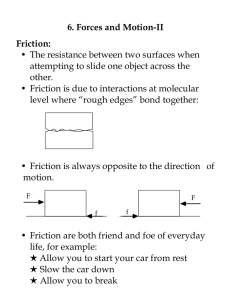
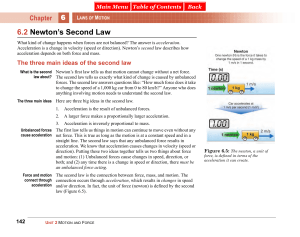
What Is a Force?
... • Fluid friction opposes the motion of an object through a fluid. • Fluid friction acting on an object moving through the air is known as air resistance. • Fluid friction increases as the speed of the object moving through the fluid increases. ...
... • Fluid friction opposes the motion of an object through a fluid. • Fluid friction acting on an object moving through the air is known as air resistance. • Fluid friction increases as the speed of the object moving through the fluid increases. ...
Lecture-1 - IIT Guwahati
... Although forces cannot be seen or directly observed, we are familiar with their effect. In Statics, bodies at rest are investigated. E.g. To prevent a stone from falling, to keep it in equilibrium, we need to exert a force on it, for example our muscle force. In other words: A force is a physical qu ...
... Although forces cannot be seen or directly observed, we are familiar with their effect. In Statics, bodies at rest are investigated. E.g. To prevent a stone from falling, to keep it in equilibrium, we need to exert a force on it, for example our muscle force. In other words: A force is a physical qu ...
9 Torque
... 1. Weigh the meter stick you use. Record the mass and estimate the uncertainty. 2. Set up the meter stick and force sensors as shown in Figure 9.1. The meter stick will be suspended from a beam via the two force sensors. (These will also be used to determine the upward vertical forces at these posit ...
... 1. Weigh the meter stick you use. Record the mass and estimate the uncertainty. 2. Set up the meter stick and force sensors as shown in Figure 9.1. The meter stick will be suspended from a beam via the two force sensors. (These will also be used to determine the upward vertical forces at these posit ...
UNIFORM CIRCULAR MOTION Rotational Motion
... • Yo-yo swings in a circle it accelerates, because its velocity is constantly changing direction • In order to have centripetal acceleration there must be a force present on the Yo-yo • Force that causes centripetal acceleration points in the same direction as the centripetal acceleration Toward ...
... • Yo-yo swings in a circle it accelerates, because its velocity is constantly changing direction • In order to have centripetal acceleration there must be a force present on the Yo-yo • Force that causes centripetal acceleration points in the same direction as the centripetal acceleration Toward ...
Lecture7_Wheels
... If this involves speeds over 5-10 mph, both vehicles will sustain damage. Which one “feels” or experiences the force of impact? The cue ball loses its energy in this head-on collision. The force of the impact pushes back in stopping it. ...
... If this involves speeds over 5-10 mph, both vehicles will sustain damage. Which one “feels” or experiences the force of impact? The cue ball loses its energy in this head-on collision. The force of the impact pushes back in stopping it. ...
CHEM-UA 127: Advanced General Chemistry I
... for their being fundamental particles. If they are fundamental charged particles, then they should have a well defined mass and charge. In this second part of the experiment, the specific trajectory followed by the particle will be used to determine the ratio of the charge to the mass of the particl ...
... for their being fundamental particles. If they are fundamental charged particles, then they should have a well defined mass and charge. In this second part of the experiment, the specific trajectory followed by the particle will be used to determine the ratio of the charge to the mass of the particl ...
Friday`s Slides
... forces of equal magnitude, and , are exerted on it. Think about the work done by each force and the net work. Is the magnitude of the velocity of the object at point B greater than, less than, or equal to the velocity of the object at point A? Explain how you can tell. A B C D ...
... forces of equal magnitude, and , are exerted on it. Think about the work done by each force and the net work. Is the magnitude of the velocity of the object at point B greater than, less than, or equal to the velocity of the object at point A? Explain how you can tell. A B C D ...
DAY ONE - Rutgers Physics
... ω02 )(ω 2 − 2ω02 ) = 0, where ω0 = g/R. Thus the normal frequencies are ω12 = 12 ω02 and ω22 = 2ω02 . There are thus two normal modes: K − ω 2 M )aa = 0, we find a1 = a2 . Here Mode 1: Substituting ω = ω1 into (K the two angles oscillate in phase with equal amplitude, and the bead does not slide rel ...
... ω02 )(ω 2 − 2ω02 ) = 0, where ω0 = g/R. Thus the normal frequencies are ω12 = 12 ω02 and ω22 = 2ω02 . There are thus two normal modes: K − ω 2 M )aa = 0, we find a1 = a2 . Here Mode 1: Substituting ω = ω1 into (K the two angles oscillate in phase with equal amplitude, and the bead does not slide rel ...
Forces and the Laws of Motion
... – A single vector can be resolved into two or more components that have the same effect. Fx = F.cosq F ...
... – A single vector can be resolved into two or more components that have the same effect. Fx = F.cosq F ...