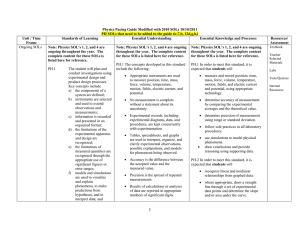
Reading Graphs and Interpreting slope: A math/Science
... Parallel mathematics and science lessons are developed by a team of teachers, each a content specialist in their own discipline, to allow the concepts from both disciplines to be almost equally taught (Vasques-Mireles & West, 2007). A strength is the team-teaching approach; conversations occur aroun ...
... Parallel mathematics and science lessons are developed by a team of teachers, each a content specialist in their own discipline, to allow the concepts from both disciplines to be almost equally taught (Vasques-Mireles & West, 2007). A strength is the team-teaching approach; conversations occur aroun ...
Chapter 13 Lecture
... Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation Every particle in the Universe attracts every other particle with a force that is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the distance between them. ...
... Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation Every particle in the Universe attracts every other particle with a force that is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the distance between them. ...
Calculating Acceleration
... • If an object is at rest, it tends to remain at rest. Its velocity is zero unless a force makes it move. • The inertia of an object is related to its mass. The greater the mass of an object is, the greater its inertia. ...
... • If an object is at rest, it tends to remain at rest. Its velocity is zero unless a force makes it move. • The inertia of an object is related to its mass. The greater the mass of an object is, the greater its inertia. ...
AP_Physics_C_-_Gravitation - St. Raymond High School for Boys
... The NEW "r" that you see is simply a unit vector like I,j, & k-hat. A unit vector, remember, tells you the direction the force is going. In this case it means that it is between the two bodies is RADIAL in nature. The NEGATIVE SIGN is meant to denote that a force produces "bound" orbits. It is only ...
... The NEW "r" that you see is simply a unit vector like I,j, & k-hat. A unit vector, remember, tells you the direction the force is going. In this case it means that it is between the two bodies is RADIAL in nature. The NEGATIVE SIGN is meant to denote that a force produces "bound" orbits. It is only ...
Slide 1
... • If an object is at rest, it tends to remain at rest. Its velocity is zero unless a force makes it move. • The inertia of an object is related to its mass. The greater the mass of an object is, the greater its inertia. ...
... • If an object is at rest, it tends to remain at rest. Its velocity is zero unless a force makes it move. • The inertia of an object is related to its mass. The greater the mass of an object is, the greater its inertia. ...
Gravity By Cindy Grigg - Alfred G. Waters Middle School
... Because the Earth's gravity has the same pull on every object, all objects fall at the same speed (in a vacuum). On Earth, we have air. Air resistance will cause some objects to fall more slowly than others will. This works to our advantage when we want to fall more slowly, for example, when a skydi ...
... Because the Earth's gravity has the same pull on every object, all objects fall at the same speed (in a vacuum). On Earth, we have air. Air resistance will cause some objects to fall more slowly than others will. This works to our advantage when we want to fall more slowly, for example, when a skydi ...
AP® Physics B – Syllabus #2
... The AP class has run since it was first offered in 1994 and has evolved to include covering AP C topics and as of the fall of 2005 part of the University of Connecticut Early College Experience. Classes meet for forty two minutes, eight times a week for the entire school year. Students who elect to ...
... The AP class has run since it was first offered in 1994 and has evolved to include covering AP C topics and as of the fall of 2005 part of the University of Connecticut Early College Experience. Classes meet for forty two minutes, eight times a week for the entire school year. Students who elect to ...
Document
... forces are all manifestations of the electromagnetic force They all are the result of attractive (and repulsive) forces of atoms and molecules within an object (normal and tension) or at the interface of two objects Applications of Newton’s 2nd Law Equilibrium – an object which has zero accelera ...
... forces are all manifestations of the electromagnetic force They all are the result of attractive (and repulsive) forces of atoms and molecules within an object (normal and tension) or at the interface of two objects Applications of Newton’s 2nd Law Equilibrium – an object which has zero accelera ...
9-2 Conservation of Momentum During a collision, measurements
... that we can ignore external forces. Since the internal forces are equal and opposite, the total momentum is constant. ...
... that we can ignore external forces. Since the internal forces are equal and opposite, the total momentum is constant. ...
Gravitation PPT
... The negative is symbolic because it means that the mass “m” is BOUND to the mass of “M” and can never escape from it. It is called a BINDING ENERGY. ...
... The negative is symbolic because it means that the mass “m” is BOUND to the mass of “M” and can never escape from it. It is called a BINDING ENERGY. ...
Chapters 5&6
... Force superposition • Forces applied to the same object are adding as vectors – superposition • The net force – a vector sum of all the forces applied to the same object ...
... Force superposition • Forces applied to the same object are adding as vectors – superposition • The net force – a vector sum of all the forces applied to the same object ...
Dynamics
... It’s a push or a pull that one object exerts on another. It can change the state of motion of an object. It may change the shape of an object. S.I. unit of a force is the newton (N). Examples of forces include friction, weight & air resistance. Forces are vectors and can be added by considering both ...
... It’s a push or a pull that one object exerts on another. It can change the state of motion of an object. It may change the shape of an object. S.I. unit of a force is the newton (N). Examples of forces include friction, weight & air resistance. Forces are vectors and can be added by considering both ...
forces christina danielle ali
... object with more mass has more inertia, which means its resistance to motion is greater than an object with less mass. Because the rock was only in the way of the skateboard, the skateboard stopped, but the skateboarder continued his motion in the positive x ...
... object with more mass has more inertia, which means its resistance to motion is greater than an object with less mass. Because the rock was only in the way of the skateboard, the skateboard stopped, but the skateboarder continued his motion in the positive x ...
2010 Pacing Pacing Guide - High School Science Help
... transformed to provide usable work. Key concepts include a) transfer and storage of energy among systems ...
... transformed to provide usable work. Key concepts include a) transfer and storage of energy among systems ...
University Physics - Erwin Sitompul
... Out of common experience, we know that any change in velocity must be due to an interaction between an object (a body) and something in its surroundings. An interaction that can cause an acceleration of a body is called a force. Force can be loosely defined as a push or pull on the body. The r ...
... Out of common experience, we know that any change in velocity must be due to an interaction between an object (a body) and something in its surroundings. An interaction that can cause an acceleration of a body is called a force. Force can be loosely defined as a push or pull on the body. The r ...
Dynamics of Uniform Circular Motion
... constant velocity throughout all three turns. At which turn will there be the greatest centripetal acceleration? If the bobsled moves at 35 m/s throughout the course and turn B has a radius of 20m and turn C is 50m how many G’s of acceleration is the sledder feeling through turns B & C ? ...
... constant velocity throughout all three turns. At which turn will there be the greatest centripetal acceleration? If the bobsled moves at 35 m/s throughout the course and turn B has a radius of 20m and turn C is 50m how many G’s of acceleration is the sledder feeling through turns B & C ? ...
Force
... Fhand on bowling ball is the force that the hand exerts upward on the bowling ball. Fbowling ball on hand is the force that Earth exerts downward on the bowling ball. Fbowling ball on Earth is the force that the bowling ball exerts upward on Earth. Fhand on bowling ball and Fbowling ball on hand; FE ...
... Fhand on bowling ball is the force that the hand exerts upward on the bowling ball. Fbowling ball on hand is the force that Earth exerts downward on the bowling ball. Fbowling ball on Earth is the force that the bowling ball exerts upward on Earth. Fhand on bowling ball and Fbowling ball on hand; FE ...