File - Carroll`s Cave of Knowledge
... A worker is pushing a 250 kg crate along level ground with a force of 1800 N. What is the coefficient of friction between the crate and the ground? ...
... A worker is pushing a 250 kg crate along level ground with a force of 1800 N. What is the coefficient of friction between the crate and the ground? ...
Newton`s Laws Review Sheet
... The big difference between going up a hill and going down is that when you go up a hill, the friction against your motion is pointing in the same direction as the parallel component of gravity instead of against it. First we reorient out frame of reference and break the force of gravity into compone ...
... The big difference between going up a hill and going down is that when you go up a hill, the friction against your motion is pointing in the same direction as the parallel component of gravity instead of against it. First we reorient out frame of reference and break the force of gravity into compone ...
Physics 100A Homework 5
... Insight: If the player were running faster, say, 8.0 m/s, a µk of 0.46 would result in a slide distance of 7.1 m, a quarter of the 27 m between the bases! He might very well overshoot the base and be tagged out. 6.12 A 45-kg crate is placed on an inclined ramp. When the angle the ramp makes with the ...
... Insight: If the player were running faster, say, 8.0 m/s, a µk of 0.46 would result in a slide distance of 7.1 m, a quarter of the 27 m between the bases! He might very well overshoot the base and be tagged out. 6.12 A 45-kg crate is placed on an inclined ramp. When the angle the ramp makes with the ...
8-23-10 Newtons laws template
... flat surface (since the normal force is less on a slope). • Increasing weight of an object increases the friction between the object and the surface it is resting on. • Weighting down a car over the drive wheels increases the friction between the drive wheels and the road (which increases the car’s ...
... flat surface (since the normal force is less on a slope). • Increasing weight of an object increases the friction between the object and the surface it is resting on. • Weighting down a car over the drive wheels increases the friction between the drive wheels and the road (which increases the car’s ...
Ppt
... A small block slides inside a hoop of radius r. The walls of the hoop are frictionless but the horizontal floor has a coefficient of sliding friction of m. The block’s initial velocity is v and is entirely tangential. How far, in angle around the circle does the block travel before coming to rest ? ...
... A small block slides inside a hoop of radius r. The walls of the hoop are frictionless but the horizontal floor has a coefficient of sliding friction of m. The block’s initial velocity is v and is entirely tangential. How far, in angle around the circle does the block travel before coming to rest ? ...
Chapter 5
... 2. Newton’s 2nd Law in component form. Now do forces in the x (r) direction: 3. ΣFx = mac = mv2/r. The only force in the x direction is the frictional force, therefore: fs = mv2/r ...
... 2. Newton’s 2nd Law in component form. Now do forces in the x (r) direction: 3. ΣFx = mac = mv2/r. The only force in the x direction is the frictional force, therefore: fs = mv2/r ...
Chapter 4 Problems
... Section 4.6 Forces of Friction 35. A dockworker loading crates on a ship finds that a 20-kg crate, initially at rest on a horizontal surface, requires a 75-N horizontal force to set it in motion. However, after the crate is in motion, a horizontal force of 60 N is required to keep it moving with a c ...
... Section 4.6 Forces of Friction 35. A dockworker loading crates on a ship finds that a 20-kg crate, initially at rest on a horizontal surface, requires a 75-N horizontal force to set it in motion. However, after the crate is in motion, a horizontal force of 60 N is required to keep it moving with a c ...
Friction Lab
... 6. Now let’s change one variable in this experiment. Do you think that changing the weight on the block will affect the force readings? ___________________________________________________ 7. Write a hypothesis for what you think will happen to the force reading as we add weight on the block. As the ...
... 6. Now let’s change one variable in this experiment. Do you think that changing the weight on the block will affect the force readings? ___________________________________________________ 7. Write a hypothesis for what you think will happen to the force reading as we add weight on the block. As the ...
