Chapter 10
... • When the horizontal push force exceeds the maximum force of static friction, the brick will accelerate. • The friction force exerted by the surfaces when they move relative to each other is call kinetic friction, which is caused by transient microscopic bonds between the two surfaces. ...
... • When the horizontal push force exceeds the maximum force of static friction, the brick will accelerate. • The friction force exerted by the surfaces when they move relative to each other is call kinetic friction, which is caused by transient microscopic bonds between the two surfaces. ...
FORCE and MOTION
... can be so small you can’t see them. These bumps and scrapes are called irregularities. Friction is caused by these irregularities getting caught on each other as two surfaces rub together. Some things like glass and ice don’t have many irregularities to get caught on, so there is little friction. Wi ...
... can be so small you can’t see them. These bumps and scrapes are called irregularities. Friction is caused by these irregularities getting caught on each other as two surfaces rub together. Some things like glass and ice don’t have many irregularities to get caught on, so there is little friction. Wi ...
lecture1423904717
... The force which opposes the movement or the tendency of movement is called Frictional force or simply friction. It is due to the resistance to motion offered by minutely projecting particles at the contact surfaces. However, there is a limit beyond which the magnitude of this force cannot increase. ...
... The force which opposes the movement or the tendency of movement is called Frictional force or simply friction. It is due to the resistance to motion offered by minutely projecting particles at the contact surfaces. However, there is a limit beyond which the magnitude of this force cannot increase. ...
Test Review Slides - University of Mount Union
... Draw picture/sketch of what is going on (object, ropes, surfaces) Draw free-body diagrams using all the forces (contact & long-range) acting on object at a common point, then identify the net force. Choose direction of axis (tilted for ramp problems) Decompose vectors into components (magnitude and ...
... Draw picture/sketch of what is going on (object, ropes, surfaces) Draw free-body diagrams using all the forces (contact & long-range) acting on object at a common point, then identify the net force. Choose direction of axis (tilted for ramp problems) Decompose vectors into components (magnitude and ...
Chapter 5 Newton`s Laws of Motion
... hemispheres fell apart when air was readmitted. Suppose von Guricke had tied both teams of horses to one side and bolted the other side to a heavy tree trunk. In this case, the tension on the hemispheres would be A) twice B) exactly the same as ...
... hemispheres fell apart when air was readmitted. Suppose von Guricke had tied both teams of horses to one side and bolted the other side to a heavy tree trunk. In this case, the tension on the hemispheres would be A) twice B) exactly the same as ...
Document
... 2. Can an object with zero net force acting on it be moving? Explain. 3. Discuss how an object’s acceleration relates to the direction of its movement. 4. A box is placed on a table. Describe the action-reaction forces between the box and the table, the box and the earth’s gravitational field, and t ...
... 2. Can an object with zero net force acting on it be moving? Explain. 3. Discuss how an object’s acceleration relates to the direction of its movement. 4. A box is placed on a table. Describe the action-reaction forces between the box and the table, the box and the earth’s gravitational field, and t ...
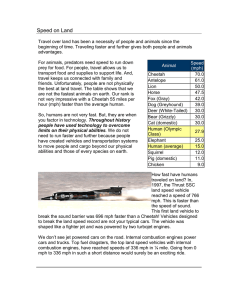
Speed on Land - Lake Mills Area School District
... overcoming these problems. Fuel cells produce electricity from hydrogen and oxygen. The byproduct is water so they are pollution free. At this time they are too expensive for mass production, but the future is promising. Hybrid vehicles have been seeing a commercial success. These vehicles are gas a ...
... overcoming these problems. Fuel cells produce electricity from hydrogen and oxygen. The byproduct is water so they are pollution free. At this time they are too expensive for mass production, but the future is promising. Hybrid vehicles have been seeing a commercial success. These vehicles are gas a ...
Newton`s First Law of Motion
... • Galileo understood that an object in constant motion is as natural as an object at rest. • It was usually friction that made moving objects slow down and eventually come to a stop. ...
... • Galileo understood that an object in constant motion is as natural as an object at rest. • It was usually friction that made moving objects slow down and eventually come to a stop. ...
