Electrostatics 12
... 2. Any excess charge on an isolated conductor resides entirely on the outside surface of the conductor. 3. The electric field just outside the charged conductor is perpendicular to the conductor’s surface. 4. On an irregularly shaped conductor, charge tends to accumulate where the radius of curvatur ...
... 2. Any excess charge on an isolated conductor resides entirely on the outside surface of the conductor. 3. The electric field just outside the charged conductor is perpendicular to the conductor’s surface. 4. On an irregularly shaped conductor, charge tends to accumulate where the radius of curvatur ...
Chapter 15
... – It is inversely proportional to the square of the separation between the two particles and is along the line joining them – It is proportional to the product of the magnitudes of the charges q1 and q2 on the two particles – It is attractive if the charges are of opposite signs and repulsive if the ...
... – It is inversely proportional to the square of the separation between the two particles and is along the line joining them – It is proportional to the product of the magnitudes of the charges q1 and q2 on the two particles – It is attractive if the charges are of opposite signs and repulsive if the ...
Electric Field
... Infinite (i.e.”large”) uniformly charged sheet Non-conductor, fixed surface charge density Infinite sheet d<
... Infinite (i.e.”large”) uniformly charged sheet Non-conductor, fixed surface charge density Infinite sheet d<
Composition and Resolution of Forces
... around the edge, a wide variety of concurrent forces may be obtained at almost any angle between the strings. Tensions are the forces produced in the strings by the suspended weights. The suspended weights are not subject to accelerated motions, so the force (or tension) in each string is equal to t ...
... around the edge, a wide variety of concurrent forces may be obtained at almost any angle between the strings. Tensions are the forces produced in the strings by the suspended weights. The suspended weights are not subject to accelerated motions, so the force (or tension) in each string is equal to t ...
Physics - Pakchoicez.com
... The collision between the two bodies is the __________ if total momentum as well as the kinetic energy of the system remain the same. ...
... The collision between the two bodies is the __________ if total momentum as well as the kinetic energy of the system remain the same. ...
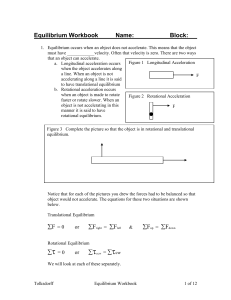
Equilibrium Workbook
... c. The longer the wrench you use the greater the radius and the greater the torque. Torque is the value that makes something turn. A small force can act with a large radius to create significant torque. Your teacher will ask for a volunteer to hold a 1 kg mass using a meter stick. What do you Tolksd ...
... c. The longer the wrench you use the greater the radius and the greater the torque. Torque is the value that makes something turn. A small force can act with a large radius to create significant torque. Your teacher will ask for a volunteer to hold a 1 kg mass using a meter stick. What do you Tolksd ...
Weightlessness

Weightlessness, or an absence of 'weight', is an absence of stress and strain resulting from externally applied mechanical contact-forces, typically normal forces from floors, seats, beds, scales, and the like. Counterintuitively, a uniform gravitational field does not by itself cause stress or strain, and a body in free fall in such an environment experiences no g-force acceleration and feels weightless. This is also termed ""zero-g"" where the term is more correctly understood as meaning ""zero g-force.""When bodies are acted upon by non-gravitational forces, as in a centrifuge, a rotating space station, or within a space ship with rockets firing, a sensation of weight is produced, as the contact forces from the moving structure act to overcome the body's inertia. In such cases, a sensation of weight, in the sense of a state of stress can occur, even if the gravitational field was zero. In such cases, g-forces are felt, and bodies are not weightless.When the gravitational field is non-uniform, a body in free fall suffers tidal effects and is not stress-free. Near a black hole, such tidal effects can be very strong. In the case of the Earth, the effects are minor, especially on objects of relatively small dimension (such as the human body or a spacecraft) and the overall sensation of weightlessness in these cases is preserved. This condition is known as microgravity and it prevails in orbiting spacecraft.