Chapter 7 Linear Momentum and Collisions
... When we talk about a collision in physics (between two particles, say) we mean that two particles are moving freely through space until they get close to one another; then, for a short period of time they exert strong forces on each other until they move apart and are again moving freely. For such a ...
... When we talk about a collision in physics (between two particles, say) we mean that two particles are moving freely through space until they get close to one another; then, for a short period of time they exert strong forces on each other until they move apart and are again moving freely. For such a ...
Lab7_StaticEquilibrium
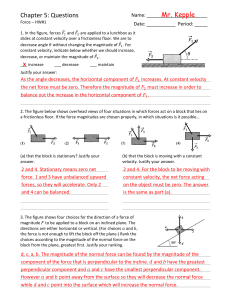
... The magnitude of the torque created by a force equals the magnitude of the force multiplied by the length of the lever arm, d, or = d F. For the wheel in Figure 1 the lever arm for F2 is equal to the radius of the wheel, while the lever arm for F1 is zero. Why? Furthermore, torque is a vector and ...
... The magnitude of the torque created by a force equals the magnitude of the force multiplied by the length of the lever arm, d, or = d F. For the wheel in Figure 1 the lever arm for F2 is equal to the radius of the wheel, while the lever arm for F1 is zero. Why? Furthermore, torque is a vector and ...
New Phenomena: Recent Results and Prospects from the Fermilab
... – Math, Torque, Angular Momentum, Energy again, but more sophisticated – The material will not be on the 3rd exam, but will help with the exam. It will all be on the ...
... – Math, Torque, Angular Momentum, Energy again, but more sophisticated – The material will not be on the 3rd exam, but will help with the exam. It will all be on the ...
Document
... • If I keep increasing the pushing force, at some point the block moves this occurs when the push P exceeds the maximum static friction force. • When the block is moving it experiences a smaller friction force called the kinetic friction force • It is a common experience that it takes more force t ...
... • If I keep increasing the pushing force, at some point the block moves this occurs when the push P exceeds the maximum static friction force. • When the block is moving it experiences a smaller friction force called the kinetic friction force • It is a common experience that it takes more force t ...
Tutorial #6 Solutions
... From Newton’s third law, the downward force exerted on the air by the helicopter is equal and opposite to the upward force on the helicopter (the engine’s thrust). If we neglect air resistance, the thrust and gravity are the only vertical forces acting, so Newton’s second law for the helicopter (pos ...
... From Newton’s third law, the downward force exerted on the air by the helicopter is equal and opposite to the upward force on the helicopter (the engine’s thrust). If we neglect air resistance, the thrust and gravity are the only vertical forces acting, so Newton’s second law for the helicopter (pos ...
Velocity and Acceleration PowerPoint
... of motion involve similar changes. In fact, rarely does any object’s motion stay the same for very long. ...
... of motion involve similar changes. In fact, rarely does any object’s motion stay the same for very long. ...
Chapter 4
... that the bullet exerts on the rifle - yet the bullet gets a much greater acceleration than the rifle. How can this be?" ...
... that the bullet exerts on the rifle - yet the bullet gets a much greater acceleration than the rifle. How can this be?" ...
Laws of Motion PPT
... If the resultant force acting on an object is not zero, all the forces are said to be unbalanced. This forms the basis of Newton’s second law of motion, which states: If the forces on an object are unbalanced, two things about the object can change: the speed of the object may change – it may eith ...
... If the resultant force acting on an object is not zero, all the forces are said to be unbalanced. This forms the basis of Newton’s second law of motion, which states: If the forces on an object are unbalanced, two things about the object can change: the speed of the object may change – it may eith ...
analysing motion - s3.amazonaws.com
... opposite directions. These two forces balance each other. However, there is no force present to balance the force of friction. As the book moves to the right, friction acts to the left to slow the book down. This is an unbalanced force; and as such, the book changes its state of motion ...
... opposite directions. These two forces balance each other. However, there is no force present to balance the force of friction. As the book moves to the right, friction acts to the left to slow the book down. This is an unbalanced force; and as such, the book changes its state of motion ...