Millikan Oil Drop Experiment
... 1. Incorporate the corrections for Stokes’ law, the buoyant force and the viscosity of air into Equation 4, 5 and 6. Are all the corrections necessary? Estimate a value for the mean free path, L, by assuming equidistant molecules in a given volume (e.g. 1mol in 22.4l). 2. If the oil density is (0.89 ...
... 1. Incorporate the corrections for Stokes’ law, the buoyant force and the viscosity of air into Equation 4, 5 and 6. Are all the corrections necessary? Estimate a value for the mean free path, L, by assuming equidistant molecules in a given volume (e.g. 1mol in 22.4l). 2. If the oil density is (0.89 ...
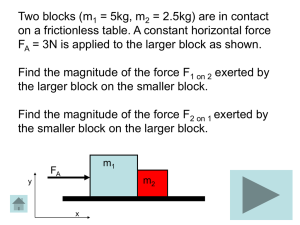
Momentum can be defined as "mass in motion
... greater mass of the Mack truck gives it a considerably greater momentum. Yet if the Mack truck were at rest, then the momentum of the least massive roller skate would be the greatest; for the momentum of any object which is at rest is 0. Objects at rest do not have momentum - they do not have any "m ...
... greater mass of the Mack truck gives it a considerably greater momentum. Yet if the Mack truck were at rest, then the momentum of the least massive roller skate would be the greatest; for the momentum of any object which is at rest is 0. Objects at rest do not have momentum - they do not have any "m ...
Introductory_Physics_Notes_May_1_2008.doc
... These notes have been compiled in order to summarize the core concepts, definitions, terms, equations, and relationships for an introductory Physics course. My objective is to provide the student with an outline of the very essentials which are to serve as a guide to my lectures and any of the very ...
... These notes have been compiled in order to summarize the core concepts, definitions, terms, equations, and relationships for an introductory Physics course. My objective is to provide the student with an outline of the very essentials which are to serve as a guide to my lectures and any of the very ...
Doris williams - HCC Learning Web
... In general, friction is the force that slows down the motion of an object. The force of friction is directed along the surface of contact between the object and surface and directed opposite to the direction of motion of object. We deal with: a) Static friction ( fs) This exists when the object is a ...
... In general, friction is the force that slows down the motion of an object. The force of friction is directed along the surface of contact between the object and surface and directed opposite to the direction of motion of object. We deal with: a) Static friction ( fs) This exists when the object is a ...
Electromagnetism - Harvard University Department of Physics
... Dielectric constant ε depends on the density Gases very close to 1 Liquids and solids 2 to 10 ...
... Dielectric constant ε depends on the density Gases very close to 1 Liquids and solids 2 to 10 ...
Weightlessness

Weightlessness, or an absence of 'weight', is an absence of stress and strain resulting from externally applied mechanical contact-forces, typically normal forces from floors, seats, beds, scales, and the like. Counterintuitively, a uniform gravitational field does not by itself cause stress or strain, and a body in free fall in such an environment experiences no g-force acceleration and feels weightless. This is also termed ""zero-g"" where the term is more correctly understood as meaning ""zero g-force.""When bodies are acted upon by non-gravitational forces, as in a centrifuge, a rotating space station, or within a space ship with rockets firing, a sensation of weight is produced, as the contact forces from the moving structure act to overcome the body's inertia. In such cases, a sensation of weight, in the sense of a state of stress can occur, even if the gravitational field was zero. In such cases, g-forces are felt, and bodies are not weightless.When the gravitational field is non-uniform, a body in free fall suffers tidal effects and is not stress-free. Near a black hole, such tidal effects can be very strong. In the case of the Earth, the effects are minor, especially on objects of relatively small dimension (such as the human body or a spacecraft) and the overall sensation of weightlessness in these cases is preserved. This condition is known as microgravity and it prevails in orbiting spacecraft.