Development of Exposure Systems and Exposure
... the rat nearer to the lid[10]. Figure 2 (a) shows the modified exposure system. This system was used in a large-scale long-term exposure experiment to study the effects of two-year exposure to 1.5 GHz PDC signals on the generation of cerebral tumors using several hundred rats[11]. During the two-ye ...
... the rat nearer to the lid[10]. Figure 2 (a) shows the modified exposure system. This system was used in a large-scale long-term exposure experiment to study the effects of two-year exposure to 1.5 GHz PDC signals on the generation of cerebral tumors using several hundred rats[11]. During the two-ye ...
U.S. Exposures Limits: A History of Their Creation
... (Page 15, column 2, emphasis added ) The Committee retained 6 minutes of averaged exposure relying on the false assumption that the only adverse biological effects from exposure to nonionizing radiation (NIR) is heating. ...
... (Page 15, column 2, emphasis added ) The Committee retained 6 minutes of averaged exposure relying on the false assumption that the only adverse biological effects from exposure to nonionizing radiation (NIR) is heating. ...
as a PDF
... ionic precursors were reduced at 300 °C under H2. In contrast, the Pd/Au catalyst that was reduced at 350 °C contained PdAu alloyed clusters.24 Photoreduction was also used for the preparation of mixed Au/Pd core-shell particles.25 Sonochemical preparation of Aucore/Pdshell particles was reported re ...
... ionic precursors were reduced at 300 °C under H2. In contrast, the Pd/Au catalyst that was reduced at 350 °C contained PdAu alloyed clusters.24 Photoreduction was also used for the preparation of mixed Au/Pd core-shell particles.25 Sonochemical preparation of Aucore/Pdshell particles was reported re ...
Grosche_ANSES-CSO 7
... In general the facts about radon have to be continuously communicated and efforts have to be made to put radon in the “right place”, as e.g. radon is seen as a “rural” problem. The public may know about the severe health effects from radon, but this risk in comparison with other risks is underestima ...
... In general the facts about radon have to be continuously communicated and efforts have to be made to put radon in the “right place”, as e.g. radon is seen as a “rural” problem. The public may know about the severe health effects from radon, but this risk in comparison with other risks is underestima ...
Radiation Chemistry of Overirradiated Aqueous Solutions of
... (Dragani6 et al. 1984). These doses are due to the energies of decay of various radionuclides that were present during accretion and imbedded in the cometary material. Of particular importance is Z6Al (Reeves 1979), the radiogenic heat o f which could be sufficient to maintain liquid water cores in ...
... (Dragani6 et al. 1984). These doses are due to the energies of decay of various radionuclides that were present during accretion and imbedded in the cometary material. Of particular importance is Z6Al (Reeves 1979), the radiogenic heat o f which could be sufficient to maintain liquid water cores in ...
12.0 Radiation Protection
... The reactor coolant chemistry for the U.S. EPR is designed to minimize the production of activated corrosion products by creating an environment that is less corrosive to the selected materials. Chemistry, which is coordinated with the boron content of the reactor coolant, is used to provide a const ...
... The reactor coolant chemistry for the U.S. EPR is designed to minimize the production of activated corrosion products by creating an environment that is less corrosive to the selected materials. Chemistry, which is coordinated with the boron content of the reactor coolant, is used to provide a const ...
12.0 Radiation Protection
... dose. The U.S. EPR includes layout considerations in the plant design that reduce personnel radiation exposure. For instance, the design of plant buildings includes anterooms that serve as entries to higher dose rate rooms to further protect workers from radiation within the room. In one example of ...
