Motion and Forces
... Gravitational force is determined by the distance between the two masses. Everything falls at an acceleration of 9.8 m/s2 in the absence of air resistance Gravity is opposed by air resistance ...
... Gravitational force is determined by the distance between the two masses. Everything falls at an acceleration of 9.8 m/s2 in the absence of air resistance Gravity is opposed by air resistance ...
Classical Mechanics
... Apply Newton’s Laws separately to each object The magnitude of the acceleration of both objects will be the ...
... Apply Newton’s Laws separately to each object The magnitude of the acceleration of both objects will be the ...
8th PS 9-Weeks 3 Exam
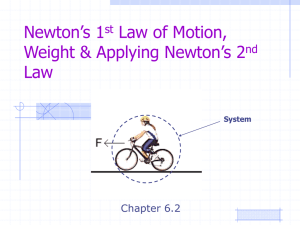
... According to Newton's second law of motion, ____. a. F = m a c. F = p a b. F = m v d. F = p v Newton's first law of motion is also called the law of ____. a. mass c. force b. inertia d. constant velocity The statement "to every action there is an equal and opposite reaction" is ____. a. the ...
... According to Newton's second law of motion, ____. a. F = m a c. F = p a b. F = m v d. F = p v Newton's first law of motion is also called the law of ____. a. mass c. force b. inertia d. constant velocity The statement "to every action there is an equal and opposite reaction" is ____. a. the ...
Force and Newtons Laws
... 3. Rolling-force acts on rolling objects (less than static or sliding) 4. Fluid-opposes motion of an object through a liquid/gas ...
... 3. Rolling-force acts on rolling objects (less than static or sliding) 4. Fluid-opposes motion of an object through a liquid/gas ...
Physical Science
... grass with a 100N force of friction. What will Patty’s acceleration be this time? (Hint: sketch a diagram first) ...
... grass with a 100N force of friction. What will Patty’s acceleration be this time? (Hint: sketch a diagram first) ...
Newton`s laws, forces
... The “action” FORCE and the “reaction” FORCE don’t act ON the same thing. If the action force is Earth’s gravity pulling on ME, then the reaction force is me pulling on the Earth. If the action force is your behind pushing down on the chair, then the reaction force is the chair pushing up on you ...
... The “action” FORCE and the “reaction” FORCE don’t act ON the same thing. If the action force is Earth’s gravity pulling on ME, then the reaction force is me pulling on the Earth. If the action force is your behind pushing down on the chair, then the reaction force is the chair pushing up on you ...
PPT - Ascension
... Newton’s Second Law: The force required to produce a change in the motion of a body is directly proportional to its mass and the rate of change in its velocity. Acceleration is a change in velocity with respect to time. It can be either an increase or decrease in velocity ...
... Newton’s Second Law: The force required to produce a change in the motion of a body is directly proportional to its mass and the rate of change in its velocity. Acceleration is a change in velocity with respect to time. It can be either an increase or decrease in velocity ...
laws of motion
... a in opposite direction of body’s motion slow down a at right angles to direction of body’s motion deflect circular Any other change in speed and direction ...
... a in opposite direction of body’s motion slow down a at right angles to direction of body’s motion deflect circular Any other change in speed and direction ...
Newtons Laws - Cardinal Newman High School
... A cheetah moves faster than a horse, but how can we determine this? ...
... A cheetah moves faster than a horse, but how can we determine this? ...