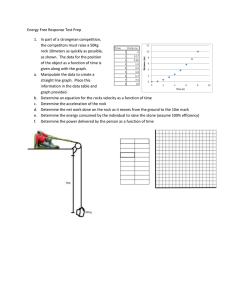
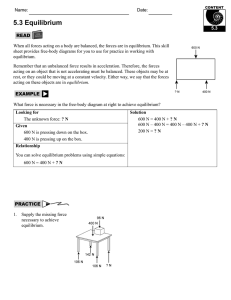
Name
... Which force will change? Which force remains the same? If the upwards acceleration is 3 m/s2, then what is the magnitude of each force? ...
... Which force will change? Which force remains the same? If the upwards acceleration is 3 m/s2, then what is the magnitude of each force? ...
Preview of Period 3: Motion and Forces
... cart demonstrated in class to accelerate? R.3 What can happen to the motion of an object when two forces act on it in opposite directions? R.4 What causes falling objects to accelerate? Which falls at a faster rate – a sheet of paper slightly crumpled or a sheet crumpled into a tight ball? Why? R.5 ...
... cart demonstrated in class to accelerate? R.3 What can happen to the motion of an object when two forces act on it in opposite directions? R.4 What causes falling objects to accelerate? Which falls at a faster rate – a sheet of paper slightly crumpled or a sheet crumpled into a tight ball? Why? R.5 ...
What Is a Force?
... downward, whereas air resistance acts in the direction opposite to the motion and reduces acceleration. ...
... downward, whereas air resistance acts in the direction opposite to the motion and reduces acceleration. ...
Electric Fields - University High School
... b. The rotational speed of the ball of gas increased. c. The increased momentum caused wider paths about the ...
... b. The rotational speed of the ball of gas increased. c. The increased momentum caused wider paths about the ...
Relative Motion - Joel K. Ness, PhD
... If the boy slides down at a constant speed of 2 m/s, can we find the frictional force acting on him? ...
... If the boy slides down at a constant speed of 2 m/s, can we find the frictional force acting on him? ...
Weightlessness

Weightlessness, or an absence of 'weight', is an absence of stress and strain resulting from externally applied mechanical contact-forces, typically normal forces from floors, seats, beds, scales, and the like. Counterintuitively, a uniform gravitational field does not by itself cause stress or strain, and a body in free fall in such an environment experiences no g-force acceleration and feels weightless. This is also termed ""zero-g"" where the term is more correctly understood as meaning ""zero g-force.""When bodies are acted upon by non-gravitational forces, as in a centrifuge, a rotating space station, or within a space ship with rockets firing, a sensation of weight is produced, as the contact forces from the moving structure act to overcome the body's inertia. In such cases, a sensation of weight, in the sense of a state of stress can occur, even if the gravitational field was zero. In such cases, g-forces are felt, and bodies are not weightless.When the gravitational field is non-uniform, a body in free fall suffers tidal effects and is not stress-free. Near a black hole, such tidal effects can be very strong. In the case of the Earth, the effects are minor, especially on objects of relatively small dimension (such as the human body or a spacecraft) and the overall sensation of weightlessness in these cases is preserved. This condition is known as microgravity and it prevails in orbiting spacecraft.