479KB - NZQA
... • Since change in momentum is the same. OR • Rubber bumpers move a distance when compressed, • so for the same amount of work done or energy changed, or the same change in velocity, acceleration is decreased due to longer time • less force is used. ...
... • Since change in momentum is the same. OR • Rubber bumpers move a distance when compressed, • so for the same amount of work done or energy changed, or the same change in velocity, acceleration is decreased due to longer time • less force is used. ...
Tue Sep 21
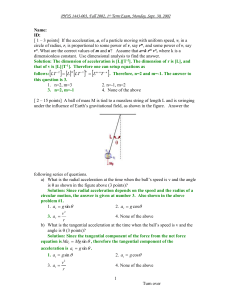
... Four identical particles of mass 0.50 kg each are placed at the vertices of a 2.0 m 2.0 m square and held there by four massless rods, which form the sides of the square. What is the rotational inertia of this rigid body about an axis that (a) passes through the center of mass, the midpoints of oppo ...
... Four identical particles of mass 0.50 kg each are placed at the vertices of a 2.0 m 2.0 m square and held there by four massless rods, which form the sides of the square. What is the rotational inertia of this rigid body about an axis that (a) passes through the center of mass, the midpoints of oppo ...
Exam #: Printed Name: Signature: PHYSICS DEPARTMENT
... d) In the special case that m = M , calculate the angular velocity around the center of mass after the collision. ...
... d) In the special case that m = M , calculate the angular velocity around the center of mass after the collision. ...
Physics of Ballet Dancing
... perpendicular to the floor (also called the normal force) will give the force of friction which acts against the motion of the dancer. Friction is very important in dancing. To increase friction many ballet dancers use a substance called Rosin. Rosin has a high coefficient of kinetic friction but a ...
... perpendicular to the floor (also called the normal force) will give the force of friction which acts against the motion of the dancer. Friction is very important in dancing. To increase friction many ballet dancers use a substance called Rosin. Rosin has a high coefficient of kinetic friction but a ...
Physics 122 – Review Sheets
... What is the gravitational field strength at a point in the Earth’s gravitational field where a 10.0 kg mass weighs 85.0 N? (8.50 m/s2) ...
... What is the gravitational field strength at a point in the Earth’s gravitational field where a 10.0 kg mass weighs 85.0 N? (8.50 m/s2) ...
A body acted on by no net force moves with constant velocity
... A small block, mass 2kg, rests on top of a larger block, mass 20 kg. The coefficient of friction between the blocks is 0.25. If the larger block is on a frictionless table, what is the largest horizontal force that can be applied to it without ...
... A small block, mass 2kg, rests on top of a larger block, mass 20 kg. The coefficient of friction between the blocks is 0.25. If the larger block is on a frictionless table, what is the largest horizontal force that can be applied to it without ...
Aim: More friction
... Aim: More friction Do Now: Why do objects at rest have more friction than objects in motion? ...
... Aim: More friction Do Now: Why do objects at rest have more friction than objects in motion? ...
Document
... 1) At the start of his jump the air resistance is _______ so he _______ downwards. 2) As his speed increases his air resistance will _______ 3) Eventually the air resistance will be big enough to _______ the skydiver’s weight. At this point the forces are balanced so his speed becomes ________ - thi ...
... 1) At the start of his jump the air resistance is _______ so he _______ downwards. 2) As his speed increases his air resistance will _______ 3) Eventually the air resistance will be big enough to _______ the skydiver’s weight. At this point the forces are balanced so his speed becomes ________ - thi ...
PHY231 Review
... FE-3. If an object is moving can you conclude there are forces acting on it? If an object is at rest, can you conclude there are no forces acting on it? Consider each of the following situations. In which one of the following cases, if any, are there no forces acting on the object? a) A bolt that c ...
... FE-3. If an object is moving can you conclude there are forces acting on it? If an object is at rest, can you conclude there are no forces acting on it? Consider each of the following situations. In which one of the following cases, if any, are there no forces acting on the object? a) A bolt that c ...
Comprehensive Final Exam Review 2014
... a) How much is the force of gravity pulling the mass down the plane? b) What is the force of static friction? c) What is the force of kinetic friction? d) What is the resulting acceleration? e) If there was no friction, what would the acceleration be? f) The inclined plane is 4.5 m long and sits dir ...
... a) How much is the force of gravity pulling the mass down the plane? b) What is the force of static friction? c) What is the force of kinetic friction? d) What is the resulting acceleration? e) If there was no friction, what would the acceleration be? f) The inclined plane is 4.5 m long and sits dir ...
Weightlessness

Weightlessness, or an absence of 'weight', is an absence of stress and strain resulting from externally applied mechanical contact-forces, typically normal forces from floors, seats, beds, scales, and the like. Counterintuitively, a uniform gravitational field does not by itself cause stress or strain, and a body in free fall in such an environment experiences no g-force acceleration and feels weightless. This is also termed ""zero-g"" where the term is more correctly understood as meaning ""zero g-force.""When bodies are acted upon by non-gravitational forces, as in a centrifuge, a rotating space station, or within a space ship with rockets firing, a sensation of weight is produced, as the contact forces from the moving structure act to overcome the body's inertia. In such cases, a sensation of weight, in the sense of a state of stress can occur, even if the gravitational field was zero. In such cases, g-forces are felt, and bodies are not weightless.When the gravitational field is non-uniform, a body in free fall suffers tidal effects and is not stress-free. Near a black hole, such tidal effects can be very strong. In the case of the Earth, the effects are minor, especially on objects of relatively small dimension (such as the human body or a spacecraft) and the overall sensation of weightlessness in these cases is preserved. This condition is known as microgravity and it prevails in orbiting spacecraft.