... dose. The U.S. EPR includes layout considerations in the plant design that reduce personnel radiation exposure. For instance, the design of plant buildings includes anterooms that serve as entries to higher dose rate rooms to further protect workers from radiation within the room. In one example of ...
experiment 8 radioactive decay of nuclei
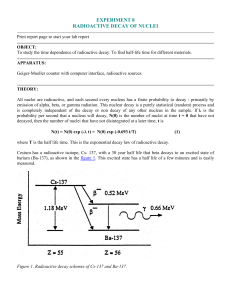
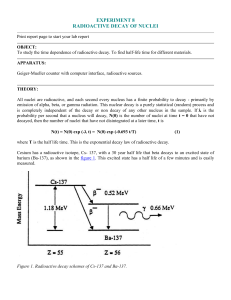
... where T is the half life time. This is the exponential decay law of radioactive decay. Cesium has a radioactive isotope, Cs- 137, with a 30 year half life that beta decays to an excited state of barium (Ba-137), as shown in the figure 1. This excited state has a half life of a few minutes and is eas ...
... where T is the half life time. This is the exponential decay law of radioactive decay. Cesium has a radioactive isotope, Cs- 137, with a 30 year half life that beta decays to an excited state of barium (Ba-137), as shown in the figure 1. This excited state has a half life of a few minutes and is eas ...
Phys 282 EXP 8
... where T is the half life time. This is the exponential decay law of radioactive decay. Cesium has a radioactive isotope, Cs- 137, with a 30 year half life that beta decays to an excited state of barium (Ba-137), as shown in the figure 1. This excited state has a half life of a few minutes and is eas ...
... where T is the half life time. This is the exponential decay law of radioactive decay. Cesium has a radioactive isotope, Cs- 137, with a 30 year half life that beta decays to an excited state of barium (Ba-137), as shown in the figure 1. This excited state has a half life of a few minutes and is eas ...
Medical Physics - University of Waterloo
... This course is an introduction to physics in medicine and is intended to introduce students to various techniques and concepts in physics, including ionizing radiation, used in medicine particularly in oncology, for diagnosis and treatments of diseases. The course has been designed to follow the bas ...
... This course is an introduction to physics in medicine and is intended to introduce students to various techniques and concepts in physics, including ionizing radiation, used in medicine particularly in oncology, for diagnosis and treatments of diseases. The course has been designed to follow the bas ...
Topic 14 - Lloyd Crosby
... b. 1 rem = 1 rad x 1 RBE c. RBE is from Relative Biological Effectiveness. d. The RBE factor depends on how destructive to biological tissues a type of radiation happens to be for the same amount of energy delivered to the tissue e. RBEs for selected radiation (1) X-rays: RBE = 0.7 (2) beta: ...
... b. 1 rem = 1 rad x 1 RBE c. RBE is from Relative Biological Effectiveness. d. The RBE factor depends on how destructive to biological tissues a type of radiation happens to be for the same amount of energy delivered to the tissue e. RBEs for selected radiation (1) X-rays: RBE = 0.7 (2) beta: ...
Nuclear Chemistry PowerPoint
... necessary for one-half of the radioactive material to decay. For example, the radioactive element bismuth (210Bi) can undergo alpha decay to form the element thallium (206Tl) with a reaction half-life equal to five days. • If we begin an experiment starting with 100 g of bismuth in a sealed lead con ...
... necessary for one-half of the radioactive material to decay. For example, the radioactive element bismuth (210Bi) can undergo alpha decay to form the element thallium (206Tl) with a reaction half-life equal to five days. • If we begin an experiment starting with 100 g of bismuth in a sealed lead con ...
1 The Nucleus Total number of nucleons: mass number Number of
... At 40,000,000 K – lowest of its kind Initiated by an atomic bomb – hydrogen bomb ...
... At 40,000,000 K – lowest of its kind Initiated by an atomic bomb – hydrogen bomb ...
Radioisotopes
... • Isotopes of an element have nuclei with the same number of protons (the same atomic number) but different numbers of neutrons. • Therefore, isotopes have different mass numbers, which give the total number of nucleons, the number of protons plus neutrons. ...
... • Isotopes of an element have nuclei with the same number of protons (the same atomic number) but different numbers of neutrons. • Therefore, isotopes have different mass numbers, which give the total number of nucleons, the number of protons plus neutrons. ...
