solns - CEMC
... We use the concept of mass to describe how much matter is inside a physical object. Anything that takes up space has matter in it. Generally, the bigger an object is, the more mass it has, but not always. If you could blow up a balloon to be the same size as an elephant, the balloon would still have ...
... We use the concept of mass to describe how much matter is inside a physical object. Anything that takes up space has matter in it. Generally, the bigger an object is, the more mass it has, but not always. If you could blow up a balloon to be the same size as an elephant, the balloon would still have ...
Lecture2_Freefall
... in still water is v1, tows a smaller boat whose maximum speed is the smaller v2. across the lake. If both outboard motors run together at full bore, the speed that they travel together with will be ...
... in still water is v1, tows a smaller boat whose maximum speed is the smaller v2. across the lake. If both outboard motors run together at full bore, the speed that they travel together with will be ...
Physics Momentum and Collisions Section Review Sheet
... 12) A rifle fires a bullet…. Prior to being fired, both objects (the bullet and the gun) were at rest….. which receives a greater change in velocity? A greater change in momentum? A greater impulse? A greater force? What was the total initial momentum of the system 13) A 1 kg object is dropped from ...
... 12) A rifle fires a bullet…. Prior to being fired, both objects (the bullet and the gun) were at rest….. which receives a greater change in velocity? A greater change in momentum? A greater impulse? A greater force? What was the total initial momentum of the system 13) A 1 kg object is dropped from ...
Newton`s 1st Law of Motion
... therefore comes back to the table very nicely because it and the table have had the same fixed horizontal speed. (Why doesn't it maintain its upwards motion? Answer: because the force of gravity on the ball is an external force!) Whether the train is at rest or moving as described, it will be an ine ...
... therefore comes back to the table very nicely because it and the table have had the same fixed horizontal speed. (Why doesn't it maintain its upwards motion? Answer: because the force of gravity on the ball is an external force!) Whether the train is at rest or moving as described, it will be an ine ...
Momentum!!!
... perfectly inelastic collision. The first ball has a mass of 0.500 kg and an initial velocity of 4.00 m/s to the right. The mass of the second ball is 0.250 kg, and it has an initial velocity of 3.00 m/s to the left. What is the final velocity of the composite ball of clay after the collision? What i ...
... perfectly inelastic collision. The first ball has a mass of 0.500 kg and an initial velocity of 4.00 m/s to the right. The mass of the second ball is 0.250 kg, and it has an initial velocity of 3.00 m/s to the left. What is the final velocity of the composite ball of clay after the collision? What i ...
Kepler`s Laws
... Johannes Kepler (1571–1630) discovered three laws of planetary motion in the early seventeenth century. These laws were discovered empirically, after studying for many years data collected primarily by the Danish astronomer Tycho Brahe (1546–1601). The first mathematical derivation of Kepler’s laws a ...
... Johannes Kepler (1571–1630) discovered three laws of planetary motion in the early seventeenth century. These laws were discovered empirically, after studying for many years data collected primarily by the Danish astronomer Tycho Brahe (1546–1601). The first mathematical derivation of Kepler’s laws a ...
momentum - Cloudfront.net
... 3. Which of the following is true about momentum? (a) it is a vector (b) it is a product of mass times velocity (c) impulses are required to change it (d) all of the above ...
... 3. Which of the following is true about momentum? (a) it is a vector (b) it is a product of mass times velocity (c) impulses are required to change it (d) all of the above ...
Slide 1
... An acrobatic physics professor stands at the center of a turntable, holding his arms extended horizontally with a 5.0 kg dumbbell in each hand. He is set rotating about a vertical axis, making one revolution in 2.0 s. Find the prof’s new angular velocity if he pulls the dumbbells in to his stomach. ...
... An acrobatic physics professor stands at the center of a turntable, holding his arms extended horizontally with a 5.0 kg dumbbell in each hand. He is set rotating about a vertical axis, making one revolution in 2.0 s. Find the prof’s new angular velocity if he pulls the dumbbells in to his stomach. ...
PHYSICS 231 INTRODUCTORY PHYSICS I Lecture 8
... Ted and his ice-boat (combined mass = 240 kg) rest on the frictionless surface of a frozen lake. A heavy rope (mass of 80 kg and length of 100 m) is laid out in a line along the top of the lake. Initially, Ted and the rope are at rest. At time t=0, Ted turns on a wench which winds 0.5 m of rope onto ...
... Ted and his ice-boat (combined mass = 240 kg) rest on the frictionless surface of a frozen lake. A heavy rope (mass of 80 kg and length of 100 m) is laid out in a line along the top of the lake. Initially, Ted and the rope are at rest. At time t=0, Ted turns on a wench which winds 0.5 m of rope onto ...
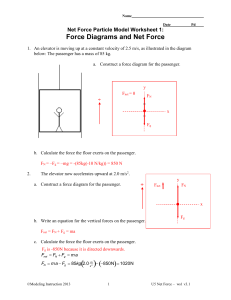
Force Diagrams and Net Force Key
... hanging masses. System C has the heaviest hanging masses, so the net force acting on the system is 2Mg. b. Which system has the least inertia? Explain how you know. If we define inertia as resistance to change in motion, and we know that in these systems the resistance is determined by the mass of t ...
... hanging masses. System C has the heaviest hanging masses, so the net force acting on the system is 2Mg. b. Which system has the least inertia? Explain how you know. If we define inertia as resistance to change in motion, and we know that in these systems the resistance is determined by the mass of t ...