HG Expert Groups - North Kitsap School District
... Decomposers consume other organisms that have died. Decomposers are nature’s “trash collectors.” Decomposers include fungi and bacteria as well as invertebrates such as earthworms and insects. They all work to break down the structures that made up any dead organism, plant or animal. In the process ...
... Decomposers consume other organisms that have died. Decomposers are nature’s “trash collectors.” Decomposers include fungi and bacteria as well as invertebrates such as earthworms and insects. They all work to break down the structures that made up any dead organism, plant or animal. In the process ...
David Golowo, Jr. Literature Analysis Assign. November 18, 2005
... These single-celled animals feed on detritus and bacteria. They, in turn, become food for larvae, copepods and larger protozoa. Bacteria have an important function in the Bay. They are essentially the decomposers. Their primary function is to break down dead matter, particularly plants. Through this ...
... These single-celled animals feed on detritus and bacteria. They, in turn, become food for larvae, copepods and larger protozoa. Bacteria have an important function in the Bay. They are essentially the decomposers. Their primary function is to break down dead matter, particularly plants. Through this ...
6th Grade Science Biomes Project
... food, timber, and oxygen for us to breathe. However, we are also the cause of some major threats to this biome, one of which is acid rain. Acid rain caused by industrial and vehicle emissions damages the leaves of trees, and causes them to produce smaller and fewer seeds. It also reduces the trees' ...
... food, timber, and oxygen for us to breathe. However, we are also the cause of some major threats to this biome, one of which is acid rain. Acid rain caused by industrial and vehicle emissions damages the leaves of trees, and causes them to produce smaller and fewer seeds. It also reduces the trees' ...
Document
... for Antarctica and therefore have a very large range of life depending on conditions in each area. ...
... for Antarctica and therefore have a very large range of life depending on conditions in each area. ...
Grasslands PowerPoin
... for Antarctica and therefore have a very large range of life depending on conditions in each area. ...
... for Antarctica and therefore have a very large range of life depending on conditions in each area. ...
Where will your first stop be?
... temperature and rainfall are used to group habitats together. Animals, which live within a same-species group, and occupy an area at the same time, are part of a population. Populations of different plants and animals interact with each other, and together, these populations form communities. Plants ...
... temperature and rainfall are used to group habitats together. Animals, which live within a same-species group, and occupy an area at the same time, are part of a population. Populations of different plants and animals interact with each other, and together, these populations form communities. Plants ...
WETLAND EXPLORATION: MAMMAL EMPHASIS
... Benchmark C: Describe Earth's resources including rocks, soil, water, air, animals and plants and the ways in which they can be conserved. Grade Three: Earth Systems 5. Investigate the properties of soil (e.g., color, texture, capacity to retain water, ability to support plant growth). Grade Five: E ...
... Benchmark C: Describe Earth's resources including rocks, soil, water, air, animals and plants and the ways in which they can be conserved. Grade Three: Earth Systems 5. Investigate the properties of soil (e.g., color, texture, capacity to retain water, ability to support plant growth). Grade Five: E ...
The most advanced cloning technology, somatic cell nuclear transfer
... community. It is one of the most important scientific breakthroughs in last century and brings many benefits to our society. The cloning of farm animals that have “superior genes” can increase the productivity of meat and milk (1). Also, the technology can be used to protect animals by increasing th ...
... community. It is one of the most important scientific breakthroughs in last century and brings many benefits to our society. The cloning of farm animals that have “superior genes” can increase the productivity of meat and milk (1). Also, the technology can be used to protect animals by increasing th ...
Lecture notes from week number 1
... biology, cell biology, protistology-protozoology, mathematics, statistics, ecological niche-modeling, and much more. The first part of parasitology probably was home-remedies, or at least cave remedies or, in the case of primates at the earliest evolutionary stages in Africa, an understanding that i ...
... biology, cell biology, protistology-protozoology, mathematics, statistics, ecological niche-modeling, and much more. The first part of parasitology probably was home-remedies, or at least cave remedies or, in the case of primates at the earliest evolutionary stages in Africa, an understanding that i ...
Paleozoic Life
... • all metazoans (animals except sponges + algae) have the same genetic controls on body organization • Hox genes: master switch in body pattern creation (‘put a leg here and an eye there’) • these genes first appeared in the Cambrian ...
... • all metazoans (animals except sponges + algae) have the same genetic controls on body organization • Hox genes: master switch in body pattern creation (‘put a leg here and an eye there’) • these genes first appeared in the Cambrian ...
Neolithic Human-Animal Relations
... as equals, and to engage in personal relationships with their prey or its spirit master or mistress. Animals must offer themselves to the hunter, and the hunter must treat them with appropriate respect.2 Herders, on the other hand, protect and care for their flocks, which are rendered into a perpetu ...
... as equals, and to engage in personal relationships with their prey or its spirit master or mistress. Animals must offer themselves to the hunter, and the hunter must treat them with appropriate respect.2 Herders, on the other hand, protect and care for their flocks, which are rendered into a perpetu ...
cycle - akjackson
... the stages of life that living things go through from the start to the end of their life ...
... the stages of life that living things go through from the start to the end of their life ...
Conserving Wildlife
... Aesthetic benefits - those that people place on wildlife for beauty and appeal. Game benefits – fishing and hunting some wildlife animals as game. Economic benefits - derived from people spending money to enjoy wildlife. Scientific benefits - using wildlife in research that solves problems. Ecologic ...
