Name - TeacherWeb
... Explain how the use of the brakes changes the motion of the bicycle. How does the mass of the bicycle affect the force that needs to be applied to the brakes? (3 points) ...
... Explain how the use of the brakes changes the motion of the bicycle. How does the mass of the bicycle affect the force that needs to be applied to the brakes? (3 points) ...
Circular Motion
... An imaginary line drawn from the center of the sun to the center of the planet will sweep out equal areas in equal intervals of time Law of Harmonies The ratios of the squares of the periods of any two planets is equal to the ratio of the cubes of their average distances from the sun. ...
... An imaginary line drawn from the center of the sun to the center of the planet will sweep out equal areas in equal intervals of time Law of Harmonies The ratios of the squares of the periods of any two planets is equal to the ratio of the cubes of their average distances from the sun. ...
1. What is the weight of a 200 kg object? 2. A woman - IES Al
... is the acceleration of the basket? 3. A 20.0 kg mass is pulled by along a surface by a horizontal force of 100 N. Friction is 20.0 N. What is the acceleration of the mass? 4. A 49-N block is pulled by a horizontal force of 50.0 N along a rough horizontal surface at a constant acceleration of 6 m/s/s ...
... is the acceleration of the basket? 3. A 20.0 kg mass is pulled by along a surface by a horizontal force of 100 N. Friction is 20.0 N. What is the acceleration of the mass? 4. A 49-N block is pulled by a horizontal force of 50.0 N along a rough horizontal surface at a constant acceleration of 6 m/s/s ...
Experiment description Microgravity
... For some experiments, 15 min of weightlessness are not enough. Another possibility for extending the length of time is orbiting a planet. Centrifugal force, which we know from merry-go-rounds, pushes us outwards while we spin around (this force is also connected to inertia). Any object circling eart ...
... For some experiments, 15 min of weightlessness are not enough. Another possibility for extending the length of time is orbiting a planet. Centrifugal force, which we know from merry-go-rounds, pushes us outwards while we spin around (this force is also connected to inertia). Any object circling eart ...
1. A good, professional baseball pitcher throws a ball straight up in
... 2. An object is moving in such a way that the force of gravity is increasing its kinetic energy. You can conclude that 1. the object is falling freely 2. there is a net force on the object 3. both A and B ...
... 2. An object is moving in such a way that the force of gravity is increasing its kinetic energy. You can conclude that 1. the object is falling freely 2. there is a net force on the object 3. both A and B ...
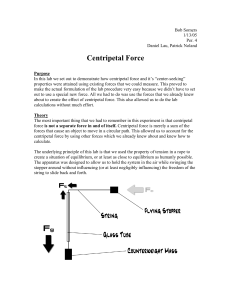
Centripetal Force
... excellent way to demonstrate circular motion and how forces can cooperate to make an object move in a circular path. Simply the fact that such large masses are able to “defy gravity” (when in all truth, they are not defying gravity at all) is a visual signal that something unseen is acting upon the ...
... excellent way to demonstrate circular motion and how forces can cooperate to make an object move in a circular path. Simply the fact that such large masses are able to “defy gravity” (when in all truth, they are not defying gravity at all) is a visual signal that something unseen is acting upon the ...
Artificial gravity

Artificial gravity is the theoretical increase or decrease of apparent gravity (g-force) by artificial means, particularly in space, but also on Earth. It can be practically achieved by the use of different forces, particularly the centripetal force and linear acceleration.The creation of artificial gravity is considered desirable for long-term space travel or habitation, for ease of mobility, for in-space fluid management, and to avoid the adverse long-term health effects of weightlessness.A number of methods for generating artificial gravity have been proposed, as well as an even larger number of science fiction approaches using both real and fictitious forces. Practical outer space applications of artificial gravity for humans have not yet been built and flown, principally due to the large size of the spacecraft required to produce centripetal acceleration.