Chapter 6 – Work and Kinetic Energy
... Example: A simple pendulum consists of a small ball of mass m suspended from a light string of length L. The mass is pulled to the side until the string makes and angle of with the vertical. The ball is released from this position and swings downward along an arc due to the pull of gravity. ...
... Example: A simple pendulum consists of a small ball of mass m suspended from a light string of length L. The mass is pulled to the side until the string makes and angle of with the vertical. The ball is released from this position and swings downward along an arc due to the pull of gravity. ...
Physics 110 Spring 2006 Work and Energy Problems
... 10. A projectile of mass 0.75kg is launched straight up in the air with an initial speed of 18m/s. a. How high would the projectile go if there were no air friction? b. If the projectile rises to a maximum height of 11.8m, what is the average force exerted on the projectile due to air resistance? a. ...
... 10. A projectile of mass 0.75kg is launched straight up in the air with an initial speed of 18m/s. a. How high would the projectile go if there were no air friction? b. If the projectile rises to a maximum height of 11.8m, what is the average force exerted on the projectile due to air resistance? a. ...
Chapter 4 Forces and Newton’s Laws of Motion continued
... A block with a weight of 15 N sits on a table. It is pushed down with a force of 11 N or pulled up with a force of 11 N. Calculate the normal force in each ...
... A block with a weight of 15 N sits on a table. It is pushed down with a force of 11 N or pulled up with a force of 11 N. Calculate the normal force in each ...
Unit 2D: Laws of Motion
... An object remains at rest or moves with uniform velocity unless it is acted upon by an unbalanced force. [Hard to prove this on earth because of all the forces such as gravity, friction, etc. Closest thing is an airhockey table. Ex. This law holds true in space.] This 1st Law is also called the “Law ...
... An object remains at rest or moves with uniform velocity unless it is acted upon by an unbalanced force. [Hard to prove this on earth because of all the forces such as gravity, friction, etc. Closest thing is an airhockey table. Ex. This law holds true in space.] This 1st Law is also called the “Law ...
HONORS PHYSICS Dynamics LESSON OBJECTIVES Students will
... 50. How much force is needed to accelerate a 68 kilogram-skier at a rate of 1.2 m/sec2? 51. What is the mass of an object that requires a force of 30 N to accelerate at a rate of 5 m/sec2? 52. What is the force on a 1,000 kilogram-elevator that is falling freely under the acceleration of gravity on ...
... 50. How much force is needed to accelerate a 68 kilogram-skier at a rate of 1.2 m/sec2? 51. What is the mass of an object that requires a force of 30 N to accelerate at a rate of 5 m/sec2? 52. What is the force on a 1,000 kilogram-elevator that is falling freely under the acceleration of gravity on ...
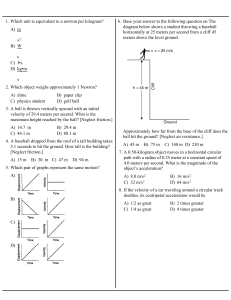
A) m s2 B) W s C) J•s D) kg•ms 1. Which unit is
... the forces acting on a planet, investigators calculated the orbit of each planet. A small discrepancy between the calculated orbit and the observed orbit of the planet Uranus was noted. It appeared that the sum of the forces on Uranus did not equal its mass times its acceleration, unless there ...
... the forces acting on a planet, investigators calculated the orbit of each planet. A small discrepancy between the calculated orbit and the observed orbit of the planet Uranus was noted. It appeared that the sum of the forces on Uranus did not equal its mass times its acceleration, unless there ...
PowerPoints
... • Mass is a property of objects, producing a reluctance to accelerate, called inertia • Velocity refers to both speed and direction • Acceleration means a change in velocity (either magnitude, or direction or both) • If an object is accelerating, it is being acted upon by a force, and F = ma. No ...
... • Mass is a property of objects, producing a reluctance to accelerate, called inertia • Velocity refers to both speed and direction • Acceleration means a change in velocity (either magnitude, or direction or both) • If an object is accelerating, it is being acted upon by a force, and F = ma. No ...