Positive angular accelerations are in the counterclockwise
... Units of angular acceleration are rad/s² Positive angular accelerations are in the counterclockwise direction and negative accelerations are in the clockwise direction When a rigid object rotates about a fixed axis, every portion of the object has the same angular speed and the same angular ...
... Units of angular acceleration are rad/s² Positive angular accelerations are in the counterclockwise direction and negative accelerations are in the clockwise direction When a rigid object rotates about a fixed axis, every portion of the object has the same angular speed and the same angular ...
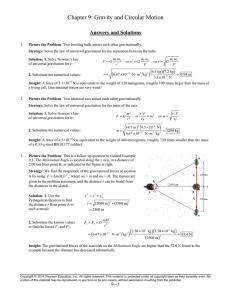
Chapter 9: Gravity and Circular Motion
... mass, the greater the force, and the greater the distance, the weaker the force of gravity. ...
... mass, the greater the force, and the greater the distance, the weaker the force of gravity. ...
Physics: Principles and Applications, 6e Giancoli
... 12. You slam on the brakes of your car in a panic, and skid a certain distance on a straight, level road. If you had been traveling twice as fast, what distance would the car have skidded, under the same conditions? A) It would have skidded 4 times farther. B) It would have skidded twice as far. C) ...
... 12. You slam on the brakes of your car in a panic, and skid a certain distance on a straight, level road. If you had been traveling twice as fast, what distance would the car have skidded, under the same conditions? A) It would have skidded 4 times farther. B) It would have skidded twice as far. C) ...
Section 7.5
... Because the spring is compressed from x = 3 to x = 6 inches less than its natural length, the work required is ...
... Because the spring is compressed from x = 3 to x = 6 inches less than its natural length, the work required is ...
Questions - Physics and Engineering Physics
... 2. The test package includes a test paper (this document), a formula sheet, and an OMR sheet. The test paper consists of 11 pages, including this cover page. It is the responsibility of the student to check that the test paper is complete. 3. Only a basic scientific calculator (e.g. Texas Instrument ...
... 2. The test package includes a test paper (this document), a formula sheet, and an OMR sheet. The test paper consists of 11 pages, including this cover page. It is the responsibility of the student to check that the test paper is complete. 3. Only a basic scientific calculator (e.g. Texas Instrument ...
FREE Sample Here
... motion do not change (including if it is at rest). Free-body diagrams: A free-body diagram shows an object and all the forces acting on it (but not forces acting on any other objects). The object itself may be represented by a single point if its size and shape are not important. Even though it is j ...
... motion do not change (including if it is at rest). Free-body diagrams: A free-body diagram shows an object and all the forces acting on it (but not forces acting on any other objects). The object itself may be represented by a single point if its size and shape are not important. Even though it is j ...
Study Notes Lesson 10 Newton`s Third Law of Motion
... The Horse-Cart System a. View the system in 3 different ways. The cart system, the horse system, and the horse-cart system. b. The cart system is only concerned with accelerating. The net force of the cart divided by the mass of the cart is the cart’s acceleration. c. In the horse system, the opposi ...
... The Horse-Cart System a. View the system in 3 different ways. The cart system, the horse system, and the horse-cart system. b. The cart system is only concerned with accelerating. The net force of the cart divided by the mass of the cart is the cart’s acceleration. c. In the horse system, the opposi ...
Focus 2 Answers
... 4a. Einstein, Galileo and Newton all made very important discoveries concerning the universe. Which of the following lists places them in their correct chronological order starting with the earliest scientist? A. B. C. D. ...
... 4a. Einstein, Galileo and Newton all made very important discoveries concerning the universe. Which of the following lists places them in their correct chronological order starting with the earliest scientist? A. B. C. D. ...
Experiment No : M8 Experiment Name: FREE FALL and ATWOOD`S
... Now let us consider the motion of bodies on Earth’s surface using Newton’s gravitational law and the spherical shell theorem. The objects that we encounter everyday are very small compared to the Earth’s size so they can be treated as point particles with respect to Earth. Furthermore, the spherical ...
... Now let us consider the motion of bodies on Earth’s surface using Newton’s gravitational law and the spherical shell theorem. The objects that we encounter everyday are very small compared to the Earth’s size so they can be treated as point particles with respect to Earth. Furthermore, the spherical ...
PH230 Week 2 Homewwork
... 55pts______13. Suppose you have already created two spheres in VPython, one named Sun and the other named Earth, to represent the planet. Before the "while" loop, you specified their masses and initial momenta as Sun.m, Earth.m, Sun.p, and Earth.p, and you've chosen a value for deltat and initialize ...
... 55pts______13. Suppose you have already created two spheres in VPython, one named Sun and the other named Earth, to represent the planet. Before the "while" loop, you specified their masses and initial momenta as Sun.m, Earth.m, Sun.p, and Earth.p, and you've chosen a value for deltat and initialize ...
ppt Review from Kahoot
... Tips: the trajectory of a satellite DOES NOT depend on the mass of the satellite. Because a satellite is in free fall its acceleration is mass-independent. Orbital Motion: FG = FC and v=2pR/T GMm/R2=mv2/R GM/R= (2pR/T)2 T depends on M, mass of central planet and R, the orbital radius ...
... Tips: the trajectory of a satellite DOES NOT depend on the mass of the satellite. Because a satellite is in free fall its acceleration is mass-independent. Orbital Motion: FG = FC and v=2pR/T GMm/R2=mv2/R GM/R= (2pR/T)2 T depends on M, mass of central planet and R, the orbital radius ...