Chapter 4 Notes - Beaumont High School
... magnitude of the net force, is in the same direction as the net force and is inversely proportional to the mass of the object. – Newton More Force = More acceleration (Directly Related) ...
... magnitude of the net force, is in the same direction as the net force and is inversely proportional to the mass of the object. – Newton More Force = More acceleration (Directly Related) ...
Transparancies for Dynamics - University of Manchester
... moves at 2 m/s. what is Alices’ velocity as seen by Bob ? • If Bob is on the boat it is just 1 m/s • If Bob is on the shore it is 1+2=3m/s • If Bob is on a boat passing in the opposite direction….. and the earth is spinning… ...
... moves at 2 m/s. what is Alices’ velocity as seen by Bob ? • If Bob is on the boat it is just 1 m/s • If Bob is on the shore it is 1+2=3m/s • If Bob is on a boat passing in the opposite direction….. and the earth is spinning… ...
Review PowerPoint
... horizontal, circular path will decrease if the A. radius of the path is increased B. mass of the object is increased C. direction of motion of the object is ...
... horizontal, circular path will decrease if the A. radius of the path is increased B. mass of the object is increased C. direction of motion of the object is ...
Newton`s Laws Notetakers
... Example: An elevator accelerates upwards. If Bart steps on the scale, what will it read? Example: Now the elevator travels upward with a constant velocity. If Bart steps on the scale, what will it read? Newton’s Third Law If two bodies interact, the force exerted on a body 1 by body 2 is equal in ma ...
... Example: An elevator accelerates upwards. If Bart steps on the scale, what will it read? Example: Now the elevator travels upward with a constant velocity. If Bart steps on the scale, what will it read? Newton’s Third Law If two bodies interact, the force exerted on a body 1 by body 2 is equal in ma ...
Lecture 16 - Circular Motion
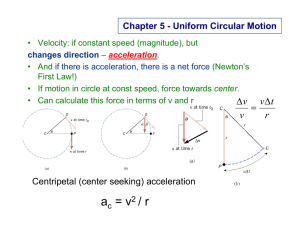
... the same ideas of kinematics (x, v, a) and Newton’s Laws of motion that we have been studying, but we will apply them to situations involving motion in circles. A new word in involved: Centripetal. This just means directed towards the center. A centripetal acceleration is one directed towards the ce ...
... the same ideas of kinematics (x, v, a) and Newton’s Laws of motion that we have been studying, but we will apply them to situations involving motion in circles. A new word in involved: Centripetal. This just means directed towards the center. A centripetal acceleration is one directed towards the ce ...
5th Grade Force and Motion Review2
... A girl walked for 30 minutes. She noticed that she traveled farther in the first 15 minutes of her walk than in the second 15 minutes. What can she conclude about her walk? ...
... A girl walked for 30 minutes. She noticed that she traveled farther in the first 15 minutes of her walk than in the second 15 minutes. What can she conclude about her walk? ...
Intro to Physics - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... How are forces and Newton’s Laws of motion used to describe motion? Unit Learning Targets (I can… Section 1 1. Explain the characteristics of force 2. Identify the basic forces (Weight, normal force and friction, spring force, tension, air resistance, applied force) 3. Draw free-body diagrams showin ...
... How are forces and Newton’s Laws of motion used to describe motion? Unit Learning Targets (I can… Section 1 1. Explain the characteristics of force 2. Identify the basic forces (Weight, normal force and friction, spring force, tension, air resistance, applied force) 3. Draw free-body diagrams showin ...
1.624, 3.7, 23.12 Name: Date: Lesson 5 – 3.5 Acceleration Due To
... function of time. In the first part of the graph (ending at A), the ball is accelerated to 39.2 m/s in a time of 0.20 s. After the ball leaves the pitcher's hand, it experiences only the acceleration due to gravity until it is caught in a glove and brought to rest in the hand of the catcher. (a) Wha ...
... function of time. In the first part of the graph (ending at A), the ball is accelerated to 39.2 m/s in a time of 0.20 s. After the ball leaves the pitcher's hand, it experiences only the acceleration due to gravity until it is caught in a glove and brought to rest in the hand of the catcher. (a) Wha ...
NEWTON`S FIRST LAW CONCEPTUAL WORKSHEET
... other end of the tube at high speed. Pick the path the ball will follow after it exits the tube. Note – you are looking down on these tubes, they are not vertical. ...
... other end of the tube at high speed. Pick the path the ball will follow after it exits the tube. Note – you are looking down on these tubes, they are not vertical. ...
Physics Final - cloudfront.net
... in a single direction on elliptical paths around the Sun. 5. T: It is possible to use Newton’s equations to derive Kepler’s relationship that T2 is proportional to R3 for any orbit around a common body, where T is the period of orbit and R is the average radius. 6. T: At any instant, an orbiting moo ...
... in a single direction on elliptical paths around the Sun. 5. T: It is possible to use Newton’s equations to derive Kepler’s relationship that T2 is proportional to R3 for any orbit around a common body, where T is the period of orbit and R is the average radius. 6. T: At any instant, an orbiting moo ...