6 Euler’s Equations of Motion. Extension of d’Alembert’s Principle to the Motion of a Rigid Body in Three Dimensions 18.7 Motion of a Rigid Body about a Fixed Point 18.8 Rotation of a Rigid Bod ...
... 18.4 Kinetic Energy of a Rigid Body in Three Dimensions 18.5 Motion of a Rigid Body in Three Dimensions 18.6 Euler’s Equations of Motion. Extension of d’Alembert’s Principle to the Motion of a Rigid Body in Three Dimensions 18.7 Motion of a Rigid Body about a Fixed Point 18.8 Rotation of a Rigid Bod ...
PHET Forces and Motion Basics Simulator Classwork
... 12. Approximately how many times larger/smaller is this acceleration than that of the crate? ...
... 12. Approximately how many times larger/smaller is this acceleration than that of the crate? ...
Lecture 06: Conservation of Angular Momentum
... A puck of mass m = 0.5 kg is attached to a taut cord passing through a small hole in a frictionless, horizontal surface. The puck is initially orbiting with speed vi = 2 m/s in a circle of radius ri = 0.2 m. The cord is then slowly pulled from below, decreasing the radius of the circle to r = 0.1 m. ...
... A puck of mass m = 0.5 kg is attached to a taut cord passing through a small hole in a frictionless, horizontal surface. The puck is initially orbiting with speed vi = 2 m/s in a circle of radius ri = 0.2 m. The cord is then slowly pulled from below, decreasing the radius of the circle to r = 0.1 m. ...