Wright State University ME 499, Spring 1997
... The skid steer loader has a mass of 1180 kg, and in the position shown the center of mass is at G1. If there is a 300-kg stone in the bucket, with center of mass at G2, determine the reactions of each pair of wheels A and B on the ground and the force in the hydraulic cylinder CD and at the pin E. T ...
... The skid steer loader has a mass of 1180 kg, and in the position shown the center of mass is at G1. If there is a 300-kg stone in the bucket, with center of mass at G2, determine the reactions of each pair of wheels A and B on the ground and the force in the hydraulic cylinder CD and at the pin E. T ...
OBJECTIVES PRE-LECTURE 2-1
... The constant of proportionality g is the magnitude of the Earth's gravitational field but it is often loosely called the acceleration due to gravity. Electromagnetic force The interactions between atoms and the charged particles within atoms are all electromagnetic. These forces determine whether a ...
... The constant of proportionality g is the magnitude of the Earth's gravitational field but it is often loosely called the acceleration due to gravity. Electromagnetic force The interactions between atoms and the charged particles within atoms are all electromagnetic. These forces determine whether a ...
Slide 1
... Orbits of Planets and Satellites (cont.) • The equations for speed and period of a satellite can be used for any object in orbit about another. Central body mass will replace mE, and r will be the distance between the centers of the orbiting body and the central body. • If the mass of the central bo ...
... Orbits of Planets and Satellites (cont.) • The equations for speed and period of a satellite can be used for any object in orbit about another. Central body mass will replace mE, and r will be the distance between the centers of the orbiting body and the central body. • If the mass of the central bo ...
2.3 Extra practice for quiz
... Answer the questions neatly on a different page. Solve problems providing givens and to find, equation in terms of unknown, substitute with units, do unit analysis and solve in correct significant figures. ...
... Answer the questions neatly on a different page. Solve problems providing givens and to find, equation in terms of unknown, substitute with units, do unit analysis and solve in correct significant figures. ...
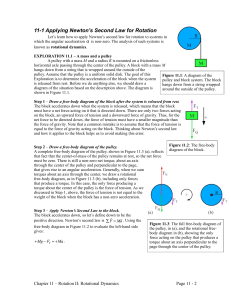
6 Newton`s Second Law of Motion–Force and Acceleration
... 6.1 Force Causes Acceleration Recall from the previous chapter that the combination of forces acting on an object is the net force. • Acceleration depends on the net force. • To increase the acceleration of an object, you must increase the net force acting on it. • An object’s acceleration is direct ...
... 6.1 Force Causes Acceleration Recall from the previous chapter that the combination of forces acting on an object is the net force. • Acceleration depends on the net force. • To increase the acceleration of an object, you must increase the net force acting on it. • An object’s acceleration is direct ...
Electrostatic Fields and Coulombs Law File
... Electric fields are always directed away from positive by convention ...
... Electric fields are always directed away from positive by convention ...
Dynamics and Space
... 55. Using your knowledge of physics comment on the use of satellites in society. 56. An astronomer is observing one particular star in the night sky, and states that the star is moving away from the Earth. Last updated by AD May 2014 ...
... 55. Using your knowledge of physics comment on the use of satellites in society. 56. An astronomer is observing one particular star in the night sky, and states that the star is moving away from the Earth. Last updated by AD May 2014 ...