Stationary charge
... A positive electric charge of negligible weight is released from rest between the poles of horseshoe magnet. What should be the direction of the acceleration of the charge caused by the magnetic field? Answer You don’t say if the magnet is in a gravitational field or not. However since the force on ...
... A positive electric charge of negligible weight is released from rest between the poles of horseshoe magnet. What should be the direction of the acceleration of the charge caused by the magnetic field? Answer You don’t say if the magnet is in a gravitational field or not. However since the force on ...
(Honors Physics) Universal Law of Gravitation
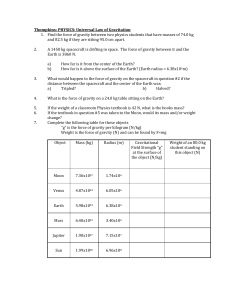
... If the weight of a classroom Physics textbook is 42 N, what is the books mass? If the textbook in question #5 was taken to the Moon, would its mass and/or weight change? Complete the following table for these objects “g” is the force of gravity per kilogram (N/kg) Weight is the force of gravity (N) ...
... If the weight of a classroom Physics textbook is 42 N, what is the books mass? If the textbook in question #5 was taken to the Moon, would its mass and/or weight change? Complete the following table for these objects “g” is the force of gravity per kilogram (N/kg) Weight is the force of gravity (N) ...
Learning Targets for Newton`s Laws I can… 1. Define inertia 2
... 6. Distinguish the difference between mass and weight, one being a force and another being a scalar 7. Using Newton’s 2nd Law, calculate the weight of an object. 8. Define applied force, gravitational force, normal force, tension force, and friction force. 9. Identify the forces of tension, gravity, ...
... 6. Distinguish the difference between mass and weight, one being a force and another being a scalar 7. Using Newton’s 2nd Law, calculate the weight of an object. 8. Define applied force, gravitational force, normal force, tension force, and friction force. 9. Identify the forces of tension, gravity, ...
Study Guide For Unit 3 Test
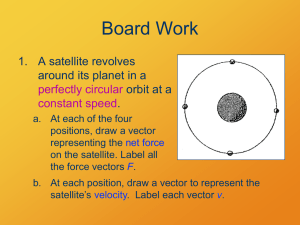
... If an object's velocity is not changing, the sum of the forces on the object is zero. If an object's velocity is changing, the sum of the forces on the object is not zero. This non-zero sum of forces is referred to as the “net force.” RECALL: Dry ice demo Newton’s 3rd law of motion Pairs o ...
... If an object's velocity is not changing, the sum of the forces on the object is zero. If an object's velocity is changing, the sum of the forces on the object is not zero. This non-zero sum of forces is referred to as the “net force.” RECALL: Dry ice demo Newton’s 3rd law of motion Pairs o ...
Universal Gravitation
... Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation states that gravity is universal and that all objects attract each other with some force of gravitational attraction ...
... Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation states that gravity is universal and that all objects attract each other with some force of gravitational attraction ...
Weightlessness

Weightlessness, or an absence of 'weight', is an absence of stress and strain resulting from externally applied mechanical contact-forces, typically normal forces from floors, seats, beds, scales, and the like. Counterintuitively, a uniform gravitational field does not by itself cause stress or strain, and a body in free fall in such an environment experiences no g-force acceleration and feels weightless. This is also termed ""zero-g"" where the term is more correctly understood as meaning ""zero g-force.""When bodies are acted upon by non-gravitational forces, as in a centrifuge, a rotating space station, or within a space ship with rockets firing, a sensation of weight is produced, as the contact forces from the moving structure act to overcome the body's inertia. In such cases, a sensation of weight, in the sense of a state of stress can occur, even if the gravitational field was zero. In such cases, g-forces are felt, and bodies are not weightless.When the gravitational field is non-uniform, a body in free fall suffers tidal effects and is not stress-free. Near a black hole, such tidal effects can be very strong. In the case of the Earth, the effects are minor, especially on objects of relatively small dimension (such as the human body or a spacecraft) and the overall sensation of weightlessness in these cases is preserved. This condition is known as microgravity and it prevails in orbiting spacecraft.