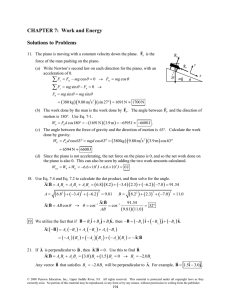
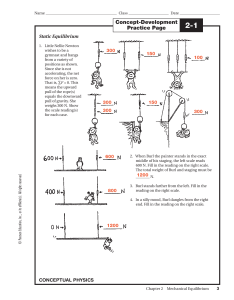
Chapter 05 Solutions
... 10. Action; your foot against the ball. Reaction; the ball against your foot. Both forces have the same magnitude, in accord with Newton’s third law. 11. Yes, it’s true. Earth can’t pull you downward without you simultaneously pulling Earth upward. The acceleration of Earth is negligibly small, and ...
... 10. Action; your foot against the ball. Reaction; the ball against your foot. Both forces have the same magnitude, in accord with Newton’s third law. 11. Yes, it’s true. Earth can’t pull you downward without you simultaneously pulling Earth upward. The acceleration of Earth is negligibly small, and ...
Uniform Circular Motion PP
... exactly equal to 0. This means the rails of the track are no longer pushing on the roller coaster cart... if the centripetal force were even the tiniest bit less (the car's speed was the tiniest bit less), the normal force FN would be less than 0. Since the rails can't physically pull the cart in th ...
... exactly equal to 0. This means the rails of the track are no longer pushing on the roller coaster cart... if the centripetal force were even the tiniest bit less (the car's speed was the tiniest bit less), the normal force FN would be less than 0. Since the rails can't physically pull the cart in th ...
Lecture Mechanics Newton ppt
... turnover (rotate). So, when we apply Newton’s Law saying that an object is motionless (or travel with uniform velocity) when total applied force is zero, we have to be careful. ...
... turnover (rotate). So, when we apply Newton’s Law saying that an object is motionless (or travel with uniform velocity) when total applied force is zero, we have to be careful. ...
Chapter 12 Forces and Motion
... force of the ground pushing against your shoe. The reaction force pushes you forward. 7. When you jump, you push against the canoe. However, the canoe also moves in the opposite direction of your jump. Because the canoe moves away, it produces a smaller reaction force on you. This small reaction f ...
... force of the ground pushing against your shoe. The reaction force pushes you forward. 7. When you jump, you push against the canoe. However, the canoe also moves in the opposite direction of your jump. Because the canoe moves away, it produces a smaller reaction force on you. This small reaction f ...
Answers - Dean Baird`s Phyz Home Page
... c. Forces are vector quantities; they have definite directions. In what direction does this force seem to act? Draw a diagram of a book sliding across the table, moving to the right. Show the total effect of the force acting on the book by drawing a vector. ...
... c. Forces are vector quantities; they have definite directions. In what direction does this force seem to act? Draw a diagram of a book sliding across the table, moving to the right. Show the total effect of the force acting on the book by drawing a vector. ...
Physics 11 Final Exam Outline
... solve problems, using the law of conservation of momentum in one dimension (e.g., inelastic collisions and explosions) to determine momentum impulse velocity mass analyse conservation of momentum in two dimensions for situations involving two objects in an oblique collision or an object expl ...
... solve problems, using the law of conservation of momentum in one dimension (e.g., inelastic collisions and explosions) to determine momentum impulse velocity mass analyse conservation of momentum in two dimensions for situations involving two objects in an oblique collision or an object expl ...
Writing Prompts
... How does Newton’s second law affect the motion of an object? 5.1.2 The student will use algebraic and geometric concepts to qualitatively and quantitatively describe an object’s motion. 5.1.3 The student will analyze and explain how Newton’s Laws describe changes in an object’s motion. ...
... How does Newton’s second law affect the motion of an object? 5.1.2 The student will use algebraic and geometric concepts to qualitatively and quantitatively describe an object’s motion. 5.1.3 The student will analyze and explain how Newton’s Laws describe changes in an object’s motion. ...
Exam 3
... Identify when an object has an angular acceleration. Identify the difference between angular acceleration and centripetal acceleration Identify the rotational equivalent of position, velocity, acceleration, force, mass and momentum. Conversely identify the linear equivalent of revolutions, angular v ...
... Identify when an object has an angular acceleration. Identify the difference between angular acceleration and centripetal acceleration Identify the rotational equivalent of position, velocity, acceleration, force, mass and momentum. Conversely identify the linear equivalent of revolutions, angular v ...
Newton`s Laws and Forces
... What direction does the friction force act? A. Perpendicular to the surface in the same direction as the motion. B. Parallel to the surface in the same direction as the motion. C. Perpendicular to the surface in the opposite direction of the motion. D. Parallel to the surface in the opposite direct ...
... What direction does the friction force act? A. Perpendicular to the surface in the same direction as the motion. B. Parallel to the surface in the same direction as the motion. C. Perpendicular to the surface in the opposite direction of the motion. D. Parallel to the surface in the opposite direct ...
Chapter 8
... rim of the disk and pulling on the rope. What constant force must be exerted on the rope to bring the merry-go-round from rest to an angular speed of 0.500 rev/s in 2.00 s? ...
... rim of the disk and pulling on the rope. What constant force must be exerted on the rope to bring the merry-go-round from rest to an angular speed of 0.500 rev/s in 2.00 s? ...