12 · Nuclear Chemistry
... Hydrogen has three isotopes: hydrogen-1, hydrogen-2, and hydrogen-3. How many neutrons in hydrogen-1? ...
... Hydrogen has three isotopes: hydrogen-1, hydrogen-2, and hydrogen-3. How many neutrons in hydrogen-1? ...
Word - chemmybear.com
... number of protons. Scientists knew that the nucleus consisted of protons and neutrons in _______ [1730 1830 1930] The number of ________ determines the identity of atoms. Isotopes have different numbers of ____________. Hydrogen has three isotopes: hydrogen-1, hydrogen-2, and hydrogen-3. How many ne ...
... number of protons. Scientists knew that the nucleus consisted of protons and neutrons in _______ [1730 1830 1930] The number of ________ determines the identity of atoms. Isotopes have different numbers of ____________. Hydrogen has three isotopes: hydrogen-1, hydrogen-2, and hydrogen-3. How many ne ...
Acrobat - chemmybear.com
... 2. Pierre and Marie Curie invented a device to detect radiation because the radioactive material caused the air to _____________ electricity… thereby completing the circuit in the machine. 3. Radioactivity interacts with atoms in the air to form positive ions and free _______________. This makes the ...
... 2. Pierre and Marie Curie invented a device to detect radiation because the radioactive material caused the air to _____________ electricity… thereby completing the circuit in the machine. 3. Radioactivity interacts with atoms in the air to form positive ions and free _______________. This makes the ...
Word - chemmybear.com
... number of protons. Scientists knew that the nucleus consisted of protons and neutrons in _______ [1730 1830 1930] The number of ________ determines the identity of atoms. Isotopes have different numbers of ____________. Hydrogen has three isotopes: hydrogen-1, hydrogen-2, and hydrogen-3. How many ne ...
... number of protons. Scientists knew that the nucleus consisted of protons and neutrons in _______ [1730 1830 1930] The number of ________ determines the identity of atoms. Isotopes have different numbers of ____________. Hydrogen has three isotopes: hydrogen-1, hydrogen-2, and hydrogen-3. How many ne ...
Acrobat - chemmybear.com
... 2. Pierre and Marie Curie invented a device to detect radiation because the radioactive material caused the air to _____________ electricity… thereby completing the circuit in the machine. 3. Radioactivity interacts with atoms in the air to form positive ions and free _______________. This makes the ...
... 2. Pierre and Marie Curie invented a device to detect radiation because the radioactive material caused the air to _____________ electricity… thereby completing the circuit in the machine. 3. Radioactivity interacts with atoms in the air to form positive ions and free _______________. This makes the ...
Types of Radiation
... Students know how to relate the position of an element in the periodic table to its atomic number and atomic mass. (1a) Students know the energy release per gram of material is much larger in nuclear fusion or fission reactions than in chemical reactions. The change in mass (calculated by E = mc ...
... Students know how to relate the position of an element in the periodic table to its atomic number and atomic mass. (1a) Students know the energy release per gram of material is much larger in nuclear fusion or fission reactions than in chemical reactions. The change in mass (calculated by E = mc ...
Chapter 21 Powerpoint: Nuclear Chemistry
... After 10 half-lives sample considered nonradioactive because it approaches the level of background radiation. Because the amount never reaches zero, radioactive waste disposal and storage causes ...
... After 10 half-lives sample considered nonradioactive because it approaches the level of background radiation. Because the amount never reaches zero, radioactive waste disposal and storage causes ...
Nuclear fallout
Nuclear fallout, or simply fallout, is the residual radioactive material propelled into the upper atmosphere following a nuclear blast or a nuclear reaction conducted in an unshielded facility, so called because it ""falls out"" of the sky after the explosion and shock wave have passed. It commonly refers to the radioactive dust and ash created when a nuclear weapon explodes, but such dust can also originate from a damaged nuclear plant. Fallout may take the form of black rain (rain darkened by particulates).This radioactive dust, consisting of material either directly vaporized by a nuclear blast or charged by exposure, is a highly dangerous kind of radioactive contamination.