... Aesthetic benefits - those that people place on wildlife for beauty and appeal. Game benefits – fishing and hunting some wildlife animals as game. Economic benefits - derived from people spending money to enjoy wildlife. Scientific benefits - using wildlife in research that solves problems. Ecologic ...
Galapagos Penguin
... mates for life. It lays one or two eggs in places such as caves and crevices, protected from direct sunlight, which can lead to the eggs overheating ...
... mates for life. It lays one or two eggs in places such as caves and crevices, protected from direct sunlight, which can lead to the eggs overheating ...
Ecosystems - Trophic Levels The organization of communities is
... An average of only 10% of the energy from the previous level moves to the next level. The rest is used up or lost as heat energy. Conservation of Matter and Energy in Ecosystems Ecosystems are generally not considered closed systems in terms of matter.Organisms in an ecosystem give off gases, water, ...
... An average of only 10% of the energy from the previous level moves to the next level. The rest is used up or lost as heat energy. Conservation of Matter and Energy in Ecosystems Ecosystems are generally not considered closed systems in terms of matter.Organisms in an ecosystem give off gases, water, ...
predationinsmallruminantsmay2010
... Scent stations can be used to lure predator species in an effort to identify them. They can be made by clearing a 1 yard diameter of vegetation. A track surface is then created by laying a substance that will maintain tracks such as flour, sand or lime. An attractive scent is placed in the clearing. ...
... Scent stations can be used to lure predator species in an effort to identify them. They can be made by clearing a 1 yard diameter of vegetation. A track surface is then created by laying a substance that will maintain tracks such as flour, sand or lime. An attractive scent is placed in the clearing. ...
Chapter 2. Interactions between Organisms and Environment
... There is a dearth of information on the sensory and physiological characteristics of wild species. Burton (1970) has published a general summary of the literature on animal senses, including references to several of the more refined sensory capabilities of some species. Information on the more commo ...
... There is a dearth of information on the sensory and physiological characteristics of wild species. Burton (1970) has published a general summary of the literature on animal senses, including references to several of the more refined sensory capabilities of some species. Information on the more commo ...
1.5 a study of an ecosystem
... Organism Distribution • Frequency: chance of finding a named species with any throw – Record presence/absence of each species with each quadrat throw – no counting involved – This method is quick and percentages of organisms can be calculated easily – The more throws and frequency checks you do, th ...
... Organism Distribution • Frequency: chance of finding a named species with any throw – Record presence/absence of each species with each quadrat throw – no counting involved – This method is quick and percentages of organisms can be calculated easily – The more throws and frequency checks you do, th ...
MARINE BIOME
... include the dogfish (a type of shark), large shrimp, squid, and marine mammals such as dolphins, seals, and whales. All nectonic creatures can swim. Most members of the BENTHOS, however, are unable to swim and are restricted to the bottom. Examples include numerous species of crabs, urchins, snails ...
... include the dogfish (a type of shark), large shrimp, squid, and marine mammals such as dolphins, seals, and whales. All nectonic creatures can swim. Most members of the BENTHOS, however, are unable to swim and are restricted to the bottom. Examples include numerous species of crabs, urchins, snails ...
Jaguar Population Dynamics
... hunting increase, the jaguars numbers are going down. As of today only an estimated 15, 000 jaguars remain in the wild. When human influences weren’t extremely close to threatening this specie the numbers for it were many times what it is found to be now. If the jaguar’s habitats continue to deterio ...
... hunting increase, the jaguars numbers are going down. As of today only an estimated 15, 000 jaguars remain in the wild. When human influences weren’t extremely close to threatening this specie the numbers for it were many times what it is found to be now. If the jaguar’s habitats continue to deterio ...
Analyze Motivation Lesson
... 3. Ask , “What does the word “consume” mean?” (to use up, to eat) “What would a consumer in the animal kingdom do?” (Consumers need to eat to get their energy. There are many different types of consumers. Some eat only plants (a consumer eating a producer), others only meat (a consumer eating a cons ...
... 3. Ask , “What does the word “consume” mean?” (to use up, to eat) “What would a consumer in the animal kingdom do?” (Consumers need to eat to get their energy. There are many different types of consumers. Some eat only plants (a consumer eating a producer), others only meat (a consumer eating a cons ...
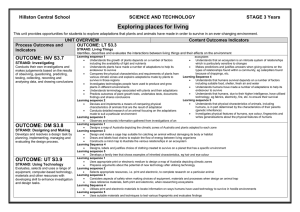
Exploring places for living
... Living things depend on other living things and non-living things such as water, soil, and a suitable temperature, for their survival Living things have adaptations such as structures and behaviours that enable them to live in their particular habitat, eg size colour, shape, habits Every organism ha ...
... Living things depend on other living things and non-living things such as water, soil, and a suitable temperature, for their survival Living things have adaptations such as structures and behaviours that enable them to live in their particular habitat, eg size colour, shape, habits Every organism ha ...
Animal

Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms of the kingdom Animalia (also called Metazoa). All animals are motile, meaning they can move spontaneously and independently, at some point in their lives. Their body plan eventually becomes fixed as they develop, although some undergo a process of metamorphosis later on in their lives. All animals are heterotrophs: they must ingest other organisms or their products for sustenance.Most known animal phyla appeared in the fossil record as marine species during the Cambrian explosion, about 542 million years ago. Animals are divided into various sub-groups, some of which are: vertebrates (birds, mammals, amphibians, reptiles, fish); molluscs (clams, oysters, octopuses, squid, snails); arthropods (millipedes, centipedes, insects, spiders, scorpions, crabs, lobsters, shrimp); annelids (earthworms, leeches); sponges; and jellyfish.