Packet #2 Why Do Objects Move?
... • The law of universal gravitation states that all objects in the universe are attracted to one another because of the force of gravity between them. • The amount of gravitational force between two objects depends on the mass of each object. • The force of gravity between two objects decreases as th ...
... • The law of universal gravitation states that all objects in the universe are attracted to one another because of the force of gravity between them. • The amount of gravitational force between two objects depends on the mass of each object. • The force of gravity between two objects decreases as th ...
Force - Kuropas 7-4 science
... • Take test home and have parents sign in order to take retest on Wednesday in ...
... • Take test home and have parents sign in order to take retest on Wednesday in ...
Assessing to Learn in the Classroom Sample Questions
... forces acting on an object. This problem provides an opportunity to practice that skill and to consider some of the ambiguities and points of confusion that can arise. Discussion: The question has many defensible answers. What matters is not which answer you pick, but the validity of your reasoning. ...
... forces acting on an object. This problem provides an opportunity to practice that skill and to consider some of the ambiguities and points of confusion that can arise. Discussion: The question has many defensible answers. What matters is not which answer you pick, but the validity of your reasoning. ...
Lab3_Friction (donot print)
... Introduction: Have you ever noticed how it is harder to start an object sliding across a surface than it is to keep the object sliding? When a block rests on a table there is, literally, some kind of bonding going on between the block and the table. To start the object moving you must apply a horizo ...
... Introduction: Have you ever noticed how it is harder to start an object sliding across a surface than it is to keep the object sliding? When a block rests on a table there is, literally, some kind of bonding going on between the block and the table. To start the object moving you must apply a horizo ...
net force - s3.amazonaws.com
... • Equilibrium is the state in which the net force on an object is zero. • Objects that are either at rest or moving with constant velocity are said to be in equilibrium. • Newton’s first law describes objects in equilibrium. Tip: To determine whether a body is in equilibrium, find the net force. If ...
... • Equilibrium is the state in which the net force on an object is zero. • Objects that are either at rest or moving with constant velocity are said to be in equilibrium. • Newton’s first law describes objects in equilibrium. Tip: To determine whether a body is in equilibrium, find the net force. If ...
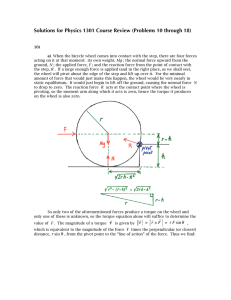
Solutions for Physics 1301 Course Review (Problems 10 through 18)
... Notice that the moment of inertia, I , of the wheel does not enter into the calculation for F . This indicates that the applied force required would be the same if the wheel were a uniform solid disk of the same mass and radius. b) The force F is applied at a height h above the floor along a vertica ...
... Notice that the moment of inertia, I , of the wheel does not enter into the calculation for F . This indicates that the applied force required would be the same if the wheel were a uniform solid disk of the same mass and radius. b) The force F is applied at a height h above the floor along a vertica ...
F w - Lyndhurst Schools
... When you stand still on the floor, your weight force of gravity is equal and opposite to the normal force the floor exerts on you. Explain whether this is an action/reaction pair. It is NOT! Both forces act on the same object (you). Action/reaction pairs sound like this: “A pushes B, so B pushes A”. ...
... When you stand still on the floor, your weight force of gravity is equal and opposite to the normal force the floor exerts on you. Explain whether this is an action/reaction pair. It is NOT! Both forces act on the same object (you). Action/reaction pairs sound like this: “A pushes B, so B pushes A”. ...
File
... drive the same distance at an average speed of only 70 KPH. How much longer does the trip take? 2. A car is stopped at a traffic light. If then travels along straight road so that its distance from the light is given by x(t ) bt 2 ct 3 , where b=2.40 m/s2 and c=0.120 m/s3. a) Calculate the avera ...
... drive the same distance at an average speed of only 70 KPH. How much longer does the trip take? 2. A car is stopped at a traffic light. If then travels along straight road so that its distance from the light is given by x(t ) bt 2 ct 3 , where b=2.40 m/s2 and c=0.120 m/s3. a) Calculate the avera ...