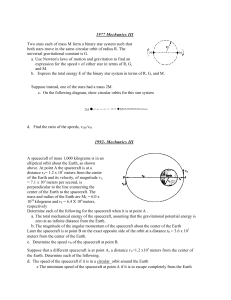
PTG2_3 - scruggsscience
... second player applies a force of 120.0 N to the north. What is the resultant force applied to the player being tackled? (Since force is a vector, you must give both the magnitude and direction of the force.) ...
... second player applies a force of 120.0 N to the north. What is the resultant force applied to the player being tackled? (Since force is a vector, you must give both the magnitude and direction of the force.) ...
Action / Reaction forces
... something MUST be pushing on it. Things don’t move all by themselves! Aristotle ...
... something MUST be pushing on it. Things don’t move all by themselves! Aristotle ...
Physics Lecture #22
... Example: An electron placed in an electric field experience an electric force of 6.1 x 10–10 N. a) What is the magnitude of the electric field? b) A proton is placed in that same electric field. What is the magnitude of the electric force on that proton? ...
... Example: An electron placed in an electric field experience an electric force of 6.1 x 10–10 N. a) What is the magnitude of the electric field? b) A proton is placed in that same electric field. What is the magnitude of the electric force on that proton? ...
Physics - Newton`s Laws
... the London plague of 1665. An interesting thing about all of it is that he didn’t publish them until 1687. Wonder why? Anyway, twenty-two years later in 1687 he finally got around to publishing them in his book, Philosophiaie Naturalis Principia Mathematica (Mathematical Principles of Natural Philos ...
... the London plague of 1665. An interesting thing about all of it is that he didn’t publish them until 1687. Wonder why? Anyway, twenty-two years later in 1687 he finally got around to publishing them in his book, Philosophiaie Naturalis Principia Mathematica (Mathematical Principles of Natural Philos ...
Forces
... • The force of friction acts in the opposite direction of an object’s motion. • The heavier an object, the more it is affected by friction than a lighter one. • Air resistance is the frictional force between air and objects moving through it. ...
... • The force of friction acts in the opposite direction of an object’s motion. • The heavier an object, the more it is affected by friction than a lighter one. • Air resistance is the frictional force between air and objects moving through it. ...
What did the boy cat say to the girl cat on
... •(putter vs. feather) •The greater the mass of the object, the less it will be accelerated by a given force •(golf ball vs. ping pong ball) ...
... •(putter vs. feather) •The greater the mass of the object, the less it will be accelerated by a given force •(golf ball vs. ping pong ball) ...
Lecture-05-09
... Assume the mass of the two objects scales with size, and the forces pictured are the same. In which case is the magnitude of the force of box 1 on box 2 larger? ...
... Assume the mass of the two objects scales with size, and the forces pictured are the same. In which case is the magnitude of the force of box 1 on box 2 larger? ...
Force and Circular Motion ppt
... against wall of a large cylinder, cylinder then starts spinning, and people are seemingly pushed against the wall, then floor drops, and people are stuck against the wall. ...
... against wall of a large cylinder, cylinder then starts spinning, and people are seemingly pushed against the wall, then floor drops, and people are stuck against the wall. ...
Chapter 7
... • Thus Earth behaves like a particle located at the center of Earth with a mass equal to that of Earth ...
... • Thus Earth behaves like a particle located at the center of Earth with a mass equal to that of Earth ...
Conservative and Non-conservative Forces F
... amount of work required to move the object from one position to the other. If a force does positive work on an object, then the stored energy of the object decreases, and vice versa. In practice, we compare stored energies for different object positions. This means that only differences in potentia ...
... amount of work required to move the object from one position to the other. If a force does positive work on an object, then the stored energy of the object decreases, and vice versa. In practice, we compare stored energies for different object positions. This means that only differences in potentia ...
chp. 8
... greater the mass of an object, the greater the force that has to be applied to cause the object to move. ...
... greater the mass of an object, the greater the force that has to be applied to cause the object to move. ...























